一. std::move
(一)std::move的原型
template<typename T> decltype(auto) move(T&& param) //注意,形参是个引用(万能引用) { using ReturnType = typename remove_reference<T>::type&&; //去除T自身可能携带的引用 return static_cast<ReturnType>(param); //强制转换为右值引用类型 }
(二)注意事项
1. std::move的本质就强制类型转换,它无条件地将实参转为右值引用类型(匿名对象,是个右值),继而用于移动语义。
2. 该函数只是将实参转为右值,除此之外并没有真正的move任何东西。实际上,它在运行期没任何作为,编译器也不会为它生成任何的可执行代码,连一个字节都没有。
3. 如果要对某个对象执行移动操作时,则不要将其声明为常量。因为针对常量对象执行移动操作将变成复制操作。
二. 移动语义
(一)深拷贝和移动的区别
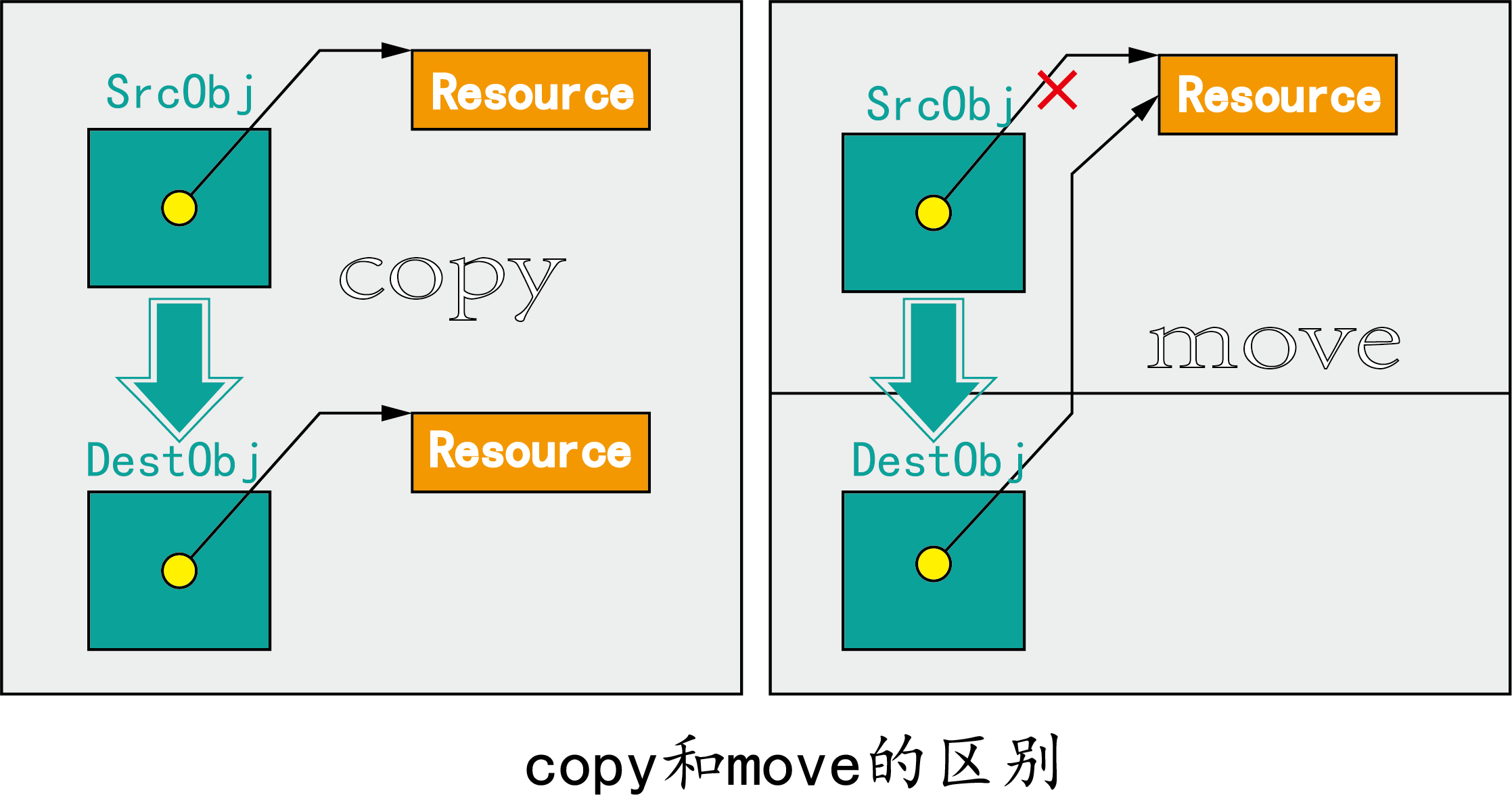
1. 深拷贝:将SrcObj对象拷贝到DestObj对象,需要同时将Resourse资源也拷贝到DestObj对象去。这涉及到内存的拷贝。
2. 移动:通过“偷”内存的方式,将资源的所有权从一个对象转移到另一个对象上。但只是转移,并没有内存的拷贝。可见Resource的所有权只是从SrcObj对象转移到DestObj对象,由于不存在内存拷贝,其效率一般要高于复制构造。
(二)复制和移动操作函数
1. 复制/移动操作的函数声明
①Object(T&); //复制构造,仅接受左值 ②Object(const T&); //复制构造,即可以接受左值又可接收右值 ③Object(T&&) noexcept; //移动构造,仅接受右值 ④T& operator=(const T&);//复制赋值函数,即可以接受左值又可接收右值 ⑤T& operator=(T&&); //移动赋值函数,仅接受右值
2. 注意事项
①移动语义一定是要修改临时对象的值,所以声明移动构造时应该形如Test(Test&&),而不能声明为Test(const Test&&)
②默认的移动构造函数实际上跟默认的拷贝构造函数一样,都是“浅拷贝”。通常情况下,必须自定义移动构造函数。
③对于移动构造函数来说,抛出异常是很危险的。因为移动语义还没完成,一个异常就抛出来,可能会造成悬挂指针。因此,应尽量通过noexcept声明不抛出异常,而一旦出现异常就可以直接调用std::terminate终止程序。
④特殊成员函数之间存在相互抑制的生成机制,可能会影响到默认拷贝构造和默认移动构造函数的自动生成。(详见《特殊成员函数的生成机制》一节)
【编程实验】move移动语义
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; //1. 移动语义 class HugeMem { public: int* buff; int size; HugeMem(int size) : size(size > 0 ? size : 1) { buff = new int[size]; } //移动构造函数 HugeMem(HugeMem&& hm) noexcept : size(hm.size), buff(hm.buff) { hm.buff = nullptr; } ~HugeMem() { delete[] buff; } }; class Moveable { public: HugeMem h; int* i; public: Moveable() : i(new int(3)), h(1024){} //移动构造函数(强制转为右值,以调用h的移动构造函数。注意m虽然是右值 //引用,但形参是具名变量,m是个左值。因此m.h也是左值,需转为右值。 Moveable(Moveable&& m) noexcept: i(m.i), h(std::move(m).h) { m.i = nullptr; } ~Moveable() { delete i; } }; Moveable GetTemp() { Moveable tmp = Moveable(); cout << hex << "Huge mem from " << __func__ << " @" << tmp.h.buff << endl; return tmp; } //2. 对常量对象实施移动将变成复制操作 class Annotation { std::string value; public: //注意:对常量的text对象实施移动操作时,由于std::move(text)返回的结果是个 //const std::string对象,由于带const,不能匹配string(&& rhs)移动构造函数, //但匹配string(const string& rhs)复制构造函数,因此当执行value(std::move(text)) //时,实际上是将text复制给value。对于非string类型的情况也一样,因此对常量对象的 //移动操作实际上会变成复制操作! explicit Annotation(const std::string text) : value(std::move(text)) { } }; //3. 利用移动语义实现高性能的swap函数 template<typename T> void Swap(T& a, T& b) noexcept //声明为noexcept以便在交换失败时,终止程序 { //如果a、b是可移动的,则直接转移资源的所有权 //如果是不可移动的,则通过复制来交换两个对象。 T tmp(std::move(a)); //先把a的资源转交给tmp a = std::move(b); b = std::move(tmp); } int main() { //1. 移动语义 Moveable a(GetTemp()); //移动构造 cout << hex << "Huge mem from " << __func__ << " @" << a.h.buff << endl; return 0; } /*输出结果 Huge mem from GetTemp @02C66248 (从中可以看出Huge mem从临时对象移动了a对象) Huge mem from main @02C66248 */
三、正确理解移动语义
(一) “移动”操作实际上是一种请求,因为有些类型不存在移动操作,对于这些对象会通过其复制操作来实现“移动”。
(二)某些类型的移动操作未必比复制操作更快。如:
1. std::vector和std::array。
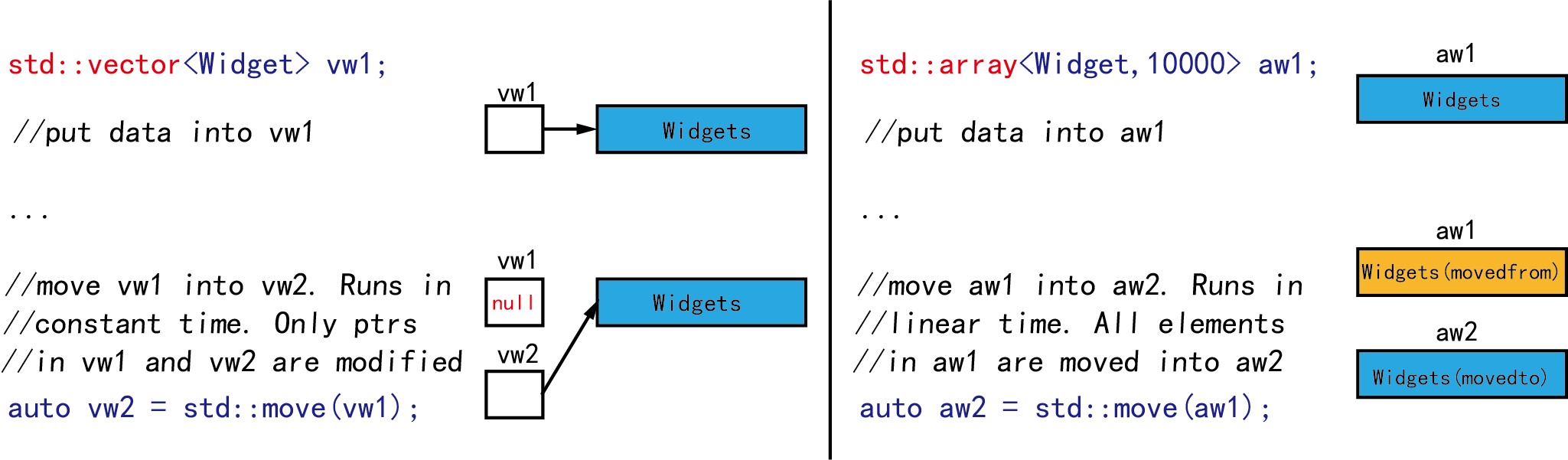
(1)标准库大部分容器类(如vector),内部是将其元素Widgets存放在堆上,然后用指针指向该堆内存。在进行移动操作时,只是进行指针的复制。整个容器内容在常数时间内便可移动完成。
(2)而std::array对象缺少这样的一根指针,因为其内容数据是直接存储对象上的。虽然std::array提供移动操作,但其移动和复制的速度哪个更快,取决于元素Widget的移动和复制速度的比较。同时std::array移动时需要对每一个元素进行移动,总是需要线性时间。
2. 许多std::string类型的实现采用了小型字符串优化(SSO)。当使用SSO后,“小型”字符串(如不超过15个字符)会存储在std::string对象内的某个缓冲区内,即内容直接存储在对象上(而不是堆上)。因此,此时是整个对象的移动,速度并比复制更快。
(三)标准库一些容器操作提供了强异常安全保证,为了兼容C++98的遗留代码在升级到C++11时仍保证正确性。库中用std::move_if_noexcept模板来替代move函数。该函数在类的移动构造函数没有声明noxcept关键字时返回一个左值引用从而使变量通过拷贝语义,而在移动构造函数有noexcept时返回一个右值引用,从而使变量可以使用移动语义。移动操作未加noexcept时,编译器仍会强制调用一个复制操作。
【编程实验】正确理解移动语义
#include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <vector> #include <array> #include <thread> using namespace std; //1. 移动不存在时,实行的是复制操作 class Foo { public: Foo(){} Foo(const Foo&) { cout <<"Foo(const Foo&)" << endl; } }; //2. 移动速度未必比复制快 //2.1 辅助类(元素类) class Widget { public: Widget() = default; Widget(const Widget&) { //模拟复制操作,假设需要1毫秒 std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1)); } Widget(Widget&&) { //模拟移动操作,假设需要2毫秒 std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(2)); } Widget& operator=(const Widget&) { //模拟复制赋值操作,假设需要1毫秒 std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1)); return *this; } Widget& operator=(Widget&&) { //模拟移动赋值操作,假设需要2毫秒 std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(2)); return *this; } }; //2.2. 计算任意函数的执行时间:auto&&用于lambda表达式形参(C++14) auto funcTimer = [](auto&& func, auto&& ... params) { //计时器启动 std::chrono::system_clock::time_point t1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); //调用func(param...)函数 std::forward<decltype(func)>(func)( //根据func的左右值特性来调用相应的重载&或&&版本的成员函数 std::forward<decltype(params)>(params)... //保持参数的左/右值特性 ); std::chrono::system_clock::time_point t2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); long long elapsed = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(t2 - t1).count(); cout << elapsed << " microseconds" << endl; }; //2.3 复制和移动操作 auto lamMove = [](auto&& src) { auto dest = std::move(src); return; }; auto lamCopy = [](auto&& src) { auto dest = src; return; }; //2.4 测试vector类 void testVector() { std::vector<Widget> vw1{ 10,Widget() }; cout <<"copy vector: " ; funcTimer(lamCopy, vw1); //测试移动操作用时 cout << "move vector: "; funcTimer(lamMove, vw1); } //2.5 测试array类 void testArray() { std::array<Widget, 10> aw1; cout << "copy array: "; funcTimer(lamCopy, aw1); //测试移动操作用时 cout << "move array: "; funcTimer(lamMove, aw1); } //3. move_if_noexcept的用法 struct Maythrow { Maythrow() {} Maythrow(const Maythrow&) { cout <<"Maythrow copy construct." << endl; } Maythrow(Maythrow&&) { cout << "Maythrow move construct." << endl; } }; struct Nothrow { Nothrow() {} Nothrow(const Nothrow&) { cout << "Nothrow copy construct." << endl; } Nothrow(Nothrow&&) noexcept { //注意,这里声明为noexcept! cout << "Nothrow move construct." << endl; } }; int main() { //1. 移动操作不存在时 Foo f1; Foo f2 = std::move(f1); //调用复制构造函数 //2. 移动速度未必比复制快 testVector(); testArray(); //3. 移动未声明为noexcept时,调用复制构造 Maythrow m; Nothrow n; Maythrow mt = move_if_noexcept(m); //move_if_noexcept返回左值引用,调用复制构造函数 Nothrow nt = move_if_noexcept(n); //move_if_noexcept返回右值引用,调用移动构造函数 return 0; } /*输出结果 Foo(const Foo&) copy vector: 19825 microseconds move vector: 5 microseconds //常量时间 copy array: 19109 microseconds move array: 29589 microseconds //移动的速度未必比复制快!取决于Widget的移动和复制速度的比较! Maythrow copy construct. //调用复制构造函数 Nothrow move construct. //调用移动构造函数 */





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
2015-08-08 第7章 线程调度、优先级和亲缘性(2)