mybatis源码分析(一)------------入门
在进行源码分析前,先写一个使用mybatis进行开发的demo,方便我们后面进行分析。
一 关于mybatis的demo
pom.xml文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.yht</groupId> <artifactId>mybatisTest</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>mybatisTest</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- 添加log4j --> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.16</version> </dependency> <!-- 添加mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.2.6</version> </dependency> <!-- 添加mysql驱动 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.12</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
配置文件spring-ibatis:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <properties resource="db.properties"></properties> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${url}" /> <property name="username" value="${username}" /> <property name="password" value="${password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!-- 映射文件 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="com/yht/mybatisTest/dao/goods.xml" /> </mappers> </configuration>
数据库连接信息 db.properties
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/silk username=root password=123456
创建一张Goods商品表
CREATE TABLE `goods` ( `id` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品ID', `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品标题', `detail` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `remark` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '备注', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='商品信息';
创建Goods实体类
public class Goods { private String id; private String name; private String remark; private String detail; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getRemark() { return remark; } public void setRemark(String remark) { this.remark = remark; } public String getDetail() { return detail; } public void setDetail(String detail) { this.detail = detail; } }
创建GoodsDao接口
public interface GoodsDao { public Goods selectGoodsById(String goodsId); }
Mapper配置文件goods.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/ibatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.yht.mybatisTest.dao.GoodsDao"> <select id="selectGoodsById" resultType="com.yht.mybatisTest.entity.Goods" > select * from goods where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
编写测试用例:
public class GoodsDaoTest { @Test public void selectGoodsTest(){
// 共有四个步骤,接下来就针对这四个步骤进行分析
// 1.加载配置文件
// 2.加载Mapper映射文件
// 3.生成Mapper代理对象
// 4.调用方法执行sql的过程
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); GoodsDao goodsMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(GoodsDao.class); Goods goods = goodsMapper.selectGoodsById("1"); System.out.println("id="+goods.getId()+";name="+goods.getName()); } public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() { SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null; String resource = "spring-ibatis.xml"; try { sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources .getResourceAsReader(resource)); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return sqlSessionFactory; } }
目录结构如图:
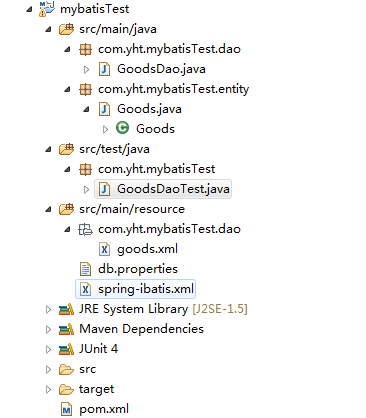
以上就是所有的代码部分,接下来进行源码分析。
二 源码分析
由测试用例可知,在对数据库进行操作前,已经把相关的配置文件信息进行了加载解析,这个加载解析过程是怎样的呢?
从这行代码 new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource)); 入手,配置文件resource转化为Reader,然后传参到build方法中,那么就进入build这个方法:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
//可以看到 build 方法可以接受多种参数组合
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) { return build(reader, null, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment) { return build(reader, environment, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties) { return build(reader, null, properties); } public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { try {
// 将配置文件包装成了XMLConfigBuilder类,进入该构造器可知,其实是把配置文件封装到了XPathParse中 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties); // 进入parser.parse方法
return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } }public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }
进入XMLConfigBuilder类:
// 这是它的三个属性
private boolean parsed; //表示此XMLConfigBuilder是否经过解析 private XPathParser parser;//资源文件信息其实是封装到了这个类中 private String environment;
//这个就是解析配置文件的方法,重点就是在这里
// parser.evalNode("/configuration")的作用就是获取此配置文件的根节点configuration public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
在这个用例中configuration根节点是什么样的呢?看下图:
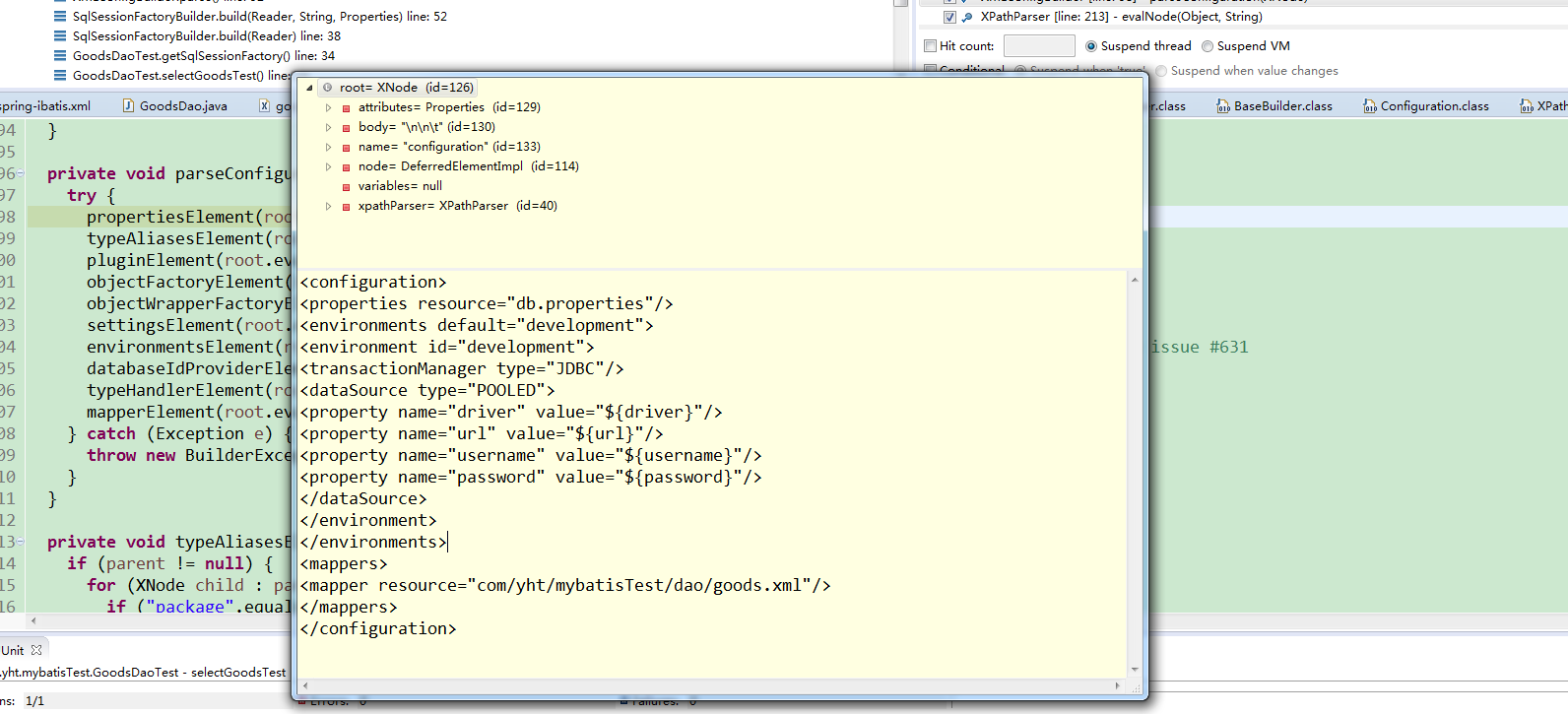
然后进入parseConfiguration方法:这个方法就是对configuration根节点下所有的子节点进行解析,并把数据存放起来方便后面使用,子节点共有十种类型。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //issue #117 read properties first typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings")); environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
现在相当于进入了大门,里面有十个小门等着我们进去一个个去探究,接下来的文章将对这十种子节点的解析过程进行讲解。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号