工具类 - 铭感词过滤 DFA算法
工具类 - 铭感词过滤 DFA算法
敏感词过滤方案
1 使用数据库模糊查询,效率太低
2 使用String.indexOf("")查找,数据库量大的话也是比较慢
3 把敏感词和内容使用全文检索(solr,ElasticSearche)技术进行分词再匹配,也是可以的,但是这种方案比较麻烦。
4 DFA算法,确定有穷自动机。本项目采用这种方案
DFA全称为:Deterministic Finite Automaton,即确定有穷自动机。其特征为:有一个有限状态集合和一些从一个状态通向另一个状态的边,每条边上标记有一个符号,其中一个状态是初态,某些状态是终态。但不同于不确定的有限自动机,DFA中不会有从同一状态出发的两条边标志有相同的符号。
- 一次性的把所有的敏感词存储到了多个map中,就是下图表示这种结构
敏感词:冰毒、大麻、大坏蛋
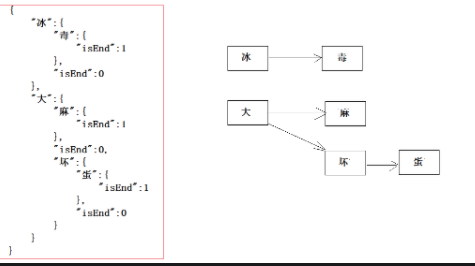
- 检索的过程,就是hashMap的get实现
1、第一个字“冰”,我们在hashMap中可以找到。得到一个新的map = hashMap.get("")。
2、如果map == null,则不是敏感词。否则跳至3
3、获取map中的isEnd,通过isEnd是否等于1来判断该词是否为最后一个。如果isEnd == 1表示该词为敏感词,否则跳至1。
通过这个步骤我们可以判断“冰毒”为敏感词,但是如果我们输入“冰箱”则不是敏感词了。
工具类:
package com.heima.utils.common;
import java.util.*;
public class SensitiveWordUtil {
public static Map<String, Object> dictionaryMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 生成关键词字典库
* @param words
* @return
*/
public static void initMap(Collection<String> words) {
if (words == null) {
System.out.println("敏感词列表不能为空");
return ;
}
// map初始长度words.size(),整个字典库的入口字数(小于words.size(),因为不同的词可能会有相同的首字)
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(words.size());
// 遍历过程中当前层次的数据
Map<String, Object> curMap = null;
Iterator<String> iterator = words.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String word = iterator.next();
curMap = map;
int len = word.length();
for (int i =0; i < len; i++) {
// 遍历每个词的字
String key = String.valueOf(word.charAt(i));
// 当前字在当前层是否存在, 不存在则新建, 当前层数据指向下一个节点, 继续判断是否存在数据
Map<String, Object> wordMap = (Map<String, Object>) curMap.get(key);
if (wordMap == null) {
// 每个节点存在两个数据: 下一个节点和isEnd(是否结束标志)
wordMap = new HashMap<>(2);
wordMap.put("isEnd", "0");
curMap.put(key, wordMap);
}
curMap = wordMap;
// 如果当前字是词的最后一个字,则将isEnd标志置1
if (i == len -1) {
curMap.put("isEnd", "1");
}
}
}
dictionaryMap = map;
}
/**
* 搜索文本中某个文字是否匹配关键词
* @param text
* @param beginIndex
* @return
*/
private static int checkWord(String text, int beginIndex) {
if (dictionaryMap == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("字典不能为空");
}
boolean isEnd = false;
int wordLength = 0;
Map<String, Object> curMap = dictionaryMap;
int len = text.length();
// 从文本的第beginIndex开始匹配
for (int i = beginIndex; i < len; i++) {
String key = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i));
// 获取当前key的下一个节点
curMap = (Map<String, Object>) curMap.get(key);
if (curMap == null) {
break;
} else {
wordLength ++;
if ("1".equals(curMap.get("isEnd"))) {
isEnd = true;
}
}
}
if (!isEnd) {
wordLength = 0;
}
return wordLength;
}
/**
* 获取匹配的关键词和命中次数
* @param text
* @return
*/
public static Map<String, Integer> matchWords(String text) {
Map<String, Integer> wordMap = new HashMap<>();
int len = text.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int wordLength = checkWord(text, i);
if (wordLength > 0) {
String word = text.substring(i, i + wordLength);
// 添加关键词匹配次数
if (wordMap.containsKey(word)) {
wordMap.put(word, wordMap.get(word) + 1);
} else {
wordMap.put(word, 1);
}
i += wordLength - 1;
}
}
return wordMap;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("冰毒");
initMap(list);
String content="我是一个好人,买卖冰毒是违法的";
Map<String, Integer> map = matchWords(content);
System.out.println(map);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号