设计模式--策略模式
简介
策略模式是一种行为设计模式,它将一组行为转换为对象,并使其在原始上下文对象内部能够相互替换
- 原始对象被称为上下文,它包含指向策略对象的引用并将执行行为的任务分派给策略对象
组成
- 策略接口(Strategy):所有具体策略的通用接口,它声明了一个上下文用于执行策略的方法
- 具体策略(Concrete Strategies):实现上下文所用算法的各种不同变体
- 上下文(Context):维护指向具体策略的引用,且仅通过策略接口与该对象进行交流
- 客户端(Client):创建一个特定策略对象并将其传递给上下文。上下文则会提供一个设置器以便客户端在运行时替换相关联的策略
案例:策略模式被用于在电子商务应用中实现各种支付方法(信用卡、支付宝、微信支付),具体策略不仅会完成实际的支付工作。如果不使用策略模式,则会出现使用if else 判断具体的支付方式,对后续的新增和修改不符合开闭原则。

实现方式
策略接口
将支付的行为抽象为一个策略接口
public interface PaymentStrategy {
/**
* 支付
*/
boolean payment(BigDecimal amount);
}具体策略的实现
public class PayByCreditCard implements PaymentStrategy{
@Override
public boolean payment(BigDecimal amount) {
//信用卡支付逻辑
System.out.println("信用卡支付逻辑");
return true;
}
}public class PayByWechatPayment implements PaymentStrategy{
@Override
public boolean payment(BigDecimal amount) {
//微信支付逻辑
System.out.println("微信支付逻辑");
return true;
}
}public class PayByAliPayment implements PaymentStrategy{
@Override
public boolean payment(BigDecimal amount) {
//支付宝支付逻辑
System.out.println("支付宝支付逻辑");
return true;
}
}上下文对象
public class PaymentContext {
private final PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy;
public PaymentContext(PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = paymentStrategy;
}
public boolean payment(BigDecimal amount) {
return paymentStrategy.payment(amount);
}
}客户端
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PaymentContext creditCard = new PaymentContext(new PayByCreditCard());
creditCard.payment(new BigDecimal(10));
PaymentContext aliPayment = new PaymentContext(new PayByAliPayment());
aliPayment.payment(new BigDecimal(10));
PaymentContext wechatPayment = new PaymentContext(new PayByWechatPayment());
wechatPayment.payment(new BigDecimal(10));
}
}项目中使用
在进行企业微信内部应用开发时,应用可以接收成员发送的信息,信息格式包括:文本、图片、语音、视频、位置、链接。每种消息的格式都有不同的处理方式,根据消息的类型进行区分选择对应的策略进行处理即可。具体的UML如下
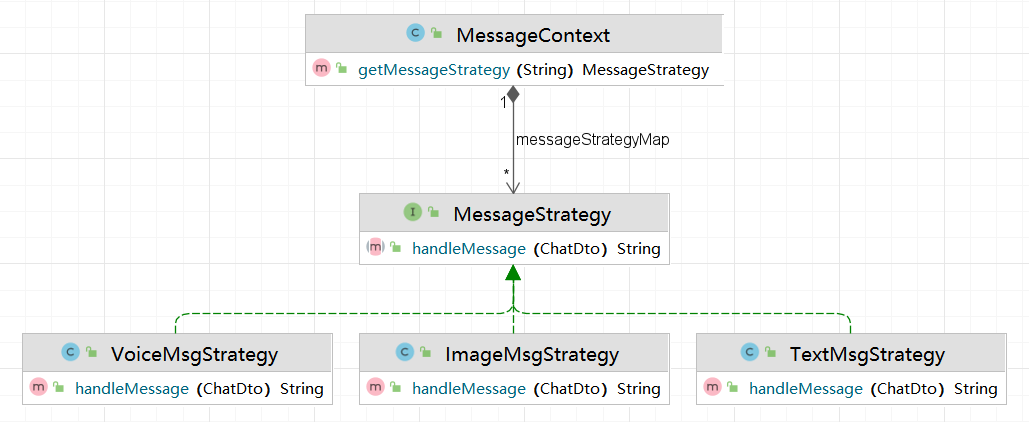
消息策略接口
public interface MessageStrategy {
/**
* 处理消息
* @param chat 解密后的明文信息
* @return 被动返回的内容
*/
String handleMessage(ChatDto chat);
}具体策略实现
@Slf4j
@Component("image")
public class ImageMsgStrategy implements MessageStrategy {
private final CommonUtils commonUtils;
public ImageMsgStrategy(CommonUtils commonUtils) {
this.commonUtils = commonUtils;
}
@Override
public String handleMessage(ChatDto chat) {
CompletableFuture<Response> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//图片消息的处理逻辑
log.info("接收到用户发送的图片消息为:" + chat.getMsg());
return Response.builder().data(Data.builder().data("image msg").build()).build();
});
//处理完后,返回信息给到企业微信推送给到具体的用户
future.thenAccept(response -> commonUtils.writeResponse(response, chat));
//被动回复
return "";
}
}@Slf4j
@Component("voice")
public class VoiceMsgStrategy implements MessageStrategy {
private final CommonUtils commonUtils;
public VoiceMsgStrategy(CommonUtils commonUtils) {
this.commonUtils = commonUtils;
}
@Override
public String handleMessage(ChatDto chat) {
CompletableFuture<Response> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//语音消息的处理逻辑
log.info("接收到用户发送的语音消息为:" + chat.getMsg());
return Response.builder().data(Data.builder().data("voice msg").build()).build();
});
//处理完后,返回信息给到企业微信推送给到具体的用户
future.thenAccept(response -> commonUtils.writeResponse(response, chat));
//被动回复
return "";
}
}@Slf4j
@Component("text")
public class TextMsgStrategy implements MessageStrategy {
private final CommonUtils commonUtils;
public TextMsgStrategy(CommonUtils commonUtils) {
this.commonUtils = commonUtils;
}
@Override
public String handleMessage(ChatDto chat) {
CompletableFuture<Response> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//文本消息的处理逻辑
log.info("接收到用户发送的文本消息为:" + chat.getMsg());
return Response.builder().data(Data.builder().data("text msg").build()).build();
});
//处理完后,返回信息给到企业微信推送给到具体的用户
future.thenAccept(response -> commonUtils.writeResponse(response, chat));
//被动回复
return "";
}
}上下文对象
@Component
public class MessageContext {
@Resource
private Map<String,MessageStrategy> messageStrategyMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MessageStrategy getMessageStrategy(String msgType) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(msgType)) {
throw new NullPointerException("msgType 消息类型为空");
}
MessageStrategy strategy = messageStrategyMap.get(msgType);
if (Objects.isNull(strategy)) {
throw new NullPointerException(String.format("不存在消息类型为:%s 的策略", msgType));
}
return strategy;
}
}测试使用
@GetMapping(value = "/msg")
public @ResponseBody Response<String> msg(@RequestParam(value = "agentId") String agentId,
@RequestParam(value = "fromUser") String fromUser,
@RequestParam(value = "msgType") String msgType) {
ChatDto chatDto = new ChatDto();
chatDto.setAgentId(agentId);
chatDto.setFromUser(fromUser);
chatDto.setMsgType(msgType);
MessageStrategy strategy = messageContext.getMessageStrategy(chatDto.getMsgType());
String msg = strategy.handleMessage(chatDto);
return Response.ok(msgType + " success" + msg);
}优势和缺点
优势
- 将算法的实现和使用算法的代码隔离开来
- 符合开闭原则。无需对上下文进行修改即可引入新的策略
缺点
- 如果算法极少发生改变,引入策略模式会使程序过于复杂
- 客户端必须知道策略间的不同——它需要选择合适的策略
使用场景
- 当想使用对象中各种不同的算法变体, 并希望能在运行时切换算法时, 可使用策略模式
- 当有许多仅在执行某些行为时略有不同的相似类时, 可使用策略模式
Java 中使用案例
-
对
java.util.Comparator#compare的调用来自Collections#sort()
识别方法: 策略模式可以通过允许嵌套对象完成实际工作的方法以及允许将该对象替换为不同对象的设置器来识别




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· PowerShell开发游戏 · 打蜜蜂
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· 百万级群聊的设计实践
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战