设计模式--原型模式(克隆)
简介
原型是一种创建型设计模式, 使你能够复制对象, 甚至是复杂对象, 而又无需使代码依赖它们所属的类
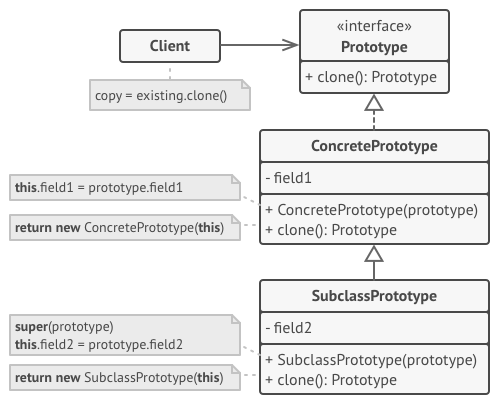
原型 (Prototype) 接口将对克隆方法进行声明。 在绝大多数情况下, 其中只会有一个名为
clone克隆的方法具体原型 (Concrete Prototype) 类将实现克隆方法。 除了将原始对象的数据复制到克隆体中之外, 该方法有时还需处理克隆过程中的极端情况, 例如克隆关联对象和梳理递归依赖等等
- 客户端 (Client) 可以复制实现了原型接口的任何对象
实现
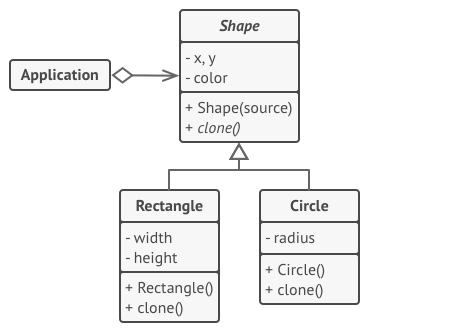
所有形状类都遵循同一个提供克隆方法的接口。 在复制自身成员变量值到结果对象前, 子类可调用其父类的克隆方法
- 基础原型--提供克隆的抽象方法
-
import java.util.Objects; public abstract class Shape { private int x; private int y; private String color; public Shape() { } /**使用已有对象的数值来初始化一个新对象*/ public Shape(Shape target) { if (Objects.nonNull(target)) { this.x = target.x; this.y = target.y; this.color = target.color; } } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Shape shape = (Shape) o; return x == shape.x && y == shape.y && Objects.equals(color, shape.color); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(x, y, color); } /**clone(克隆)操作会返回一个形状子类*/ public abstract Shape clone(); public int getX() { return x; } public void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } public int getY() { return y; } public void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Shape{" + "x=" + x + ", y=" + y + ", color='" + color + '\'' + '}'; } }
-
- 具体原型
-
import java.util.Objects; public class Rectangle extends Shape{ private int width; private int height; public Rectangle(){ } public Rectangle(Rectangle target){ // 需要调用父构造函数来复制父类中定义的私有成员变量 super(target); if (Objects.nonNull(target)) { this.width = target.width; this.height = target.height; } } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; if (!super.equals(o)) return false; Rectangle rectangle = (Rectangle) o; return width == rectangle.width && height == rectangle.height; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), width, height); } @Override public Shape clone() { return new Rectangle(this); } public int getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(int width) { this.width = width; } public int getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(int height) { this.height = height; } @Override public String toString() { return "Rectangle{" + "width=" + width + ", height=" + height + "} " + super.toString(); } } -
import java.util.Objects; public class Circle extends Shape{ private int radius; public Circle(){ } public Circle(Circle target){ // 需要调用父构造函数来复制父类中定义的私有成员变量 super(target); if (Objects.nonNull(target)){ this.radius = target.radius; } } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; if (!super.equals(o)) return false; Circle circle = (Circle) o; return radius == circle.radius; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), radius); } @Override public Shape clone() { return new Circle(this); } public int getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(int radius) { this.radius = radius; } @Override public String toString() { return "Circle{" + "radius=" + radius + "} " + super.toString(); } }
-
- 客户端
-
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Circle circle = new Circle(); circle.setX(10); circle.setY(20); circle.setColor("green"); circle.setRadius(5); Shape clone = circle.clone(); System.out.println(circle.equals(clone));//true Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); circle.setX(5); circle.setY(10); circle.setColor("red"); rectangle.setWidth(5); rectangle.setHeight(2); Shape shape = rectangle.clone(); System.out.println(rectangle.equals(shape));//true } }
-
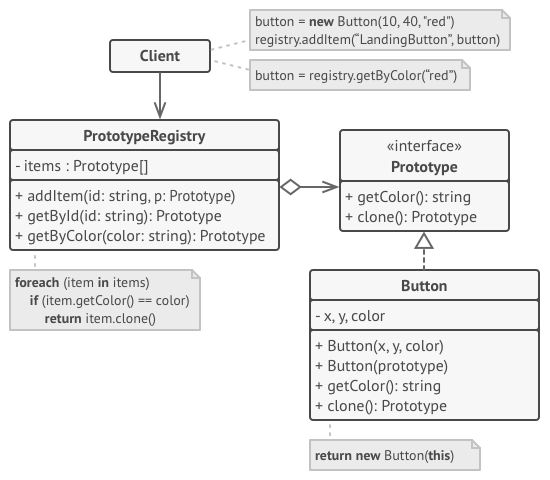
原型注册表模式
名称 → 原型
/**
* @describe 原型工厂
* 实现中心化的原型注册站 (或工厂), 其中包含一系列预定义的原型对象。
* 这样一来, 你就可以通过传递对象名称或其他参数的方式从工厂处获得新的对象。
* 工厂将搜索合适的原型, 然后对其进行克隆复制, 最后将副本返回给你。
*/
public class BundledShapeCache {
/**中心化的原型注册站*/
private Map<String,Shapes> cache = new HashMap<>(8);
/**包含一系列预定义的原型对象*/
public BundledShapeCache() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.x = 5;
circle.y = 7;
circle.radius = 45;
circle.color = "Green";
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.x = 6;
rectangle.y = 9;
rectangle.width = 8;
rectangle.height = 10;
rectangle.color = "Blue";
cache.put("Big green circle", circle);
cache.put("Medium blue rectangle", rectangle);
}
public Shapes put(String key,Shapes shapes){
cache.put(key,shapes);
return shapes;
}
/**根据key获取预定义的对象克隆返回*/
public Shapes get(String key){
return cache.get(key).clone();
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.radius = 12;
circle.x = 10;
circle.y = 10;
circle.color = "yellow";
Circle clone = (Circle) circle.clone();
System.out.println(circle.equals(clone));//true
//从注册工厂
BundledShapeCache shapeCache = new BundledShapeCache();
Shapes green_circle = shapeCache.get("Big green circle");
System.out.println(green_circle.toString());
Circle circle1 = (Circle) shapeCache.put("clone", circle);
System.out.println(circle1.toString());
System.out.println(shapeCache.get("clone"));
}
}优势和缺点
优势:
- 克隆对象, 而无需与它们所属的具体类相耦合
- 用继承以外的方式来处理复杂对象的不同配置
- 克隆预生成原型, 避免反复运行初始化代码
缺点:
- 克隆包含循环引用的复杂对象可能会非常麻烦
使用场景
-
如果你需要复制一些对象, 同时又希望代码独立于这些对象所属的具体类, 可以使用原型模式
这一点考量通常出现在代码需要处理第三方代码通过接口传递过来的对象时。 即使不考虑代码耦合的情况, 你的代码也不能依赖这些对象所属的具体类, 因为你不知道它们的具体信息
原型模式为客户端代码提供一个通用接口, 客户端代码可通过这一接口与所有实现了克隆的对象进行交互, 它也使得客户端代码与其所克隆的对象具体类独立开来
-
如果子类的区别仅在于其对象的初始化方式, 那么你可以使用该模式来减少子类的数量。 别人创建这些子类的目的可能是为了创建特定类型的对象
在原型模式中, 你可以使用一系列预生成的、 各种类型的对象作为原型。客户端不必根据需求对子类进行实例化, 只需找到合适的原型并对其进行克隆即可
Java 中使用案例
Java 的 Cloneable (可克隆) 接口就是立即可用的原型模式。任何类都可通过实现该接口来实现可被克隆的性质
java.lang.Object#clone()(类必须实现java.lang.Cloneable接口,重写Object中的 clone()方法)
参考:https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/prototype




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· PowerShell开发游戏 · 打蜜蜂
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· 百万级群聊的设计实践
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战