Python Automated Machine Learning tool :TPOT
TPOT是一个开源的机器学习项目,项目地址为:https://github.com/EpistasisLab/tpot
1. TPOT with code
1 2 | <button id="btn0" onclick="view_code('pre0');">view code</button>step 1: 导入类模块from tpot import TPOTClassifier #分类器from tpot import TPOTRegressor #回归器 |
step 2: 实例化(default)
#创建默认分类器 default_pipeline_optimizer_classifier = TPOTClassifier() #创建默认回归器 default_pipeline_optimizer_regressor = TPOTRegressor()
step 2: 实例化(custom)
#创建自定义分类器 custom_pipeline_optimezer_classifier = TPOTClassifier(generations=50,population_size=50,cv=5,random_state=100, verbosity=2) #创建自定义回归器 custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor =TPOTRegressor(generations=5,population_size=5,cv=5,random_state=20, verbosity=1)
step 3: 准备训练集、测试集 X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = ? #可以使用sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split()函数 step 4: 训练 custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor.fit(X_train, y_train) step 5: 测试 print(custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor.score(X_test, y_test)) step 6: export the corresponding Python code for the optimized pipeline custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor.export('tpot_exported_pipeline.py')
2.scoring function
方式一:pass a string to the attribute scoring
属性值可以为
'accuracy', 'adjusted_rand_score', 'average_precision', 'balanced_accuracy',
'f1','f1_macro', 'f1_micro', 'f1_samples', 'f1_weighted', 'neg_log_loss', 'neg_mean_absolute_error',
'neg_mean_squared_error', 'neg_median_absolute_error', 'precision', 'precision_macro', 'precision_micro',
'precision_samples', 'precision_weighted','r2', 'recall', 'recall_macro', 'recall_micro', 'recall_samples',
'recall_weighted', 'roc_auc', 'my_module.scorer_name*'
方式二:用户自定义
# Make a custom metric function def my_scoring_func(y_true, y_pred): return mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred) # Make a custom a scorer from the custom metric function # Note: greater_is_better=False in make_scorer below would mean that the scoring function should be minimized. my_scorer = sklearn.metrics.scorer.make_scorer(my_scoring_func,greater_is_better=False)
custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor =TPOTRegressor(generations=5,population_size=5,cv=5,random_state=20, verbosity=1,scoring=my_scorer)
3.config_dict
有四个默认的configuration options
- Default TPOT
- TPOT light
- TPOT MDR
- TPOT sparse
具体说明:http://epistasislab.github.io/tpot/using/#built-in-tpot-configurations
1 2 | <button id="btn6" onclick="view_code('pre6');">view code</button>custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor =TPOTRegressor(generations=5,population_size=5,cv=5,random_state=20, verbosity=1,config_dict='TPOT light') |
4.用户自定义config
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | <button id="btn7" onclick="view_code('pre7');">view code</button>tpot_config = { 'sklearn.naive_bayes.GaussianNB': { }, 'sklearn.naive_bayes.BernoulliNB': { 'alpha': [1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1., 10., 100.], 'fit_prior': [True, False] }, 'sklearn.naive_bayes.MultinomialNB': { 'alpha': [1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1., 10., 100.], 'fit_prior': [True, False] }}custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor =TPOTRegressor(generations=5,population_size=5,cv=5,random_state=20, verbosity=1,config_dict=tpot_config) |
5.分布式环境训练
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <button id="btn8" onclick="view_code('pre8');">view code</button>from sklearn.externals import joblibimport distributed.joblibfrom dask.distributed import Client# connect to the clusterclient = Client('schedueler-address')# create the estimator normallyestimator = TPOTClassifier(n_jobs=-1)# perform the fit in this context managerwith joblib.parallel_backend("dask"): estimator.fit(X, y) |
6.实际项目(回归问题)
项目目标是预测下游水库的进水量,其源数据内容如下,共有2161条记录
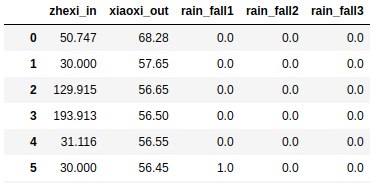
第一列是下游水库的进水量,第二列是上游水库的出水量,其余的是上下游之间降雨观测点的雨量信息 . 现只考虑上下游进出水量之间的影响,预测下游水库的进水量。
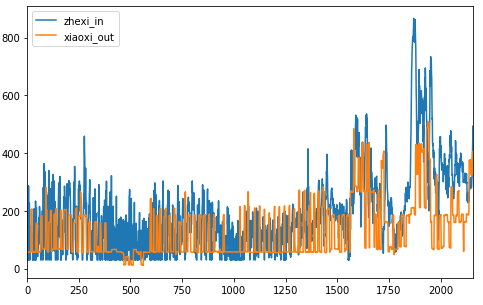
两者的趋势如下图
完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | <button id="btn9" onclick="view_code('pre9');">view code</button>from tpot import TPOTClassifierfrom tpot import TPOTRegressorfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errorfrom sklearn.metrics.scorer import make_scorerfrom sklearn.externals import joblibfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressorfrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV#import distributed.joblibfrom dask.distributed import Clientfrom dask.distributed import LocalClusterimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pddef get_train_test_by_OP(data,offset,period): xiaoxi_out = data[:,1] zhexi_in = data[:,0] size = len(zhexi_in) source_xiaoxi_out=[[] for i in range(period)] source_zhexi_in = [[] for i in range(period)] for i in range(period): source_xiaoxi_out[i]=xiaoxi_out[i :size-offset-period+i] source_zhexi_in[i] = zhexi_in[i+offset:size-period+i] data_vec = np.hstack((np.array(source_xiaoxi_out).transpose(1,0), np.array(source_zhexi_in).transpose(1,0))) label = zhexi_in[offset+period:] X, _X, y , _y = train_test_split(data_vec,label,test_size=0.1,random_state=13) return X, y , _X, _ydef my_scoring_func(y_true,y_pred): return (sum((y_true - y_pred)**2)/len(y_true))custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor =TPOTRegressor(generations=5,population_size=5,cv=5,random_state=20, verbosity=2,scoring=my_scorer)data = np.array(pd.read_csv('seasons/2015_spring.csv',header=None))X, y ,_X, _y = get_train_test_by_OP(data,54,44)custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor.fit(X, y)print(custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor.score(_X, _y))custom_pipeline_optimezer_regressor.export('tpot_exported_pipeline.py') |
结果如下
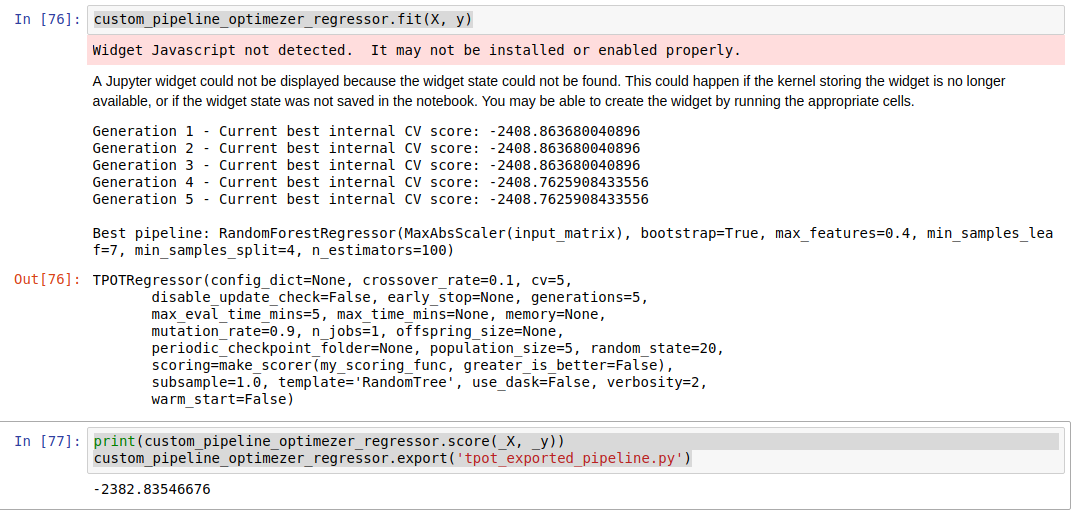
训练完成后,TPOT已经给出了最佳模型及其参数信息,我们可以这些信息建模预测,分析结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <button id="btn10" onclick="view_code('pre10');">view code</button>model = RandomForestRegressor(bootstrap=True, max_features=0.4, min_samples_leaf=7, min_samples_split=4, n_estimators=100)model.fit(X,y)pre = model.predict(_X)mse = mean_squared_error(_y, pre)plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))plt.plot(_y)plt.plot(pre)plt.legend(('true','predict'))plt.title('mse:'+str(mse))plt.show() |
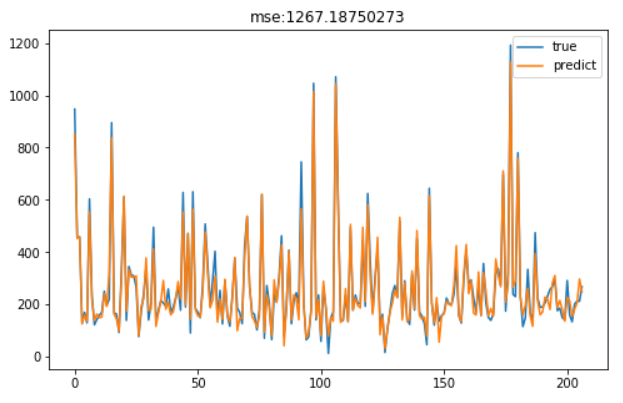
可见,效果不错。当然我们也可以用grid_searh来调参
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | <button id="btn11" onclick="view_code('pre11');">view code</button>tuned_parameters = [{'max_features':[i/10 for i in range(1,10)], 'min_samples_leaf':[i for i in range(1,10)], 'bootstrap':[True,False], 'min_samples_split':[i for i in range(2,10)], 'n_estimators':[i for i in range(80,150)], 'max_features':[i/10 for i in range(1,10)]}]clf = GridSearchCV(RandomForestRegressor(),tuned_parameters)clf.fit(X,y)pre = model.predict(_X)print(mean_squared_error(_y, pre))print(clf.best_estimator_) |
上面我们用到的是2015年春季的数据训练的模型,我们希望该模型能准确预测春季下游水库的进水量。为此,利用该模型预测2018年春季的下游水库进水量,看其是否达到一个很好的效果。结果如下
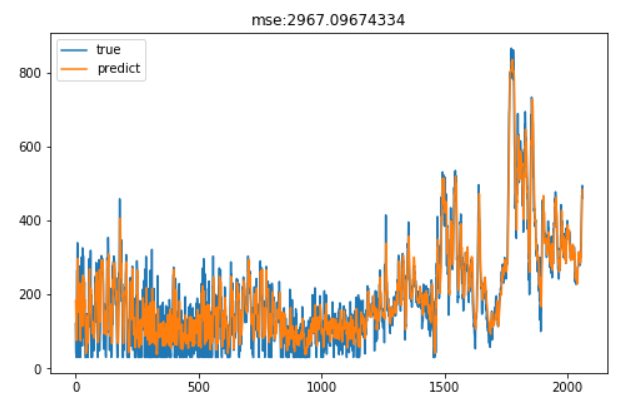
可以看到,预测效果较好。
7.mnist手写数字识别(分类问题)
from tpot import TPOTClassifier from sklearn.datasets import load_digits from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split digits = load_digits() X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target, train_size=0.75, test_size=0.25) pipeline_optimizer = TPOTClassifier(generations=5, population_size=50, cv=5, random_state=42, verbosity=2,n_jobs=6) pipeline_optimizer.fit(X_train, y_train) print(pipeline_optimizer.score(X_test, y_test)) pipeline_optimizer.export('tpot_exported_pipeline_classifier.py')
结果如下
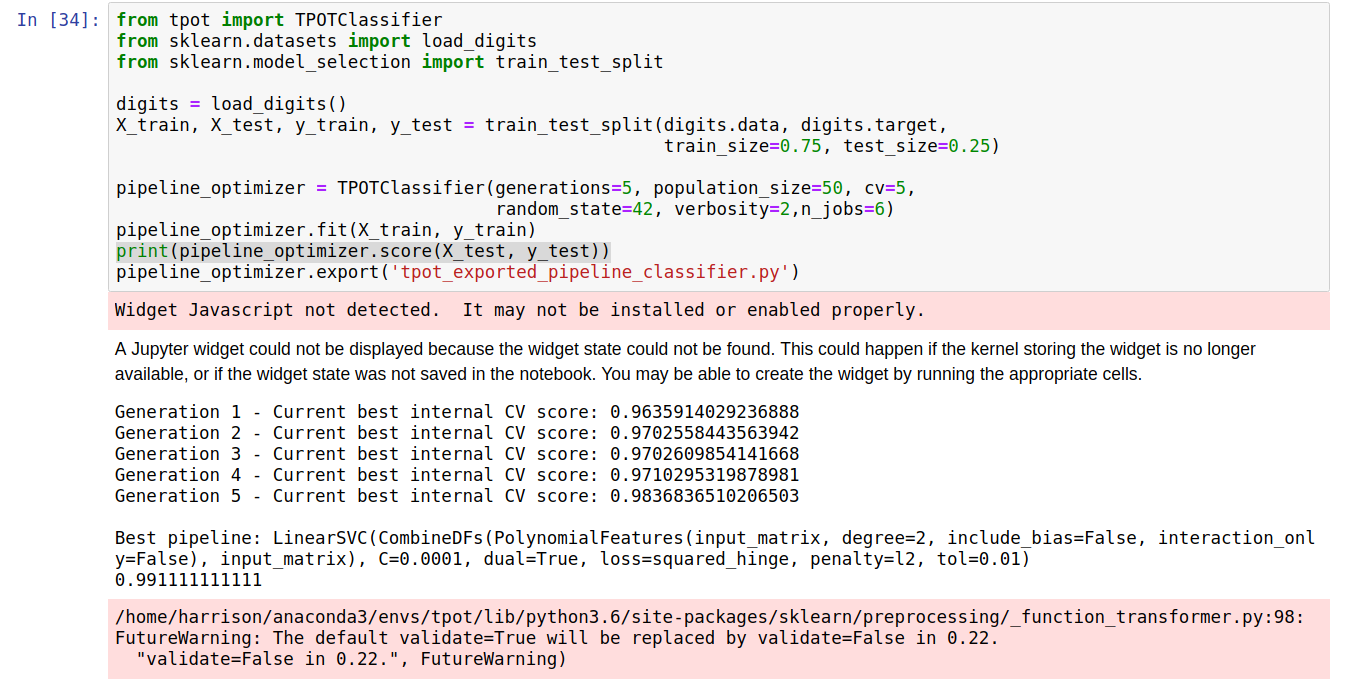
最终的准确度达到了0.991111111111,由于笔者电脑硬件限制,跑起来有些吃力,大家可尝试将generations, population_size的值增大,观察跑的结果
8. 总结
由两次实验的结果可见,无论是回归问题还是分类问题,TPOT都可以为我们寻找一个比较优秀的解决方案,但是整个训练过程比较费时,对硬件资源要求较高。总的说来,这是一个非常优秀的机器学习工具。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!