Hellow spring
1.导入相应的依赖
导入此依赖会帮助导入其它的五个spring依赖,是最好用的
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.3.24</version> </dependency>
2.构造一个配置实体类
package top.lostyou.pojo;
public class Hello {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("Hellow"+name);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hello{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
3.配置spring专用xml,官网:Application.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 使用spring来创建对象,在spring这些都称为bean 类型 变量名 = new 类型(); Hello hello = new hellow(); id = 变量名(类名,对象名) class = 类(对象)所在的包的位置 property 相当于给对象中的属性设置一个值 --> <bean id="Hello" class="top.lostyou.pojo.Hello"> <!-- ref:引用spring容器中创建好的对象 value:具体的值基本的数据类型(int,float) --> <property name="name" value="Hell,spring"/> </bean> </beans>
4.测试结果
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import top.lostyou.pojo.Hello;
public class mytest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取spring的上下文对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//我们的对象都在spring中管理了,我们要使用直接取出来就行了
Hello hello = (Hello)classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("Hello");
System.out.println(hello.toString());
}
}
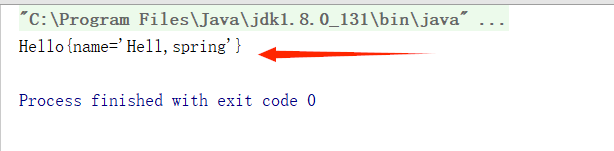
通过测试我们发现,利用spring后,我们没有用到 new 去拿到一个对象,而是通过上下文对象的getBean()方法拿取对象,当ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 来加载 spring的xml文件时,就已经读取了配置文件中所有的类(对象)。
到了这里,我们可以逐渐认识到,我们可以不用从程序中去改动了,要实现不同的操作,只需要在xml中进行配置就可以修改,所谓的IOC:对象由spring来创建,管理,装配!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!