LinkedList源码分析
LinkedList,链接列表,它的底层结构是链表。它的特点是增删效率高,查询效率低。下面我们仍然从属性,构造器和方法三个方面来分析源码。
1.LinkedList的属性
transient int size = 0; //元素的个数 /** * Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */ transient Node<E> first;//列表的头结点 /** * Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */ transient Node<E> last;//列表的尾节点
这里有一个Node类,它是LinkedList的节点元素,承载着存放在LinkedList中的值,看下Node类
private static class Node<E> {
//值 E item; Node<E> next; //指向后一个节点的引用 Node<E> prev; //指向前一个节点的引用 //构造器 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
附上LinkedList的结构图
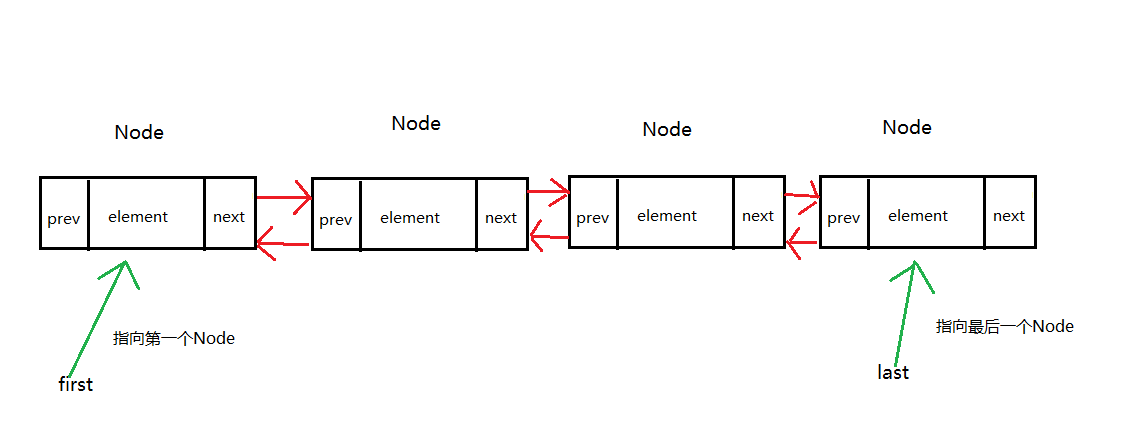
2.LinkedList的构造器
/** * Constructs an empty list. */ public LinkedList() { } /** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
3.LinkedList的方法
add(E e):添加指定元素e到列表的尾部
//添加指定元素到列表的尾部
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } /** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //创建一个新的Node作为尾节点,设置它的前引用为l last = newNode;//使last指向这个尾节点 if (l == null) first = newNode; //如果只有这一个节点,first也指向这一个节点 else l.next = newNode;//否则,设置l的后引用为newNode size++; //元素个数+1 modCount++; //修改次数+1 }
//注意:凡是节点做了改动的,都需要重新设置它的前引用或后引用,对于新建的节点可能两个都要设置;如果是头结点或者尾节点做了改动的,同时要设置first和last的引用
remove(Object o):移除此链表中首次出现的指定元素
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
//确定指定元素所在的Node节点 if (o.equals(x.item)) {
//移除该节点 unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
//这里主要做的是把指定节点x移除,此时会涉及到三个步骤
// 1.x.prev = null && x.next = null,x.item = null 这表明x节点已经和这个链表没关系了。
// 2.prev.next = next && next.prev = prev,这是为了将prev节点和next节点连接起来
// 3.要 考虑到prev和next节点为null的情况,这时first和last指向的Node节点也会改变,
总之,当add,remove操作时,对涉及到有改动的Node节点都要做处理,如果first和last指向的节点有变化也要处理
remove(int index):移除此列表中指定位置的元素
public E remove(int index) {
//检验下标index是否越界 checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); }
Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //采用二分法查找指定位置index的元素 if (index < (size >> 1)) {
//从头开始查找 Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else {
//从尾开始查找 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
当根据指定index找到对应的节点后,再调用E unlink(Node<E> x)方法移除该节点
E get(int index):获取指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index);
//根据指定位置index获取对于的Node节点,然后就可以获取节点中的元素值了 return node(index).item; }
其他的一些方法也是类似,都是基于链表结构的操作。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号