Java线程间通信的几种方式
文章目录
一、使用同一个共享变量控制
二、PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream
三、利用BlockingQueue
四、利用LockSupport
一、使用同一个共享变量控制
Synchronized、wait、notify
public class Demo1 {
private final List<Integer> list =new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 demo =new Demo1();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
synchronized (demo.list){
if(demo.list.size()%2==1){
try {
demo.list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
demo.list.add(i);
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(demo.list);
demo.list.notify();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
synchronized (demo.list){
if(demo.list.size()%2==0){
try {
demo.list.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
demo.list.add(i);
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(demo.list);
demo.list.notify();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
Lock、Condition
public class Task {
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition addConditon = lock.newCondition();
private final Condition subConditon = lock.newCondition();
private volatile int num = 0;
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
public void add() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (list.size() == 10) {
addConditon.await();
}
num++;
Thread.sleep(100);
list.add("add " + num);
System.out.println("The list size is " + list.size());
System.out.println("The add thread is " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("-------------");
subConditon.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public void sub() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (list.size() == 0) {
subConditon.await();
}
num--;
Thread.sleep(100);
list.remove(0);
System.out.println("The list size is " + list.size());
System.out.println("The sub thread is " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("-------------");
addConditon.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task = new Task();
new Thread(task::add).start();
new Thread(task::sub).start();
}
}
利用volatile
volatile修饰的变量值直接存在主内存里面,子线程对该变量的读写直接写住内存,而不是像其它变量一样在local thread里面产生一份copy。volatile能保证所修饰的变量对于多个线程可见性,即只要被修改,其它线程读到的一定是最新的值。
public class Demo2 {
private volatile List<Integer> list =new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo2 demo =new Demo2();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
demo.list.add(i);
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(demo.list);
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
demo.list.add(i);
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(demo.list);
}
}).start();
}
}
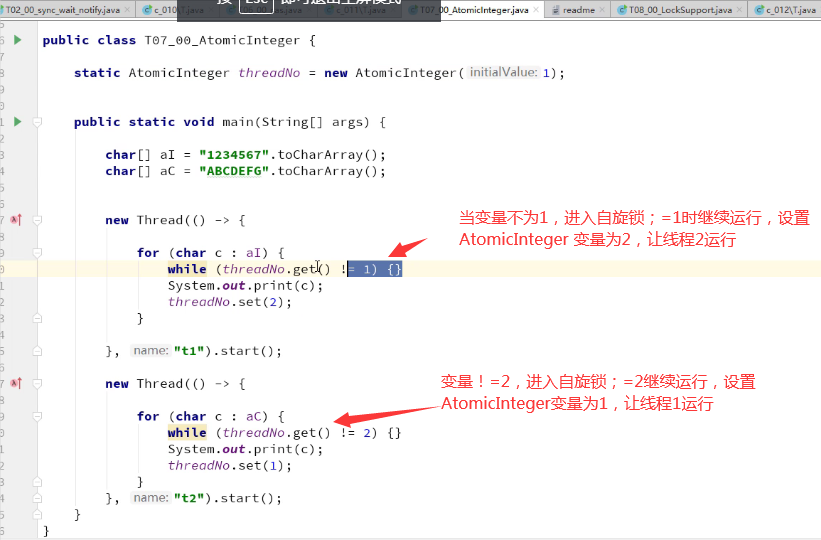
利用AtomicInteger
和volatile类似, 只是原子操作达到预估值非A即B
二、PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream
这里用流在两个线程间通信,但是Java中的Stream是单向的,所以在两个线程中分别建了一个input和output
public class PipedDemo {
private final PipedInputStream inputStream1;
private final PipedOutputStream outputStream1;
private final PipedInputStream inputStream2;
private final PipedOutputStream outputStream2;
public PipedDemo(){
inputStream1 = new PipedInputStream();
outputStream1 = new PipedOutputStream();
inputStream2 = new PipedInputStream();
outputStream2 = new PipedOutputStream();
try {
inputStream1.connect(outputStream2);
inputStream2.connect(outputStream1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**程序退出时,需要关闭stream*/
public void shutdown() throws IOException {
inputStream1.close();
inputStream2.close();
outputStream1.close();
outputStream2.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PipedDemo demo =new PipedDemo();
new Thread(()->{
PipedInputStream in = demo.inputStream2;
PipedOutputStream out = demo.outputStream2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
byte[] inArr = new byte[2];
in.read(inArr);
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": "+i+" ");
System.out.println(new String(inArr));
while(true){
if("go".equals(new String(inArr)))
break;
}
out.write("ok".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
PipedInputStream in = demo.inputStream1;
PipedOutputStream out = demo.outputStream1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
out.write("go".getBytes());
byte[] inArr = new byte[2];
in.read(inArr);
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName()+": "+i+" ");
System.out.println(new String(inArr));
while(true){
if("ok".equals(new String(inArr)))
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
// demo.shutdown();
}
}
输出:
Thread-0: 0 go Thread-1: 0 ok Thread-0: 1 go Thread-1: 1 ok Thread-0: 2 go Thread-1: 2 ok Thread-0: 3 go Thread-1: 3 ok Thread-0: 4 go Thread-1: 4 ok Thread-0: 5 go Thread-1: 5 ok Thread-0: 6 go Thread-1: 6 ok Thread-0: 7 go Thread-1: 7 ok Thread-0: 8 go Thread-1: 8 ok Thread-0: 9 go Thread-1: 9 ok
三、利用BlockingQueue
BlockingQueue定义的常用方法如下:
- add(Object):把Object加到BlockingQueue里,如果BlockingQueue可以容纳,则返回true,否则抛出异常。
- offer(Object):表示如果可能的话,将Object加到BlockingQueue里,即如果BlockingQueue可以容纳,则返回true,否则返回false。
- put(Object):把Object加到BlockingQueue里,如果BlockingQueue没有空间,则调用此方法的线程被阻断直到BlockingQueue里有空间再继续。
- poll(time):获取并删除BlockingQueue里排在首位的对象,若不能立即取出,则可以等time参数规定的时间,取不到时返回null。当不传入time值时,立刻返回。
- peek():立刻获取BlockingQueue里排在首位的对象,但不从队列里删除,如果队列为空,则返回null。
- take():获取并删除BlockingQueue里排在首位的对象,若BlockingQueue为空,阻断进入等待状态直到BlockingQueue有新的对象被加入为止。
BlockingQueue有四个具体的实现类:
- ArrayBlockingQueue:数组阻塞队列,规定大小,其构造函数必须带一个int参数来指明其大小。其所含的对象是以FIFO(先入先出)顺序排序的。
- LinkedBlockingQueue:链阻塞队列,大小不定,若其构造函数带一个规定大小的参数,生成的BlockingQueue有大小限制,若不带大小参数,所生成的BlockingQueue的大小由Integer.MAX_VALUE来决定。其所含的对象是以FIFO顺序排序的。
- PriorityBlockingQueue:类似于LinkedBlockingQueue,但其所含对象的排序不是FIFO,而是依据对象的自然排序顺序或者是构造函数所带的Comparator决定的顺序。
- SynchronousQueue:特殊的BlockingQueue,它的内部同时只能够容纳单个元素,对其的操作必须是放和取交替完成的。
- DelayQueue:延迟队列,注入其中的元素必须实现 java.util.concurrent.Delayed 接口
所有BlockingQueue的使用方式类似,以下例子一个线程写入,一个线程读取,操作的是同一个Queue:
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
//读线程
new Thread(() -> {
int i =0;
while (true) {
try {
String item = queue.take();
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i + " ");
System.out.println(item);
i++;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
//写线程
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
String item = "go"+i;
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i + " ");
System.out.println(item);
queue.put(item);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
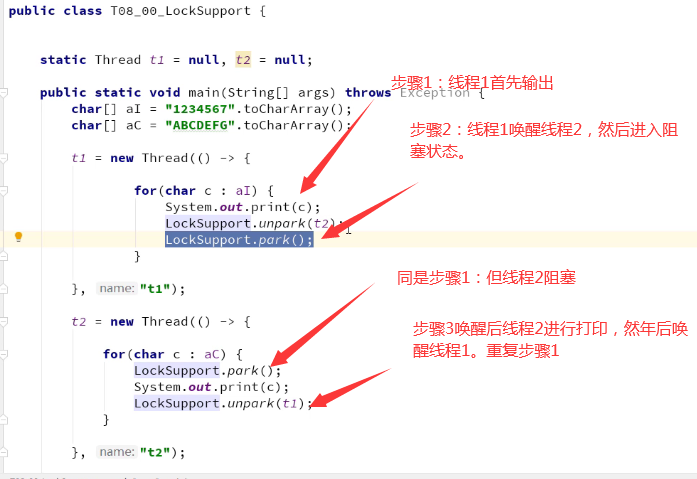
四、利用LockSupport
用LockSupport的unpark()和park()方法,实现线程间通信。
五、利用ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal,即线程变量,是一个以 ThreadLocal 对象为键、任意对象为值的存储结构。这个结构被依附在线程上,也就是说一个线程可以根据一个 ThreadLocal 对象查询到绑定在这个线程上的一个值。
可以通过 set(T) 方法来设置一个值,在当前线程下再通过 get() 方法获取到原先设置的值。
public class ThreadLocalDemo {
private static final ThreadLocal<Long> TIME_THREADLOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>() {
@Override
protected Long initialValue() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
};
public static final void begin() {
TIME_THREADLOCAL.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public static final long end() {
return System.currentTimeMillis() - TIME_THREADLOCAL.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadLocalDemo.begin();
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(ThreadLocalDemo.end());
}
}
//输出 2003



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号