DI依赖注入
一.依赖注入
1.构造器注入
参考上一节,有参无参构造器注入。
<!-- 默认无参构造器-->
<bean id="User" class="com.cqust.demo1.pojo.User">
<property name="id" value="10"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
<property name="name" value="maming"/>
</bean>
<!-- 通过有参构造器创建对象-->
<bean id="user2" class="com.cqust.demo1.pojo.User" name="u3">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="1"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"/>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="admin"/>
</bean>
二.set方式注入【重点】
依赖注入:set注入!
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖容器!
注入:bean中所有对象的属性,由容器来注入!
使用Set方式注入对应的就是 <property name="address" ref="address"/> 其中property就是调用setter方法注入属性值,对于注入的值是对象的使用ref绑定对方的bean就可以完成注入
【环境搭建】
1.复杂类型
package top.lostyou.pojo;
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
2.真实测试对象
public class Student { private String name; private Address address; private String[] books; private List<String> hobbys; private Map<String,String> card; private Set<String> games; private String wife; private Properties info;
}
3.beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="address" class="top.lostyou.pojo.Address"> <property name="address" value="重庆"/> </bean> <bean id="Student" class="top.lostyou.pojo.Student"> <!-- 第一种,普通值注入 --> <property name="name" value="msf"/> <!-- 第二种,bean(对象)注入 --> <property name="address" ref="address"/> <!-- 数组注入 --> <property name="books"> <array> <value>三国演义</value> <value>西游记</value> <value>水浒传</value> <value>红楼梦</value> </array> </property> <!-- list(集合)注入 --> <property name="hobbys"> <list> <value>听歌</value> <value>写程序</value> <value>看电视剧</value> </list> </property> <!-- map注入 --> <property name="card"> <map> <entry key="username" value="maming"/> <entry key="password" value="123456"/> </map> </property> <!-- set注入 --> <property name="games"> <set> <value>原神</value> <value>部落冲突</value> <value>数独</value> </set> </property> <!-- null注入 --> <property name="wife"> <null/> </property> <!-- properties注入 --> <property name="info"> <props> <prop key="driver">mysql.jdbc.java.Driver</prop> <prop key="username">root</prop> <prop key="password">123456</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
4.测试类
public class mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("Student");
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}
5.测试结果
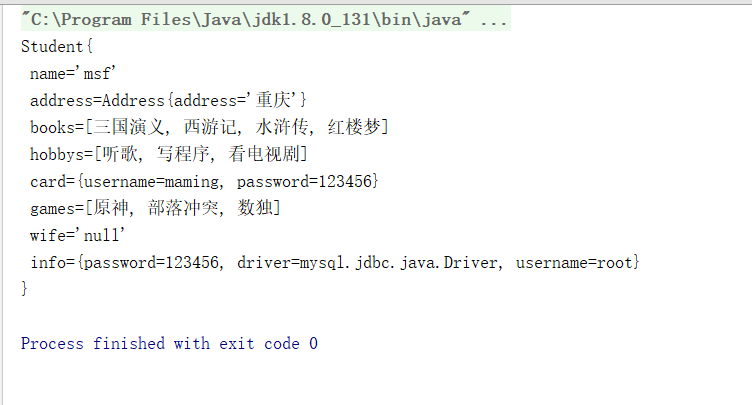
总结:spring为了给我们提供容器,把绝大部分的属性和对象类型装载了,十分方便的可以是我们完成注入,其中最常用的包括:普通注入,bean注入,数组注入,map注入
三.其它注入(p命名空间,c命名空间)
1.工具类
package top.lostyou.pojo;
public class user {
private String name;
private String sex;
public user() {
}
public user(String name, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "user{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2.spring的xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- P命名空间注入,可以直接注入属性的值,适用于无参构造,property --> <bean id="user" class="top.lostyou.pojo.user" p:name="jay周" p:sex="男"/> <!-- C命名空间注入,通过构造器注入,适用于有参构造,construct-args --> <bean id="user2" class="top.lostyou.pojo.user" c:name="程奕迅" c:sex="男"/> </beans>
3.测试
@Test
public void tset1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext con = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("userBeans.xml");
user user2 = con.getBean("user2", user.class);
System.out.println(user2);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号