Redis 源码简洁剖析 03 - Dict Hash 基础
Redis Hash 源码#
- dict.h:定义 Hash 表的结构、哈希项,和 Hash 表的各种函数操作
- dict.c:函数的具体实现
Redis Hash 数据结构#
在 dict.h 文件中,Hash 表是一个二维数组(dictEntry **table)。
typedef struct dictht {
// 二维数组
dictEntry **table;
// Hash 表大小
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
dictEntry **table 是个二维数组,其中第一维是 bucket,每一行就是 bucket 指向的元素列表(因为键哈希冲突,Redis 采用了链式哈希)。
为了实现链式哈希,Redis 的 dictEntry 结构中,除了包含键和值的指针,还包含了一个指向下一个哈希项的指针 next。
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
整体的哈希流程都是老生常谈了,和 Java 几乎是一样的,这里就不叙述了。
Redis rehash 原理#
为什么要 rehash?#
为了性能。如果哈希表 bucket 的数量是 1,但是里面有了 1000 个元素,不管怎么样都变成了一个链表,查询效率变得很低。同理,当哈希表里元素的个数比 bucket 数量多很多的时候,效率也会低很多。
Redis dict 数据结构#
Redis 实际使用的是 dict 数据结构,内部用两个 dictht(ht[0] 和 ht[1]),用于 rehash 使用。
typedef struct dict {
……
// 两个 Hash 表,交替使用,用于 rehash 操作
dictht ht[2];
// Hash 表是否进行 rehash 的标识,-1 表示没有进行 rehash
long rehashidx;
……
} dict;
Redis rehash 过程#
- 正常请求阶段,所有的键值对都写入哈希表 ht[0]
- 进行 rehash 时,键值对被迁移到 ht[1]
- 迁移完成后,是否 ht[0] 空间,把 ht[1] 的地址赋值给 ht[0],ht[1] 的表大小设置为 0
什么时候触发 rehash?#
- ht[0] 大小=0
- ht[0] 里的元素个数已经超过 ht[0] 大小 && Hash 表可以扩容
- ht[0] 里的元素个数,是 ht[0] 大小的 5 倍(dict_force_resize_ratio)(类似于 Java 里 HashMap 的负载因子)
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
/* Incremental rehashing already in progress. Return. */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
// Hash 表为空,将 Hash 表扩展为初始大小 DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE(4)
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
// Hash 表当前的元素数量超过表的大小 && (可以扩容 || 当前数量是表大小的 5 倍以上)
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio) &&
dictTypeExpandAllowed(d))
{
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used + 1);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
上面代码中有个参数 dict_can_resize,设置函数为:
void dictEnableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 1;
}
void dictDisableResize(void) {
dict_can_resize = 0;
}
这两个函数被封装在了 server.c 中的 updateDictResizePolicy:
void updateDictResizePolicy(void) {
if (!hasActiveChildProcess())
dictEnableResize();
else
dictDisableResize();
}
/* Return true if there are active children processes doing RDB saving,
* AOF rewriting, or some side process spawned by a loaded module. */
int hasActiveChildProcess() {
return server.child_pid != -1;
}
我们可以看到,hasActiveChildProcess 函数是判断 Redis 存在 RDB 子进程、AOF 子进程是否存在。可以看到 dict_can_resize 只有在不存在 RDB 子进程、AOF 子进程时才为 TRUE。
那 _dictExpandIfNeeded 是在哪里调用的呢?
rehash 扩容多大?#
_dictExpandIfNeeded 里调用了扩容函数 dictExpand。
/* return DICT_ERR if expand was not performed */
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size) {
return _dictExpand(d, size, NULL);
}
int _dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size, int* malloc_failed)
{
……
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
……
}
里面有一个 _dictNextPower 函数,啥都不说了,都在注释里。
static unsigned long _dictNextPower(unsigned long size) {
unsigned long i = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
// 要扩容的大小已经超过了最大值
if (size >= LONG_MAX) return LONG_MAX + 1LU;
// 要扩容的大小没有超过最大值,找到第一个比 size 大的 2^i
while (1) {
if (i >= size)
return i;
i *= 2;
}
}
渐进式 rehash#
为什么需要渐进式 rehash?#
Hash 表空间很大,全量 rehash 时间会很长,阻塞 Redis 主线程。为了降低 rehash 开销,Redis 使用了「渐进式 rehash」。
具体一点#
渐进式 rehash 并不是一次性把当前 Hash 表的所有键,都拷贝到新的位置,而是「分批拷贝」,每次只拷贝 Hash 表中一个 bucket 中的哈希项。
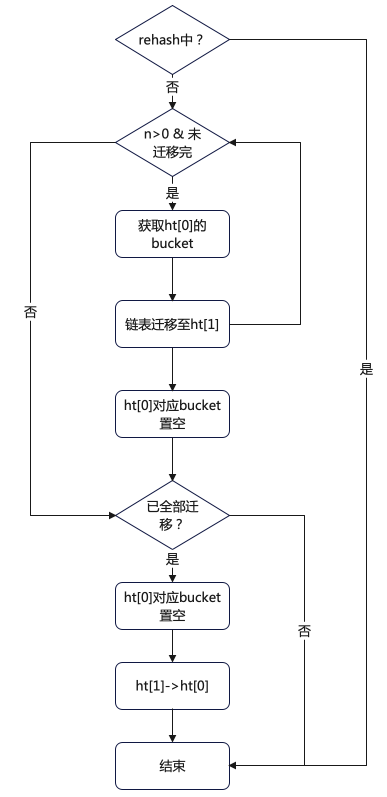
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
// 循环 n 次后停止,或 ht[0] 迁移完成
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long) d->rehashidx);
// 如果要迁移的 bucket 中没有元素
while (d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
// 获取待迁移的 ht[0] 的 bucket
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while (de) {
uint64_t h;
// 获取下一个迁移项
nextde = de->next;
// 计算 de 在 ht[1](扩容后)中的位置
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
// 将当前的哈希项放到扩容后的 ht[1] 中
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
//指向下一个哈希项
de = nextde;
}
// 当前 bucket 已经没有哈希项了,将该 bucket 设置为 null
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
// 将 rehash+1,下次迁移下一个 bucket
d->rehashidx++;
}
// 判断 ht[0] 是否已经全部迁移
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
// ht[0] 已经全部迁移到 ht[1] 了,释放 ht[0]
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
// ht[0] 指向 ht[1]
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
// 重置 ht[1] 大小为 0
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
//设置全局哈希表的 rehashidx=-1,表示 rehash 结束
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
// ht[0] 中仍然有元素没有迁移完
return 1;
}
几点说明:
- rehashidx 表示当前 rehash 在对哪个 bucket 做数据迁移,每次迁移完对应 bucket 时,会将 rehashidx+1。
- empty_visits 表示连续 bucket 为空的情况,此时渐进式 rehash 不会一直递增检查 rehashidx,因为一直检测会阻塞主线程,Redis 主线程就无法处理其他请求了。
那么 rehash 是在什么哪些步骤进行操作的呢?查看源码发现 dictRehash 是在 _dictRehashStep 函数中调用的,且传入的 n=1。
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
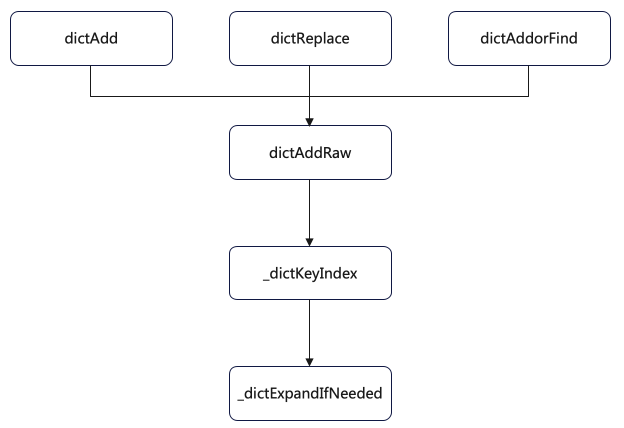
而 _dictRehashStep 分别被 5 个方法调用了:
- dictAddRaw
- dictGenericDelete
- dictFind
- dictGetRandomKey
- dictGetSomeKeys
下面是 dictAddRaw 部分代码:
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
……
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
……
}
下面是 dictAdd 部分代码:
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
Redis 源码简洁剖析系列#
Java 编程思想-最全思维导图-GitHub 下载链接,需要的小伙伴可以自取~
原创不易,希望大家转载时请先联系我,并标注原文链接。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义