剑指 Offer II 029. 排序的循环链表
给定循环单调非递减列表中的一个点,写一个函数向这个列表中插入一个新元素 insertVal ,使这个列表仍然是循环升序的。
给定的可以是这个列表中任意一个顶点的指针,并不一定是这个列表中最小元素的指针。
如果有多个满足条件的插入位置,可以选择任意一个位置插入新的值,插入后整个列表仍然保持有序。
如果列表为空(给定的节点是 null),需要创建一个循环有序列表并返回这个节点。否则。请返回原先给定的节点。
示例 1:
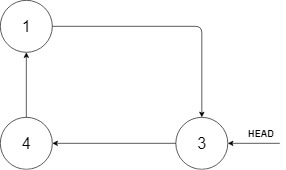
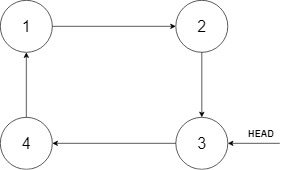
输入:head = [3,4,1], insertVal = 2 输出:[3,4,1,2] 解释:在上图中,有一个包含三个元素的循环有序列表,你获得值为 3 的节点的指针,我们需要向表中插入元素 2 。新插入的节点应该在 1 和 3 之间,插入之后,整个列表如上图所示,最后返回节点 3 。
示例 2:
输入:head = [], insertVal = 1
输出:[1]
解释:列表为空(给定的节点是 null),创建一个循环有序列表并返回这个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], insertVal = 0 输出:[1,0]
我的代码,思路很清晰,但是比较繁琐
class Solution { public: Node* insert(Node* head, int insertVal) { Node *ins = new Node(insertVal); if (head == NULL) { head = ins; ins->next = ins; return head; } int ma , mi; ma = mi = head->val; Node *h = head->next; while (h&&h != head) { ma = max(ma, h->val); mi = min(mi, h->val); h = h->next; } //全是一样的数 if (ma==mi) { ins->next = head->next; head->next = ins; return head; } if (insertVal<ma&&insertVal>mi) { while (!(h->val<=insertVal&&h->next->val>=insertVal)) h = h->next; ins->next = h->next; h->next = ins; return head; } if (insertVal>=ma) { while (!(h->val==ma&&h->next->val<ma)) h = h->next; ins->next = h->next; h->next = ins; return head; } if (insertVal <= mi) { while (!(h->val>mi && h->next->val == mi)) h = h->next; ins->next = h->next; h->next = ins; return head; } return head; } };
别人的代码:
class Solution { public: Node* insert(Node* head, int insertVal) { if(head==nullptr) { head = new Node(insertVal); head->next = head; return head; } auto cur = head; while(cur->next!=head){ if((cur->val<=insertVal)^(cur->next->val>=insertVal)^(cur->next->val>=cur->val)) break; cur = cur->next; } cur->next = new Node(insertVal, cur->next); return head; } }
有点没明白这个逻辑,,作者又写了一版清晰的
class Solution { public: Node* insert(Node* head, int insertVal) { if(head==nullptr) { head = new Node(insertVal); head->next = head; return head; } auto cur = head; while(cur->next!=head){ if(cur->next->val<cur->val){ if(cur->next->val>=insertVal) break; else if(cur->val<=insertVal) break; } if(cur->val<=insertVal&&cur->next->val>=insertVal) break; cur = cur->next; } cur->next = new Node(insertVal, cur->next); return head; } }
分类:
剑指offer






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理