线性表结构:队列
什么是队列#
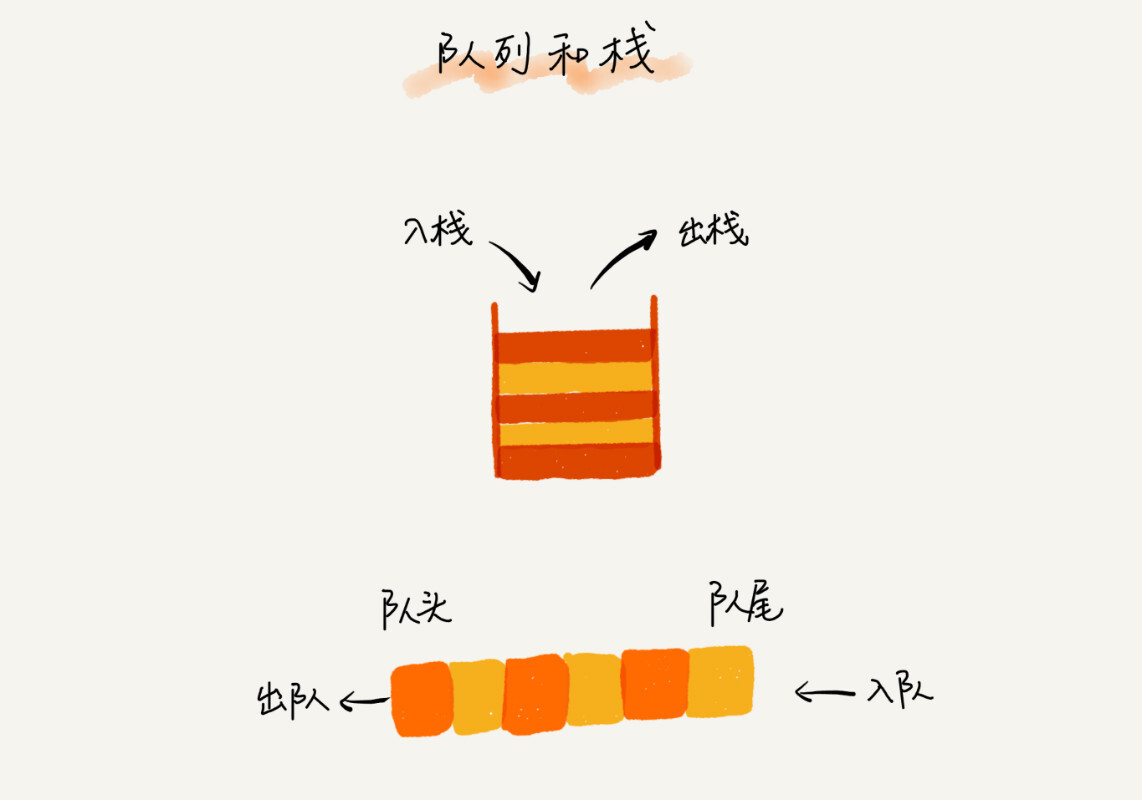
队列是一种先进入的元素先出的线性表结构。这个特性正好和栈的特性相反。
我们知道,栈只支持两个基本操作:入栈 push()和出栈 pop()。队列跟栈非常相似,支持的操作也很有限,最基本的操作也是两个:入队 enqueue(),放一个数据到队列尾部;出队 dequeue(),从队列头部取一个元素。
手动实现队列#
队列的实现方式也有两种,一种是通过数组实现,叫顺序队列,另外一种是通过链表实现,叫链式队列。
顺序队列
public static class MyQueue<E> {
private Object[] array;
private int head;
private int tail;
public MyQueue(int capacity) {
this.array = new Object[capacity];
}
public boolean enqueue(E e) {
array[tail] = e;
int length = array.length;
tail = (++tail) % length;
if (tail == head) {
// 扩容
Object[] data = new Object[length * 2];
int index = 0;
int i = head;
do {
data[index++] = array[i];
i = (++i) % length;
} while (i != head);
tail = length;
head = 0;
array = data;
}
return true;
}
public E dequeue() {
if (head == tail) {
return null;
}
E item = (E) array[head];
array[head] = null;
head = (++head) % (array.length);
return item;
}
}
链式队列
public static class MyQueue<E> {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public MyQueue() {
}
public MyQueue(E data) {
head = tail = new Node(data);
}
public boolean enqueue(E data) {
if (head == null) {
this.head = new Node(data);
this.tail = head;
} else {
Node node = new Node(data);
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
}
return true;
}
public E dequeue() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
} else {
E item = (E) head.data;
head = head.next;
return item;
}
}
}
public static class Node<E> {
private E data;
private Node next;
public Node(E data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public Node(E data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
JDK 中的队列实现#
如果不想自己实现队列,那么我们可以使用 JDK 提供的队列实现。
主要实现有:
- ArrayDeque
- LinkedList
下面看下使用LinkedList来实现Queue的例子:
public static class MyQueue<E> {
private LinkedList<E> queue;
public MyQueue() {
this.queue = new LinkedList<E>();
}
public MyQueue(E e) {
this.queue = new LinkedList<E>();
queue.add(e);
}
public boolean enqueue(E e) {
queue.offer(e);
return true;
}
public E dequeue() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
return null;
} else {
return queue.pop();
}
}
}
常见的队列种类#
循环队列、阻塞队列、并发队列。它们在很多偏底层系统、框架、中间件的开发中,起着关键性的作用。比如高性能队列 Disruptor、Linux 环形缓存,都用到了循环并发队列;Java concurrent 并发包利用 ArrayBlockingQueue 来实现公平锁等。
循环队列#
在上面的顺序队列的实现过程中,我们使用了循环队列的实现方式。使用循环队列,可以避免在数组中对数据进行搬移。
阻塞队列#
所谓阻塞队列是指:在队列是空的情况下从队列头部取一个元素,操作会被阻塞直到队列中被插入一个元素,在队列满的情况下,向队列中插入一个元素,操作也会被阻塞,直到其他操作从队列中取出一个元素为止。
我们发现,通过阻塞队列可以很好的实现一个生产者和消费者模式。
- ArrayBlockingQueue.java
- BlockingDeque.java
- DelayQueue.java
- LinkedBlockingDeque.java
- LinkedBlockingQueue.java
- LinkedTransferQueue.java
- PriorityBlockingQueue.java
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
- SynchronousQueue.java
- TransferQueue.java
Java 中提供了以上的阻塞队列相关的实现或者接口,其中的队列实现也是线程安全的。
并发队列#
线程安全的队列实现,参考Java并发包下面的队列实现。
队列的应用场景#
队列可以应用在任何有限资源池中,用于排队请求,比如数据库连接池等。实际上,对于大部分资源有限的场景,当没有空闲资源时,基本上都可以通过“队列”这种数据结构来实现请求排队。
作者:程序员自由之路
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/54chensongxia/p/14831231.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?