第二次Blog作业
一、前言
这次的三次题目集相比上次难度大了很多,题量适中,前两次都有六七道题目,第三次只有一道boss题目,主要考察了数组,正则表达式,还有三大特性,封装,继承和多态,还有日期的迭代和菜单的迭代。题目很难,时间没有把握好,很多都没做完。
二、设计与分析
第四次题目集题目是菜单的第三代,前两代都没有做过所以暂时跳过先做后面的题目题目基本要求:设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
第四次题目集7-4单词统计与排序,题目要求:从键盘录入一段英文文本(句子之间的标点符号只包括“,”或“.”,单词之间、单词与标点之间都以" "分割。
要求:按照每个单词的长度由高到低输出各个单词(重复单词只输出一次),如果单词长度相同,则按照单词的首字母顺序(不区分大小写,首字母相同的比较第二个字母,以此类推)升序输出。
源码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String a = input.nextLine(); String[] arr1 = a.split("\\,|\\ |\\."); ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i <arr1.length; i++){ if(arr1[i] == null){ for (int j : arr1){ arr.add(j); } arr.remove(i+1); } } Arrays.sort(arr); Arrays.sort(arr, (x, y) -> y.length() - x.length()); for(int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++){ if(arr[i].length()==arr[i+1].length()){ if(arr[i].compareToIgnoreCase(arr[i+1])>0){ String t = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[i+1]; arr[i+1] = t; } } } for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){ System.out.println(arr[i]); } } }
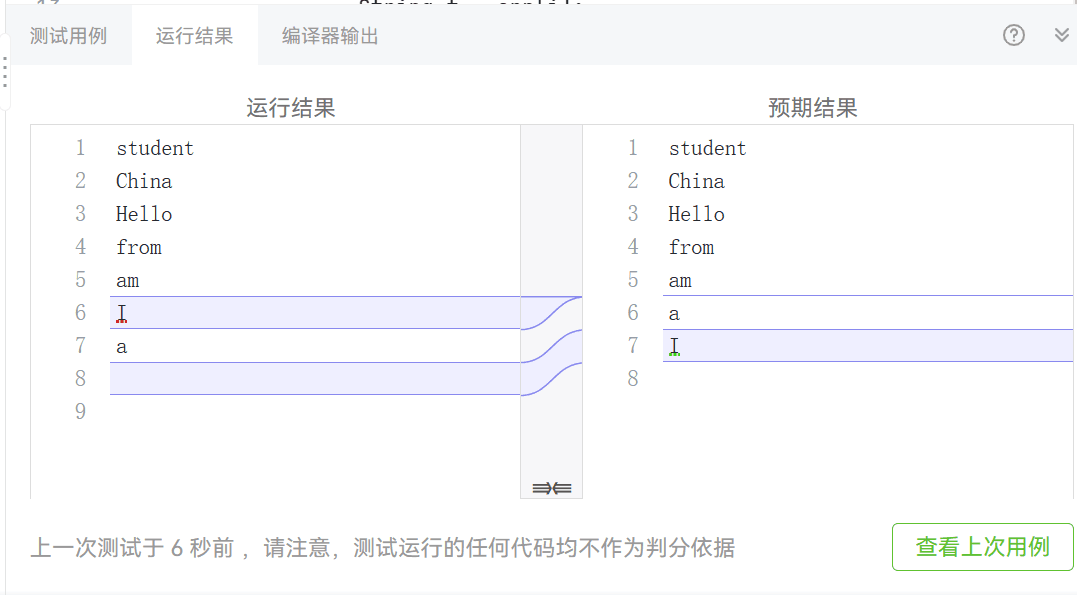
解释与心得:这题的流程很清晰,先用split截取各个单词存入数组,然后Arrays.sort进行单词长度排序,当单词长度一样时再用compareToIgnoreCase按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不过还有空字符的存在,我没有去除导致没有得到分,事后和同学讨论可以用到哈希 Set<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<>();进行空字符的删除。这题中还学到了compareToIgnoreCase和compareTo的区别,前者不区分大小写,后者则区分大小写,一开始没有注意,导致China和Hello还有I和am顺序出错。
第四题目集7-5面向对象编程(封装性),题目要求:Student类具体要求如下:
私有成员变量:学号(sid,String类型),姓名(name,String类型),年龄(age,int类型),专业(major,String类型) 。
提供无参构造和有参构造方法。(注意:有参构造方法中需要对年龄大小进行判定)
普通成员方法:print(),输出格式为“学号:6020203100,姓名:王宝强,年龄:21,专业:计算机科学与技术”。
普通成员方法:提供setXxx和getXxx方法。(注意:setAge()方法中需要对年龄进行判定)
注意:
年龄age不大于0,则不进行赋值。
print()中的“:”和“,”为均为中文冒号和逗号。
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //调用无参构造方法,并通过setter方法进行设值 String sid1 = sc.next(); String name1 = sc.next(); int age1 = sc.nextInt(); String major1 = sc.next(); Student student1 = new Student(); student1.setSid(sid1); student1.setName(name1); student1.setAge(age1); student1.setMajor(major1); //调用有参构造方法 String sid2 = sc.next(); String name2 = sc.next(); int age2 = sc.nextInt(); String major2 = sc.next(); Student student2 = new Student(sid2, name2, age2, major2); //对学生student1和学生student2进行输出 student1.print(); student2.print(); } } class Student{ private String sid; private String name; private int age; private String major; public Student(){ } public String getSid(){ return sid; } public void setSid(String sid){ this.sid=sid; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name=name; } public int getAge(){ return age; } public void setAge(int age){ if(age>0){ this.age=age; } } public String getMajor(){ return major; } public void setMajor(String major){ this.major=major; } public Student(String sid,String name,int age,String major){ this.sid=sid; this.name=name; this.age=age; this.major=major; } public void print(){ System.out.println("学号:" + sid + ",姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",专业:" + major); } }
类图如下:
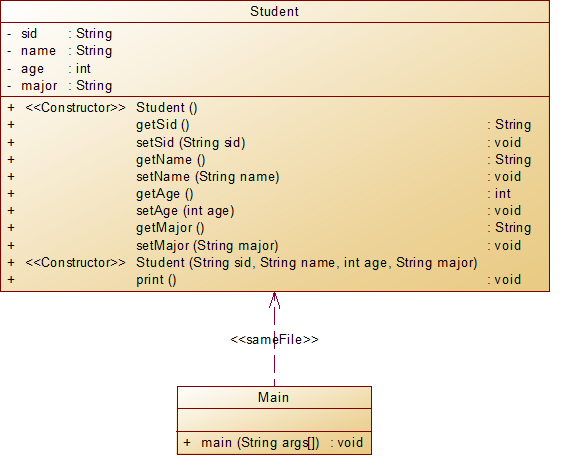
解释与心得:这题比较简单,通过类图可以看出,主要考察对java封装特性的理解和运用。封装从字面上来理解就是包装的意思,专业点就是信息隐藏,是指利用抽象数据类型将数据和基于数据的操作封装在一起,使其构成一个不可分割的独立实体,数据被保护在抽象数据类型的内部,尽可能地隐藏内部的细节,只保留一些对外接口使之与外部发生联系。系统的其他对象只能通过包裹在数据外面的已经授权的操作来与这个封装的对象进行交流和交互。也就是说用户是无需知道对象内部的细节,但可以通过该对象对外的提供的接口来访问该对象。使用封装的好处:1、良好的封装能够减少耦合。2、类内部的结构可以自由修改。3、可以对成员进行更精确的控制。4、隐藏信息,实现细节。封装可以使我们容易地修改类的内部实现,而无需修改使用了该类的客户代码。就可以对成员变量进行更精确的控制。
第五次题目集7-5日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
类图如下
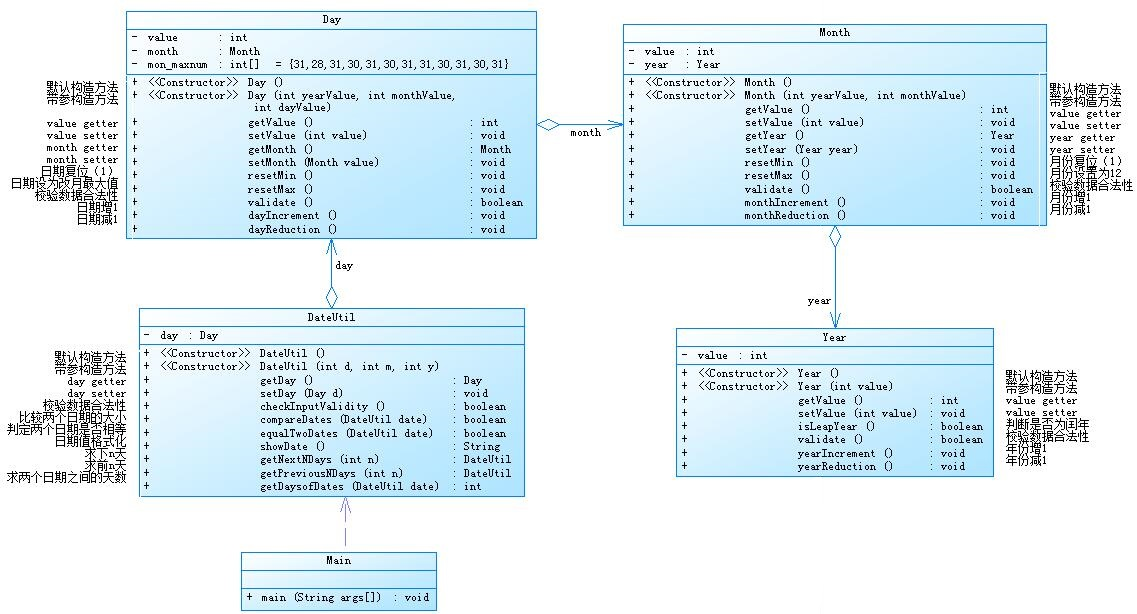
源码如下:
import java.util.*; class Year{ int value; public Year(){ } public Year(int value){ this.value = value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public boolean isLeapYear(){ boolean isleapYear; isleapYear = (value % 4 == 0&&value % 100 != 0)||value % 400 == 0; return isleapYear; } public boolean validate(){ boolean validate; if (value >= 1900&&value <= 2050){ validate = true; } else { validate = false; } return validate; } public void yearIncrement(){ value = value + 1; } public void yearReduction(){ value = value - 1; } } class Month{ int value; Year year; public Month(){ } public Month(int yearValue, int monthValue){ this.year = new Year(yearValue); this.value = monthValue; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public Year getYear(){ return year; } public void setYear(Year year){ this.year = year; } public void resetMin(){ value = 1; } public void resetMax(){ value = 12; } public boolean validate(){ boolean validate; if (value >= 1&&value <= 12){ validate = true; } else { validate = false; } return validate; } public void monthIncrement(){ value = value + 1; } public void monthReduction(){ value = value - 1; } } class Day{ int value; Month month; int mon_maxnum[]= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public Day(){ } public Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue){ this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value = dayValue; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public Month getMonth(){ return month; } public void setMonth(Month value){ this.month = value; } public void resetMin(){ value = 1; } public void resetMax(){ if (month.getYear().isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]; } public boolean validate(){ boolean validate; if (month.getYear().isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if (value >= 1&&value <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]){ validate = true; } else { validate = false; } return validate; } public void dayIncrement(){ value = value + 1; } public void dayReduction(){ value = value - 1; } } class DateUtil{ Day day; int mon_maxnum[]= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public DateUtil(){ } public DateUtil(int y, int m, int d){ this.day = new Day(y, m, d); } public Day getDay(){ return day; } public void setDay(Day d){ this.day = d; } public boolean checkInputValidity(){ boolean checkInputValidity; if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()==true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&day.validate()){ checkInputValidity = true; } else { checkInputValidity = false; } return checkInputValidity; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){ if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()){ return true; } else if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&& this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){ return true; } else if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&& this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&& this.getDay().getValue() > date.getDay().getValue()){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&& this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&& this.getDay().getValue() == date.getDay().getValue()){ return true; } else { return false; } } public String showDate(){ return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getValue(); } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if (this.getDay().getValue() == mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]){ if (this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 12){ this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); this.getDay().getMonth().resetMin(); this.getDay().resetMin(); } else{ this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement(); this.getDay().resetMin(); } } else{ this.getDay().dayIncrement(); } } return this; } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if (this.getDay().getValue() == 1){ if (this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == 1){ this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); this.getDay().getMonth().resetMax(); this.getDay().resetMax(); } else { this.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction(); this.getDay().resetMax(); } } else { this.getDay().dayReduction(); } } return this; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ if (equalTwoDates(date)) return 0; int Sum = 0; int fromYear,fromMonth,fromDay; int toYear,toMonth,toDay; if (compareDates(date)){ fromYear = date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); fromMonth = date.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); fromDay = date.getDay().getValue(); toYear = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); toMonth = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); toDay = this.getDay().getValue(); } else{ toYear = date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); toMonth = date.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); toDay = date.getDay().getValue(); fromYear = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); fromMonth = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); fromDay = this.getDay().getValue(); } while (fromYear < toYear || fromMonth < toMonth || fromDay < toDay){ Sum++; fromDay++; if((fromYear %4 == 0 && fromYear % 100 != 0) || fromYear % 400 == 0){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else { mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if(fromDay > mon_maxnum[fromMonth]){ fromMonth++; fromDay = 1; } if(fromMonth == 13){ fromMonth = 1; fromYear++; } } return Sum; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
解释与心得:通过类图很容易就能写出各个类的方法和属性,类间关系很清晰,Month中调用Year,Day中调用Month,DateUtil调用Day,this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(),调用年份,其他和之前的日期题目类似。
第五次题目集7-6日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
类图如下:
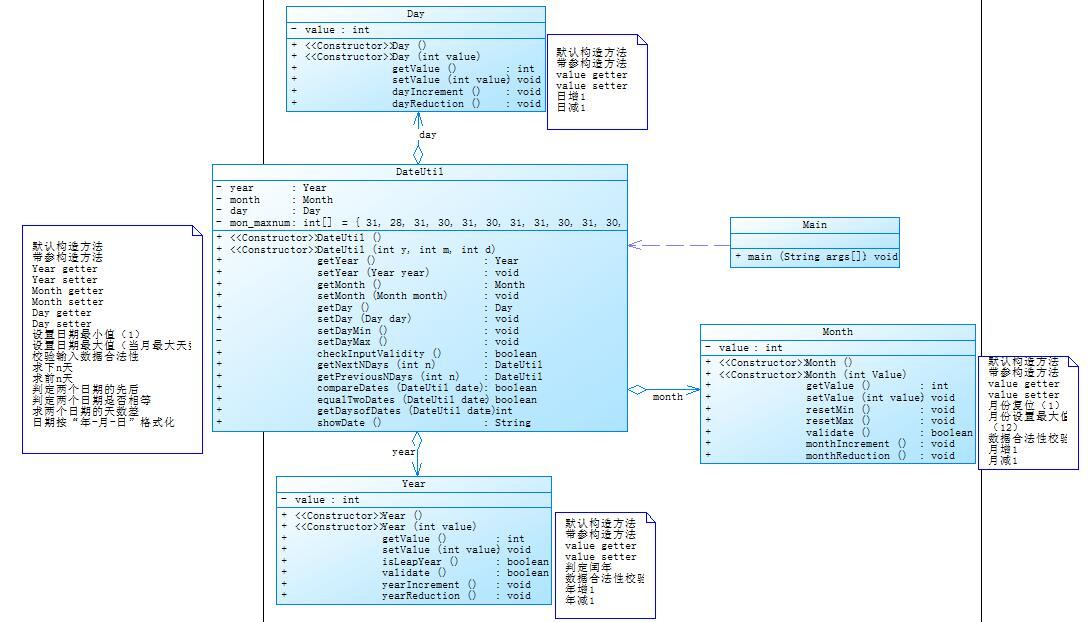
源码如下
import java.util.*; class Year{ int value; public Year(){ } public Year(int value){ this.value = value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public boolean isLeapYear(){ boolean isleapYear; isleapYear = (value % 4 == 0&&value % 100 != 0)||value % 400 == 0; return isleapYear; } public boolean validate(){ boolean validate; if (value >= 1820&&value <= 2020){ validate = true; } else { validate = false; } return validate; } public void yearIncrement(){ value = value + 1; } public void yearReduction(){ value = value - 1; } } class Month{ int value; public Month(){ } public Month(int value){ this.value = value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public void resetMin(){ value = 1; } public void resetMax(){ value = 12; } public boolean validate(){ boolean validate; if (value >= 1&&value <= 12){ validate = true; } else { validate = false; } return validate; } public void monthIncrement(){ value = value + 1; } public void monthReduction(){ value = value - 1; } } class Day{ int value; public Day(){ } public Day(int value){ this.value = value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public void dayIncrement(){ value = value + 1; } public void dayReduction(){ value = value - 1; } } class DateUtil{ Year year; Month month; Day day; int mon_maxnum[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; public DateUtil(){ } public DateUtil(int y, int m, int d){ this.year = new Year(y); this.month = new Month(m); this.day = new Day(d); } public Year getYear(){ return year; } public void setYear(Year year){ this.year = year; } public Month getMonth(){ return month; } public void setMonth(Month month){ this.month = month; } public Day day(){ return day; } public void setDay(Day day){ this.day = day; } public void setDayMin(){ this.day.value = 1; } public void setDayMax(){ if (this.year.isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } this.day.value = mon_maxnum[this.month.value]; } public boolean checkInputValidity(){ boolean checkInputValidity; if (this.year.isLeapYear()==true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } if (this.year.validate()&&this.month.validate()&& (this.day.value >=1 &&this.day.value <= mon_maxnum[this.month.value])){ checkInputValidity = true; } else { checkInputValidity = false; } return checkInputValidity; } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if (this.year.isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if (this.day.value == mon_maxnum[this.month.value]){ if (this.month.value == 12){ this.year.yearIncrement(); this.month.resetMin(); this.setDayMin(); } else{ this.month.monthIncrement(); this.setDayMin(); } } else{ this.day.dayIncrement(); } } return this; } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if (this.year.isLeapYear() == true){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if (this.day.value == 1){ if (this.month.value == 1){ this.year.yearReduction(); this.month.resetMax(); this.setDayMax(); } else { this.month.monthReduction(); this.setDayMax(); } } else { this.day.dayReduction(); } } return this; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){ if (this.year.value > date.year.value){ return true; } else if (this.year.value == date.year.value&& this.month.value > date.month.value){ return true; } else if (this.year.value == date.year.value&& this.month.value == date.month.value&& this.day.value > date.day.value){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ if (this.year.value == date.year.value&& this.month.value == date.month.value&& this.day.value == date.day.value){ return true; } else { return false; } } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ if (equalTwoDates(date)) return 0; int Sum = 0; int fromYear,fromMonth,fromDay; int toYear,toMonth,toDay; if (compareDates(date)){ fromYear = date.year.value; fromMonth = date.month.value; fromDay = date.day.value; toYear = this.year.value; toMonth = this.month.value; toDay = this.day.value; } else{ toYear = date.year.value; toMonth = date.month.value; toDay = date.day.value; fromYear = this.year.value; fromMonth = this.month.value; fromDay = this.day.value; } while (fromYear < toYear || fromMonth < toMonth || fromDay < toDay){ Sum++; fromDay++; if((fromYear %4 == 0 && fromYear % 100 != 0) || fromYear % 400 == 0){ mon_maxnum[2] = 29; } else { mon_maxnum[2] = 28; } if(fromDay > mon_maxnum[fromMonth]){ fromMonth++; fromDay = 1; } if(fromMonth == 13){ fromMonth = 1; fromYear++; } } return Sum; } public String showDate(){ return this.year.value + "-" + this.month.value + "-" + this.day.value; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " next " + m + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " previous " + n + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } }
解释与心得:根据类图,Day,Month,Year在这里都是各自独立的,都是通过DateUtil调用,其他也是一样。
第六次题目集7-1菜单计价程序-4,这次题目集就只有7-1这道题,很难,题目字数都有三千多字,根据题目中的提示,先写出了菜品Dish类,菜谱Menu类,点菜记录Record类,订单Order类,根据要求还需设计Table类用于处理订单时间,然后就是主函数,要考虑17中异常输入,很多种情况,头晕眼花想了几天写了几天还是没写出来放弃了。
三、采坑心得
第四次题目集7-4的踩坑:空字符的存在,我没有去除导致没有得到分,事后和同学讨论可以用到哈希 Set<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<>();进行空字符的删除。这题中还学到了compareToIgnoreCase和compareTo的区别,前者不区分大小写,后者则区分大小写,一开始没有注意,导致China和Hello还有I和am顺序出错。
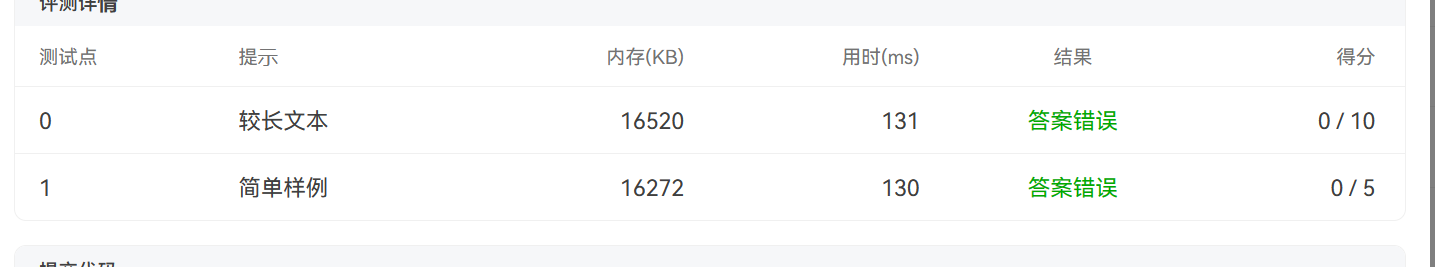
第四次题目集7-6GPS测绘中度分秒转换,最后输出时System.out.printf("%d°%d′%.2f″ = %.6f\n",d,m,s,t);这样时只能得到5分,经过高人指点改成
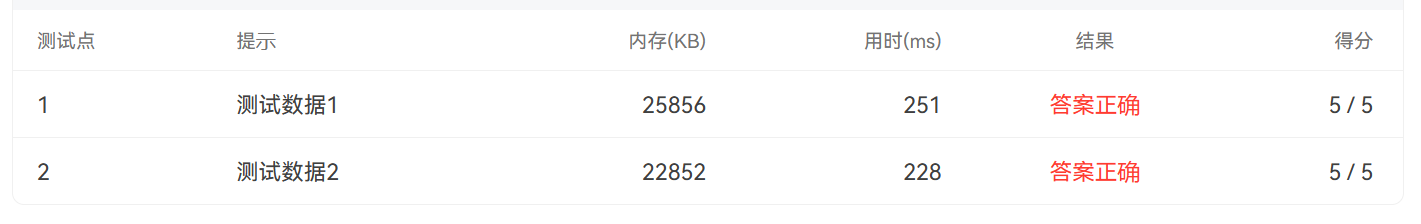
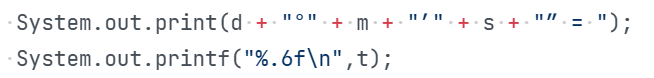 两行输出
两行输出
四、改进建议
把握好做题时间,多动笔花类图,写好注释,写代码遵循七大原则,减少耦合度,还有最近学的模式多多试着运用。
五、总结
通过这三次题目集,掌握了正则表达式,对三大特性有了更深刻的理解,还是要多看看书。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号