关于AWS-VPC中的公有子网与私有子网-Public and private subnets
Posted on 2023-05-27 08:18 520_1351 阅读(336) 评论(0) 收藏 举报关于AWS-VPC中的公有子网与私有子网的详细说明
可以参考我们可以参考官网文档 Amazon VPC / User Guide 中有如下说明:
Public and private subnets
If a subnet is associated with a route table that has a route to an internet gateway,it's known as a public subnet.
If a subnet is associated with a route table that does not have a route to an internet gateway, it's known as a private subnet.
In your public subnet's route table, you can specify a route for the internet gateway to all destinations not explicitly known
to the route table (0.0.0.0/0 for IPv4 or ::/0 for IPv6). Alternatively, you can scope the route to a narrower range of IP addresses;
for example, the public IPv4 addresses of your company’s public endpoints outside of AWS, or the Elastic IP addresses of other Amazon EC2 instances outside your VPC.
IP addresses and NAT
To enable communication over the internet for IPv4, your instance must have a public IPv4 address.
You can either configure your VPC to automatically assign public IPv4 addresses to your instances, or you can assign Elastic IP addresses to your instances.
Your instance is only aware of the private (internal) IP address space defined within the VPC and subnet.
// 因此如果实例的网络接口上配置有公有IP地址,我们在操作系统OS里面,也能只查询到私有IP地址,公有IP在外面的网络接口上才能看到
The internet gateway logically provides the one-to-one NAT on behalf of your instance, so that when traffic leaves your VPC subnet and goes to the internet,
the reply address field is set to the public IPv4 address or Elastic IP address of your instance, and not its private IP address.
Conversely, traffic that's destined for the public IPv4 address or Elastic IP address of your instance has its destination address
translated into the instance's private IPv4 address before the traffic is delivered to the VPC.
To enable communication over the internet for IPv6, your VPC and subnet must have an associated IPv6 CIDR block,
and your instance must be assigned an IPv6 address from the range of the subnet. IPv6 addresses are globally unique, and therefore public by default.
In the following diagram, the subnet in Availability Zone A is a public subnet.
The route table for this subnet has a route that sends all internet-bound IPv4 traffic to the internet gateway.
The instances in the public subnet must have public IP addresses or Elastic IP addresses to enable communication with the internet over the internet gateway.
For comparison, the subnet in Availability Zone B is a private subnet because its route table does not have a route to the internet gateway.
Instances in the private subnet can't communicate with the internet over the internet gateway, even if they have public IP addresses.
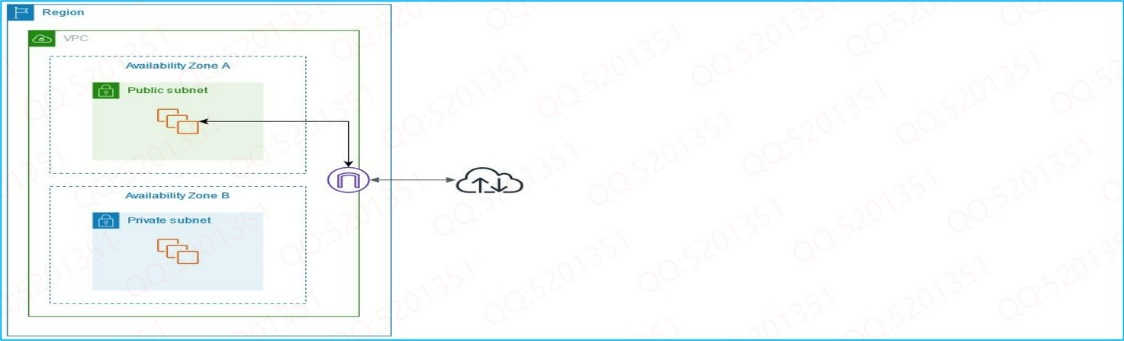
To provide your instances with internet access without assigning them public IP addresses, you can use a NAT device instead.
A NAT device enables instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet, but prevents hosts on the internet from initiating connections with the instances.
For more information, see Connect to the internet or other networks using NAT devices.
作者:一名卑微的IT民工
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/5201351
本博客所有文章仅用于学习、研究和交流目的,欢迎非商业性质转载。
由于博主的水平不高,文章没有高度、深度和广度,只是凑字数,不足和错误之处在所难免,希望大家能够批评指出。
博主是利用读书、参考、引用、复制和粘贴等多种方式打造成自己的文章,请原谅博主成为一个卑微的IT民工!

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号