Linux内核socket系统调用源码分析
一、环境说明
内核版本:Linux 3.10
内核源码地址:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v3.10/source (包含各个版本内核源码,且网页可全局搜索函数)
二、应用层-socket()函数
应用层创建 socket 对象返回整型的文件描述符。
/* family:被称为协议族,或者协议域。 * type:套接字类型。 * protocol:某个协议的类型常值,可以设置为 0。 * return:返回整型的文件描述符,如果返回 -1 就失败。 */ #include <sys/socket.h> //socket(int domain/family, int type, int protocol) int socket_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
三、BSD Socket层-sys_socketcall()函数
网络栈专用操作函数集的总入口函数,主要是将请求分配,调用具体的底层函数进行处理:
// file: net/socket.c SYSCALL_DEFINE2(socketcall, int, call, unsigned long __user *, args) { ...... switch (call) { case SYS_SOCKET: err = sys_socket(a0, a1, a[2]); break; case SYS_BIND: err = sys_bind(a0, (struct sockaddr __user *)a1, a[2]); break; case SYS_CONNECT: err = sys_connect(a0, (struct sockaddr __user *)a1, a[2]); break; case SYS_LISTEN: err = sys_listen(a0, a1); break; case SYS_ACCEPT: err = sys_accept4(a0, (struct sockaddr __user *)a1, (int __user *)a[2], 0); break; ...... } return err; }
四、INET Socket层-sys_socket()函数
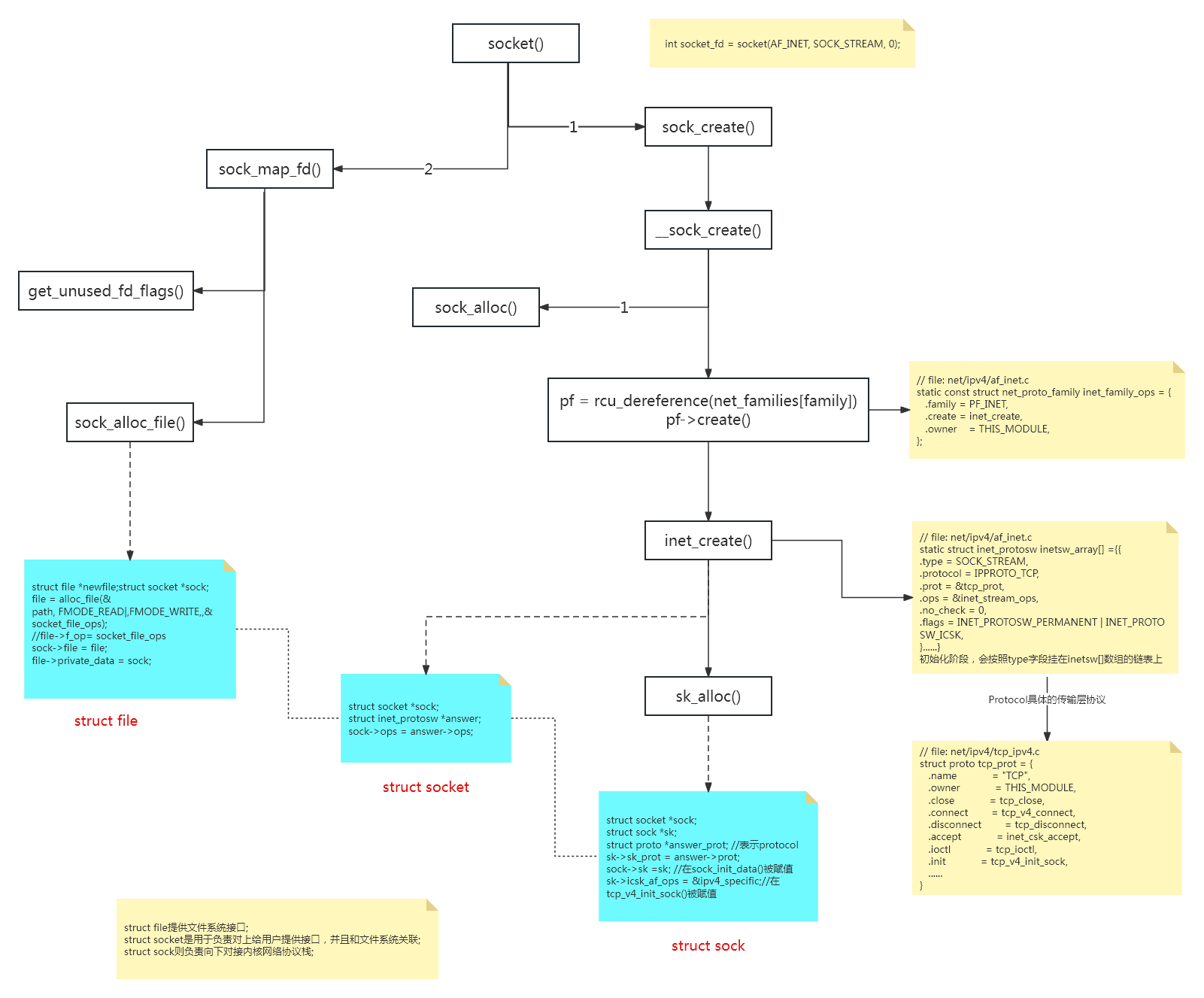
sys_socket()主要包含两个部分:sock_create和sock_map_fd
// file: net/socket.c SYSCALL_DEFINE3(socket, int, family, int, type, int, protocol) { int retval; struct socket *sock; int flags; ...... //省略参数合法性校验代码 retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock); //创建socket if (retval < 0) goto out; retval = sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK)); //将socket与file关联 if (retval < 0) goto out_release; out: /* It may be already another descriptor 8) Not kernel problem. */ return retval; out_release: sock_release(sock); return retval; }
4.1 sock_create()函数
// file: net/socket.c int sock_create(int family, int type, int protocol, struct socket **res) { return __sock_create(current->nsproxy->net_ns, family, type, protocol, res, 0); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(sock_create); int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol, struct socket **res, int kern) { int err; struct socket *sock; const struct net_proto_family *pf; ...... err = security_socket_create(family, type, protocol, kern); //SElinux相关,跳过 if (err) return err; /* * Allocate the socket and allow the family to set things up. if * the protocol is 0, the family is instructed to select an appropriate * default. */ sock = sock_alloc(); //创建struct socket结构体 if (!sock) { net_warn_ratelimited("socket: no more sockets\n"); return -ENFILE; /* Not exactly a match, but its the closest posix thing */ } sock->type = type; //设置套接字的类型 ...... rcu_read_lock(); pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]); //获取对应协议族的协议实例对象 ...... rcu_read_unlock(); err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern); //调用对应协议create方法 if (err < 0) goto out_module_put; ...... }
4.1.1 pf->create()函数
pf由net_families[]数组获得:
// file: include/linux/socket.h #define AF_MAX 41 /* For now.. */ #define PF_INET AF_INET // file: include/uapi/linux/net.h #define NPROTO AF_MAX // file: net/socket.c static const struct net_proto_family __rcu *net_families[NPROTO] __read_mostly;
net_families[]数组的初始化在inet_init()函数:
// file: net/ipv4/af_inet.c static const struct net_proto_family inet_family_ops = { .family = PF_INET, .create = inet_create, .owner = THIS_MODULE, }; static int __init inet_init(void) { ...... (void)sock_register(&inet_family_ops); ...... } // file: net/socket.c int sock_register(const struct net_proto_family *ops) { ...... // net_families[]数组里存放的是各个协议族的信息,以family字段作为下标 rcu_assign_pointer(net_families[ops->family], ops); ...... }
因此,pf->create()最终调用的是inet_create()函数。
4.1.2 inet_create()函数
inet_create()主要完成以下工作:
设置socket的状态为SS_UNCONNECTED;
根据socket的type找到对应的套接字类型,获取对应协议类型的接口操作集信息;
使用匹配的协议族操作集初始化sk;
分配并初始化sock结构;
// file: net/ipv4/af_inet.c static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol, int kern) { struct sock *sk; struct inet_protosw *answer; struct inet_sock *inet; struct proto *answer_prot; unsigned char answer_flags; char answer_no_check; int try_loading_module = 0; int err; if (unlikely(!inet_ehash_secret)) if (sock->type != SOCK_RAW && sock->type != SOCK_DGRAM) build_ehash_secret(); sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED; //设置socket的状态 /* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */ lookup_protocol: err = -ESOCKTNOSUPPORT; rcu_read_lock(); //根据socket传入的protocal在inetsw[]数组中查找对应的元素,获取对应协议类型的接口操作集信息 list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) { //sock->type应用层传入的是SOCK_STREAM err = 0; /* Check the non-wild match. */ if (protocol == answer->protocol) { //如果我们在socket的protocal传入的是6,即TCP协议,那么走这个分支 if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP) break; } else { //如果socket的protocal传入的是0,那么走这个分支(我们应用层传入的是0) /* Check for the two wild cases. */ if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) { //IPPROTO_IP内核定义,值为0 protocol = answer->protocol; //重新给protocal赋值,因此socket中protocal传入的是0或者6,都是可以的 break; } if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol) break; } err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT; } //循环结束后,answer的prot和ops,对应的就是inetsw[SOCK_STREAM]协议族信息 ...... sock->ops = answer->ops; //将查找到的对应协议族的协议函数操作集赋值给我们之前创建的socket answer_prot = answer->prot; answer_no_check = answer->no_check; answer_flags = answer->flags; rcu_read_unlock(); WARN_ON(answer_prot->slab == NULL); err = -ENOBUFS; sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot); //创建sock结构体 if (sk == NULL) goto out; err = 0; sk->sk_no_check = answer_no_check; if (INET_PROTOSW_REUSE & answer_flags) sk->sk_reuse = SK_CAN_REUSE; inet = inet_sk(sk); //强制类型转化,初始化inet_sock结构 inet->is_icsk = (INET_PROTOSW_ICSK & answer_flags) != 0; inet->nodefrag = 0; if (SOCK_RAW == sock->type) { inet->inet_num = protocol; if (IPPROTO_RAW == protocol) inet->hdrincl = 1; } if (ipv4_config.no_pmtu_disc) inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT; else inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT; inet->inet_id = 0; sock_init_data(sock, sk); //sock初始化 sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct; sk->sk_protocol = protocol; sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv; inet->uc_ttl = -1; inet->mc_loop = 1; inet->mc_ttl = 1; inet->mc_all = 1; inet->mc_index = 0; inet->mc_list = NULL; inet->rcv_tos = 0; sk_refcnt_debug_inc(sk); if (inet->inet_num) { /* It assumes that any protocol which allows * the user to assign a number at socket * creation time automatically * shares. */ inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num); /* Add to protocol hash chains. */ sk->sk_prot->hash(sk); } //另一部分初始化,根据不同协议类型,调用对应init函数 if (sk->sk_prot->init) { err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk); //调用相对应4层协议的初始化函数 if (err) sk_common_release(sk); } out: return err; out_rcu_unlock: rcu_read_unlock(); goto out; }
4.1.2.1 inetsw[]数组
inetsw[]数组存放的是各个sock_type的信息,它也是在inet_init()函数中初始化:
// file:net/ipv4/af_inet.c static struct list_head inetsw[SOCK_MAX]; static int __init inet_init(void) { ...... /* Register the socket-side information for inet_create. */ for (r = &inetsw[0]; r < &inetsw[SOCK_MAX]; ++r) INIT_LIST_HEAD(r); for (q = inetsw_array; q < &inetsw_array[INETSW_ARRAY_LEN]; ++q) inet_register_protosw(q); ...... }
其中inetsw_array[]存放的就是具体的每种sock的信息,包括操作函数,协议号等,其中prot和ops两个成员是比较重要的,后续很多操作依赖于这两个成员:
// file: net/ipv4/af_inet.c static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] = { { .type = SOCK_STREAM, .protocol = IPPROTO_TCP, .prot = &tcp_prot, .ops = &inet_stream_ops, .no_check = 0, .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT | INET_PROTOSW_ICSK, }, { .type = SOCK_DGRAM, .protocol = IPPROTO_UDP, .prot = &udp_prot, .ops = &inet_dgram_ops, .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT, .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT, }, { .type = SOCK_DGRAM, .protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP, .prot = &ping_prot, .ops = &inet_dgram_ops, .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT, .flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE, }, { .type = SOCK_RAW, .protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */ .prot = &raw_prot, .ops = &inet_sockraw_ops, .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT, .flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE, } };
通过inet_register_protosw()函数,将上述inetsw_array[]里的元素,按照type字段挂在inetsw[]数组的链表上。
void inet_register_protosw(struct inet_protosw *p) { ...... list_add_rcu(&p->list, last_perm); //按照type的值,添加到inetsw[type]数组中的链表中 ...... }
4.1.2.2 sock初始化
sock_init_data()函数,将之前分配的struct socket和struct sock联系在一起:
// file: net/core/sock.c void sock_init_data(struct socket *sock, struct sock *sk) { ...... sk->sk_send_head = NULL; init_timer(&sk->sk_timer); sk->sk_allocation = GFP_KERNEL; sk->sk_rcvbuf = sysctl_rmem_default; sk->sk_sndbuf = sysctl_wmem_default; sk->sk_state = TCP_CLOSE; sk_set_socket(sk, sock); ...... sock->sk = sk; ...... } // file: include/net/sock.h static inline void sk_set_socket(struct sock *sk, struct socket *sock) { sk_tx_queue_clear(sk); sk->sk_socket = sock; }
sk->sk_prot->init(),对于TCP协议,这个init成员指向的是tcp_v4_init_sock()函数:
// file: net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c struct proto tcp_prot = { .name = "TCP", .owner = THIS_MODULE, .close = tcp_close, .connect = tcp_v4_connect, .disconnect = tcp_disconnect, .accept = inet_csk_accept, .ioctl = tcp_ioctl, .init = tcp_v4_init_sock, ...... } // file: net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c static int tcp_v4_init_sock(struct sock *sk) { struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk); tcp_init_sock(sk); icsk->icsk_af_ops = &ipv4_specific; ...... }
4.2 sock_map_fd()函数
这个函数主要有两个部分:
创建file文件结构,fd文件描述符;
将file文件结构和fd文件描述符关联,同时将上一步返回的socket也一起绑定,形成一个完整的逻辑;
// file: net/socket.c static int sock_map_fd(struct socket *sock, int flags) { struct file *newfile; int fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags); //获取一个未使用的文件描述符 if (unlikely(fd < 0)) return fd; newfile = sock_alloc_file(sock, flags, NULL); //分配file结构体 if (likely(!IS_ERR(newfile))) { fd_install(fd, newfile); return fd; } put_unused_fd(fd); return PTR_ERR(newfile); } // file: net/socket.c struct file *sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, int flags, const char *dname) { ...... sock->file = file; file->f_flags = O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK); file->private_data = sock; //file与socket关联 return file; }
4.3 总结一下
socket系统调用的操作:
首先在内核生成一个socket_alloc和tcp_sock类型的对象,其中sock_alloc对象中的socket和tcp_sock对象的sock绑定,sock_alloc对象中的inode和file类型对象绑定。
然后将分配的文件描述符fd和file对象关联,最后将这个文件描述符fd返回给用户使用。
经过这一连串操作,用户只要使用fd,内核就能根据这个fd进行网络连接管理的各种操作。
fd与内核sock各个结构的关系,如下图所示:

五、socket代码流程图





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人