Springboot配置
作者:gqk
SpringBoot可以识别两种格式的配置文件,分别是yml文件与properties文件,我们可以将application.properties文件换成application.yml,这两个文件都可以被SpringBoot自动识别并加载,但是如果是自定义的配置文件,就最好还是使用properties格式的文件,因为SpringBoot中暂时还并未提供手动加载yml格式文件的功能(这里指注解方式)。
application.properties配置文件欲被SpringBoot自动加载,需要放置到指定的位置:src/main/resource目录下,一般自定义的配置文件也位于此目录之下。
1:application.properties
配置改变端口号
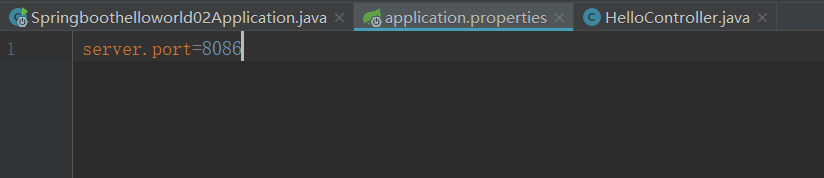
2:application.yml的配置
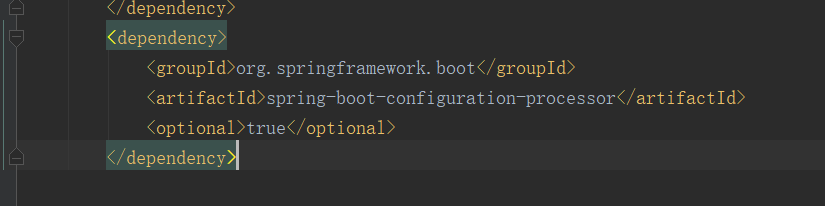
配置类智能提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
实体类的创建
Person.class
package com.gqk.springboot.bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @Component//交给容器处理 public class Person { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Boolean getBoss() { return boss; } public void setBoss(Boolean boss) { this.boss = boss; } public Date getBirth() { return birth; } public void setBirth(Date birth) { this.birth = birth; } public Map<String, Object> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public List<Object> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<Object> lists) { this.lists = lists; } public Dog getDog() { return dog; } public void setDog(Dog dog) { this.dog = dog; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "lastName='" + lastName + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", boss=" + boss + ", birth=" + birth + ", maps=" + maps + ", lists=" + lists + ", dog=" + dog + '}'; } }
Dog.class
package com.gqk.springboot.bean; public class Dog { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
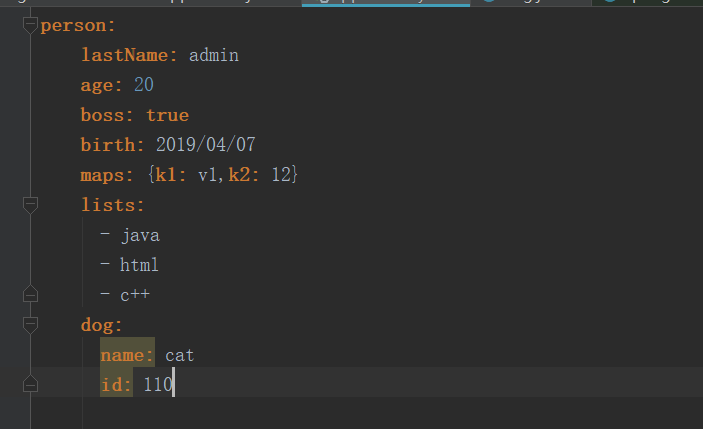
application.yml配置
测试:
package com.gqk.springboot; import com.gqk.springboot.bean.Person; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class Springboothelloworld02ApplicationTests { @Autowired private Person person; @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.print(person); } }
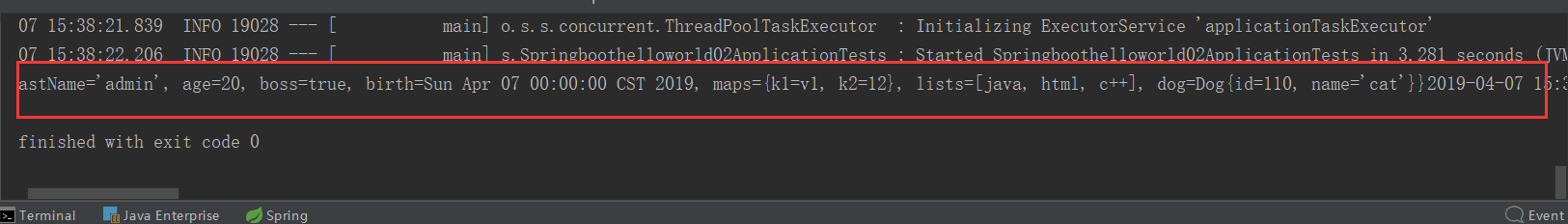
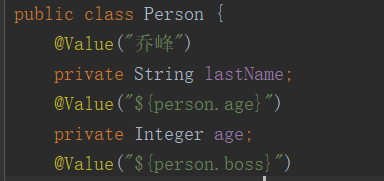
@Value注解
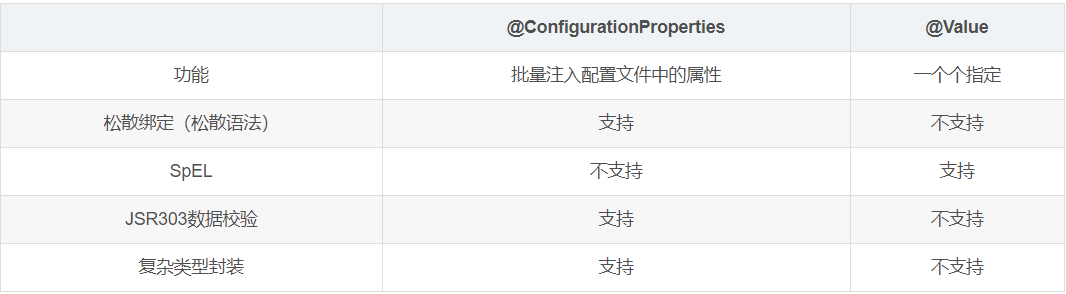
@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
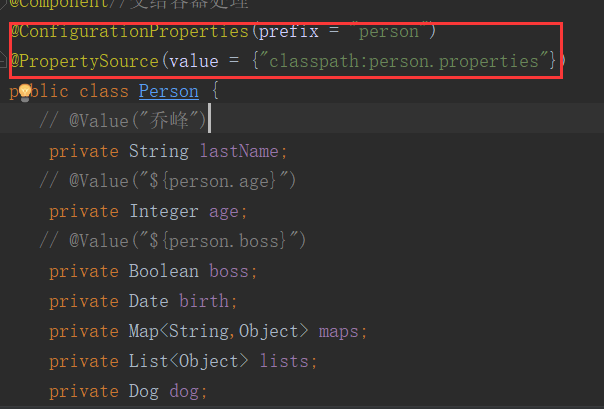
@PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
application.properties/yml代表的是全局的配置文件,我们可以用自定义的名称来定义配置文件,比如说person.properties
person.properties
person.last-name=李四 person.age=23 person.boss=true
注解测试没有任何结果的需要将配置文件引入
注意:一定还要加载全局配置文件否则获取不到值(坑我了!)
@PropertySource
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
之前的Spring配置文件
但是Springboot不认识此配置文件需要在主配置上添加@ImportResource注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="student" class="com.gqk.springboot.bean.Student"></bean> </beans>
package com.gqk.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource; @ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"}) @SpringBootApplication public class Springboothelloworld02Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Springboothelloworld02Application.class, args); } }
测试:
package com.gqk.springboot; import com.gqk.springboot.bean.Person; import com.gqk.springboot.bean.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class Springboothelloworld02ApplicationTests { @Autowired private Person person; @Resource private ApplicationContext ac; @Test public void getStu(){ Student stu = (Student) ac.getBean("student"); System.out.print(stu); } @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.print(person); } }
Spring提倡全配置不提倡配置文件:直接通过一个类来替换之前的配置文件
@Configuration:表示一个配置文件
@Bean:表示一个组件
student()方法名称表示为bean的id
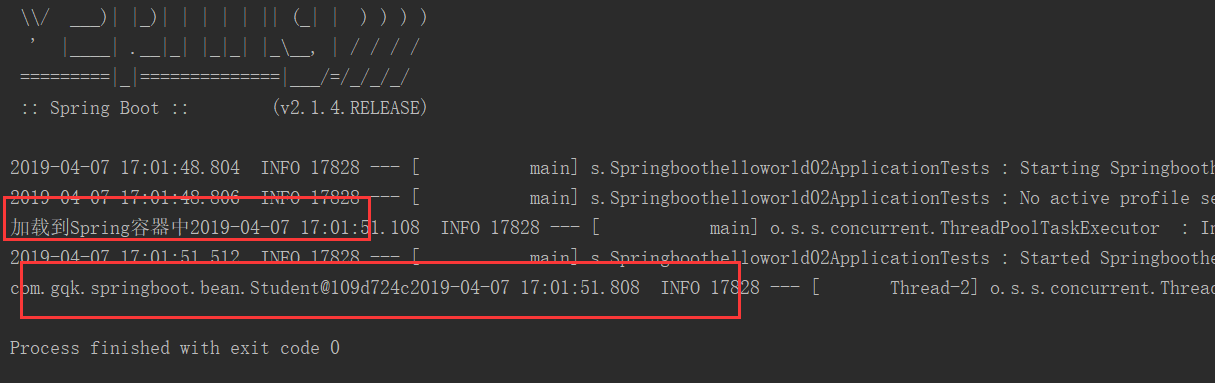
package com.gqk.springboot.config; import com.gqk.springboot.bean.Student; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class MyConfig { @Bean public Student student(){ System.out.print("加载到Spring容器中"); return new Student(); } }
测试:
package com.gqk.springboot; import com.gqk.springboot.bean.Person; import com.gqk.springboot.bean.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class Springboothelloworld02ApplicationTests { @Autowired private Person person; @Resource private ApplicationContext ac; @Test public void getStu(){ Student stu = (Student) ac.getBean("student"); System.out.print(stu); } @Test public void contextLoads() { System.out.print(person); } }