Linux 目录结构及详细操作
目录

Linux 目录结构及详细操作
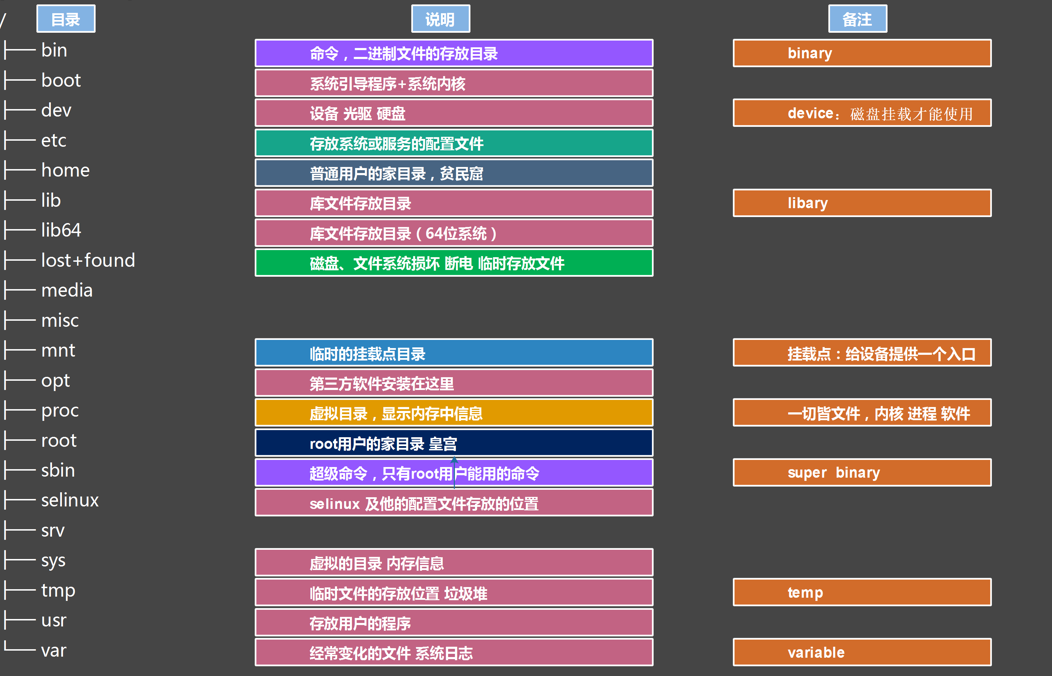
目录结构
常见的目录结构
- Windows下:
- D: \ProgramFiles
- Linux下:
- /etc/sysconfig
根目录结构示意图(倒挂树),图中的箭头代表软连接的关系,相当于Windows的快捷方式
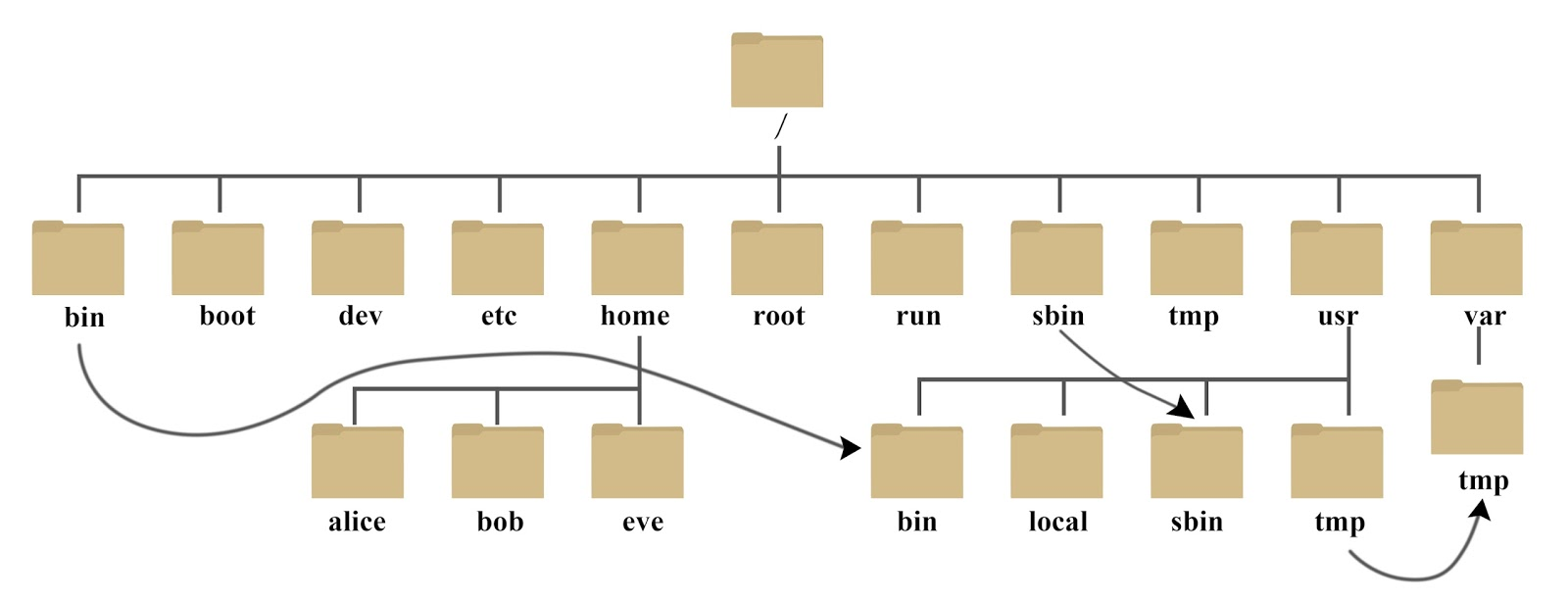
目录结构的特点
- Linux系统中的目录一切从根开始
- Linux系统中的目录结构拥有层次
- Linux系统中的目录需要挂载使用
目录结构挂载
系统目录可以挂载任何磁盘设备上
磁盘空间没有被挂载是不能使用的
# 挂载命令及格式
mount [磁盘路径] [挂载的路径]
# 查看本机挂载的命令
[root@localhost dev]# df -h
# 卸载挂载的磁盘
[root@localhost dev]# umount /mnt/
目录结构发展
- 第一块磁盘:用来存放系统程序 ---> /
- 第二块磁盘:存储数据(数据盘)---> /usr
- 第三块磁盘:用于分类管理用户 ---> /home
关闭selinux(了解)
临时关闭
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
永久关闭
[root@localhost ~]# vim/etc/selinux/config
修改文件内参数
SELINUX=disabled
重要目录说明(etc目录说明)
etc目录详细操作
1、网卡配置文件
1、文件信息如下:
# 网卡配置文件(有以下几种情况,通过ip a 查看自己的名称)
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
2、重载网卡信息:
# 查看本机网络信息的命令
ip a 或 ip address show (老版本的命令:ifconfig)
# 重载网卡信息
systemctl restart network
或
ifdown [网卡名称] && ifup [网卡名称]
# 确认网卡配置是否正确
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
# 关闭网络管理器(因为已经有了network)
systemctl stop NetworkManager
systemctl disable NetworkManager
或
systemctl disable --now NetworkManager
2、解析配置文件
作用:用于设置DNS解析地址
文件信息:/etc/resolv.conf # 临时dns配置文件
nameserver 114.114.114.114
# 判断SSH服务是否开启
systemctl status sshd
# 查看操作系统的DNS:
[root@localhost sys]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 114.114.114.114
# DNS可以修改,# vim /etc/resolv.conf
# 多种DNS
114.114.114.114 中国电信
223.5.5.5/223.6.6.6 中国阿里云
8.8.8.8 谷歌
3、主机名称文件
文件信息:/etc/hostname
配置主机名称信息,永久生效
# 主机名称文件
1、查看当前主机名称信息/临时修改
查看:hostname
临时修改:hostname baidu
2、永久修改
[root@baidu ~]# vim /etc/hostname # 需要重启生效
[root@baidu ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname oldboy # 立即生效
# 区别上
3、ps:自定义系统登录用户信息
PS1 环境变量
[root@localhost ~]# echo $PS1
[\u@\h \W]\$
[root@localhost ~]# PS1='[\u@\h --- \W]\$'
# 补充:通过域名查看ip地址,百度举例
[root@localhost ~]# ping www.baidu.com
PING www.a.shifen.com (112.80.248.75) 56(84) bytes of data.
# 远程的ip地址:112.80.248.75
4、解析映射文件
相当于windows 系统中,C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts;
解析映射文件相当于本地的DNS;
-
文件信息:/etc/hosts
-
作用说明:用于设置DNS域名与IP地址对应关系
# 本地解析,可以在windows中的hosts文件中添加解析
106.13.91.75 《==》 www.test.com
# 这样通过ip地址或者映射后的域名都可以访问到服务器
5、磁盘挂载文件
- 文件信息:/etc/fstab
- 作用说明:实现指定设备文件信息,进行开机自动挂载
[root@localhost /]# cat /etc/fstab
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Thu Dec 9 18:57:52 2021
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=046a66f5-d610-42fd-a0ec-c98793ff6320 /boot xfs defaults
# 通过df -h 查看挂载信息
[root@localhost /]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 475M 0 475M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 7.6M 479M 2% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 100G 2.2G 98G 3% /
/dev/sda1 509M 132M 378M 26% /boot
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
可以发现/boot和/的挂载信息是一样的
6、开机加载脚本
- 文件信息:/etc/rc.local
- 作用说明:实现系统启动后,读取文件中的命令,从而实现一些操作随系统启动自动运行
- 使用方法:chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local (centos7中需要执行此命令,才能使用此文件)
说明:类似Windows中开机启动的文件,可以通过任务管理器中的启动查看在Windows中开机启动的程序有哪些
# 验证Linux中开机自启动示例
# 在/etc/rc.local中加入执行语句
vim /etc/rc.local
echo 'hello' > test
# 设置开机自启动权限
chomd +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
# 重启系统
reboot
# 查看test文件是否写入了hello
cat test
7、系统启动级别
级别对应参数一览表:
| 启动级别 | 级别对应命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | shutdown.target | 关机(不要设置,不然会一直关机) |
| 1 | emergency.target | 单用户模式,root权限 |
| 2 | rescure.target | 多用户模式,没有NFS和网络支持 |
| 3 | multi-user.target | 完整的多用户文本模式,有NFS和网络,登录后进入控制台命令行模式 |
| 4 | 无 | 待定 |
| 5 | graphical.target | 图形化模式,登录后进入图形GUI模式 |
| 6 | 无 | 重启模式,默认运行级别不能设为6,否则不能正常启动。运行init6机器就会重启 |
-
命令格式:
- systemctl [command] [unit.target]
-
command参数如下表
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| get-default | 取得当前的target |
| set-default | 设置指定的target为默认的运行级别 |
| isolate | 切换到指定的运行级别 |
| unit.target | 上面列出的运行级别 |
-
设置系统级别:
init [编号] ---临时设置 systemctl set-default [系统启动级别] ---永久 -
查看系统级别文件保存路径
[root@localhost /]# cd /usr/lib/systemd/system [root@localhost system]# ls lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 15 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel0.target -> poweroff.target lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 13 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel1.target -> rescue.target drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 50 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel1.target.wants lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 17 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel2.target -> multi-user.target drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 50 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel2.target.wants lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 17 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel3.target -> multi-user.target drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 50 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel3.target.wants lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 17 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel4.target -> multi-user.target drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 50 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel4.target.wants lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 16 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel5.target -> graphical.target drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 50 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel5.target.wants lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 13 Dec 9 18:58 runlevel6.target -> reboot.target -
示例如下:
# 1、获得当前的运行级别 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default multi-user.target # 2、设置默认的运行级别为mulit-user [root@localhost ~]# systemctl set-default multi-user.target [root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default multi-user.target # 3、在不重启的情况下,切换到运行级别mulit-user下 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl isolate multi-user.target # 4、在不重启的情况下,切换到图形界面下 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl isolate graphical.target -
补充:解决忘记密码问题,通过单用户模式解决
# 通过单用户模式修改密码 重启,虚拟机 在启动选择系统内核界面,按 e 键进入单用户模式 找到 linux16 开头行,删除 ro , 并且在 ro 处添加 rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh 按 ctrl + x 进行系统重新引导 执行 chroot /sysroot 执行 passwd root 执行 touch /.autorelabel 执行 Ctrl + D 两次 reboot重启系统
8、变量加载文件(环境变量)
-
文件信息:/etc/profile
-
作用说明:配置环境变量和别名文件
-
增加环境变量有两种方式:
- 临时添加
- 永久添加
-
增加环境变量的格式:
- export ’[环境变量名] = [路径]
示例如下:
export PYTHON_HOME='D:/python' -
查看本机的环境变量:
- printenv命令 : 查看所有的环境变量
- echo $PYTHON_HOME : 查看某一个环境变量
示例如下:
# 修改或添加环境变量主要修改以下四个文件和目录内添加.shw
# 修改下面两个文件
/etc/profile
/etc/bashrc
# 修改下面两个文件
~/.bash_profile
~/.bashrc
# 目录
/etc/profile.d/ # 在该目录下创建文件后要添加执行权限
# 读取环境变量的几种情况,以及使用文件的先后顺序
1、重启
/etc/profile.d --> /etc/profile --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc --> ~/.bash_profile
2、切换用户
/etc/profile.d --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc
ps:
useradd [用户名]
su [用户名]
3、重新登录用户
1、su - [用户名]
/etc/profile.d --> /etc/profile --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc --> ~/.bash_profile
2、ssh root@192.168.15.101
/etc/profile.d --> /etc/profile --> /etc/bashrc --> ~/.bashrc --> ~/.bash_profile
9、登录提示文件
- 文件信息 1:/etc/motd (登录之后提示的信息)
- 作用说明:文件中内容,会在用户登录系统之后进行显示
- 文件信息 2:/etc/issue (登录之前提示的信息)
- 作用说明:文件中内容,会在用户登录系统之前进行显示
示例如下:
# 登录之后提示小火龙图画,issue文件也是一样的
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/motd
\ / \ //\
\ |\___/| / \// \\
/0 0 \__ / // | \ \
/ / \/_/ // | \ \
@_^_@'/ \/_ // | \ \
//_^_/ \/_ // | \ \
( //) | \/// | \ \
( / /) _|_ / ) // | \ _\
( // /) '/,_ _ _/ ( ; -. | _ _\.-~ .-~~~^-.
(( / / )) ,-{ _ `-.|.-~-. .~ `.
(( // / )) '/\ / ~-. _ .-~ .-~^-. \
(( /// )) `. { } / \ \
(( / )) .----~-.\ \-' .~ \ `. \^-.
///.----..> \ _ -~ `. ^-` ^-_
///-._ _ _ _ _ _ _}^ - - - - ~ ~-- ,.-~
/.-~
重要目录说明(/usr目录说明)
- 文件信息:/usr/local
- 作用说明:编译安装软件的默认目录
示例如下:
# yum安装python:
yum install python3
重要目录说明(/var目录说明)
-
重要文件-重要日志文件1:
- 文件信息:/var/log/messages
- 作用说明:软件安装运行以及系统运行异常日志文件
-
重要文件-重要日志文件2:
-
文件信息:/var/log/secure (说明:此文件具有日志切割功能)
-
作用说明:系统用户登录情况日志信息
-
文件使用:grep 'Failed' /var/log/secure
-
查看日志:
# 先查看5行吧,太多了占地
[root@localhost log]# head -5 /var/log/messages
Dec 12 16:13:02 localhost rsyslogd: [origin software="rsyslogd" swVersion="8.24.0-55.el7" x-pid="1470" x-info="http://www.rsyslog.com"] rsyslogd was HUPed
Dec 12 16:47:59 localhost systemd: Started Delayed Shutdown Service.
Dec 12 16:47:59 localhost systemd-shutdownd: Shutting down at Sun 2021-12-12 16:57:59 CST (poweroff)...
Dec 12 16:48:08 localhost systemd-shutdownd: Shutdown canceled.
Dec 12 17:01:01 localhost systemd: Started Session 3 of user root.
重要目录说明(/proc目录说明)
- 重要文件-重要信息文件1:
- 文件信息:/proc/cpuinfo
- 作用说明:用于查看系统CPU信息情况文件
- 相关命令:lscpu
[root@localhost proc]# lscpu
或
[root@localhost proc]# cat cpuinfo
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 1
On-line CPU(s) list: 0
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 1
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 158
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-8300H CPU @ 2.30GHz
Stepping: 10
CPU MHz: 2303.999
BogoMIPS: 4607.99
Hypervisor vendor: VMware
Virtualization type: full
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 8192K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0
- 重要文件-重要信息文件
- 文件信息:/proc/meminfo
- 作用说明:用于查看系统内存信息情况文件
- 相关命令:free -h
示例如下:
[root@localhost proc]# head -5 /proc/meminfo
MemTotal: 995676 kB
MemFree: 689728 kB
MemAvailable: 672864 kB
Buffers: 2104 kB
Cached: 94548 kB
# 用free看内存信息会更直观
[root@localhost proc]# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 972M 185M 673M 7.5M 113M 656M
Swap: 0B 0B 0B
- 重要文件-重要信息文件
- 文件信息:/proc/loadavg
- 作用说明:用于查看系统负载信息情况文件,用于衡量系统繁忙程度
- 相关命令:w
示例如下:
[root@localhost proc]# cat loadavg
0.13 0.04 0.05 1/113 1839
0.13 :1分钟内CPU负载
0.04 :5分钟内CPU负载
0.05 :15分钟内CPU负载
负载:当前系统的所有进程占用CPU的时间比
[root@localhost proc]# w
19:19:11 up 1:55, 1 user, load average: 0.08, 0.04, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 192.168.15.1 17:24 7.00s 0.10s 0.01s w
# w命令的数据来源是/proc/loadavg
-
重要文件-重要信息文件
-
文件信息:/proc/mounts
-
作用说明:用于查看系统挂载信息情况文件
-
相关命令:mount : 挂载
umount : 卸载挂载
df - h : 查看挂载
-
示例如下:
[root@localhost proc]#
[root@localhost proc]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 475M 0 475M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 7.6M 479M 2% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 100G 2.2G 98G 3% /
/dev/sda1 509M 132M 378M 26% /boot
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
补充知识:
- dev是操作硬件的入口
- 解析文件顺序,先本地(hosts)后配置


 Linux 目录结构及详细操作,详细操作都在这里面了,看完不会这个锅我背了,小白必看~~~
Linux 目录结构及详细操作,详细操作都在这里面了,看完不会这个锅我背了,小白必看~~~

