Collection接口(容器)中的Set接口;Set的3个实现类:HashSet ; LinkedHashSet;TreeSet;完善Collection接口Collections类
package day03; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; /**Set接口: * Set接口表示一个唯一、无序的容器(和添加顺序无关) * * */ public class Set01 { public static void main(String[] args) { /**Set接口提供的方法 * 增:add/addAll * 删:clear/remove/removeAll/retainAll * 改: * 查:contains/containsAll * 遍历:iterator * 其他:size/isEmpty */ Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<Integer>(); // [1]添加 // 无序 set.add(10); set.add(20); set.add(30); set.add(1); set.add(0); // 不能添加重复元素 boolean r=set.add(1); System.out.println(r);//输出结果:false(元素1没有重复添加进去) System.out.println(set);//输出结果:[0, 1, 20, 10, 30](元素是无序的) // 【2】删除 set.remove(10);//删除元素10 System.out.println(set);//输出结果:[0, 1, 20, 30] set.clear();//清空所有元素 System.out.println(set);//输出结果:[] // 【3】查看是否包含 System.out.println(set.contains(1));//输出结果:false // 【4】其他 System.out.println(set.size());//输出结果:0(集合里有多少位元素) System.out.println(set.isEmpty());//输出结果:true( 如果 set 不包含元素,则返回 true。) set.add(10); set.add(20); set.add(30); set.add(1); set.add(0); // 快速遍历 for (Integer item:set){ System.out.println(item);//输出结果:0 1 20 10 30 } // 迭代器 Iterator<Integer> it= set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Integer item1=it.next(); System.out.println(item1);//输出结果:0 1 20 10 30 } } }
package day03; //实现Comparable<Pen> public class Pen implements Comparable<Pen>{ private String name; private int health; private int love; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getHealth() { return health; } public void setHealth(int health) { if(health < 0) { this.health = 100; System.out.println("健康值不合法!"); }else { this.health = health; } } public int getLove() { return love; } public void setLove(int love) { this.love = love; } public Pen() { super(); this.health = 100; this.love = 0; } /*为了比较自定义类的内容重写hashCode方法和equals方法(用编译器自动生成) @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + health; result = prime * result + love; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Pen other = (Pen) obj; if (health != other.health) return false; if (love != other.love) return false; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; return true; }*/ public Pen(String name, int health, int love) { super(); this.name = name; this.setHealth(health); this.setLove(love); } public void showInfo() { System.out.print("我的姓名:"+this.getName()); System.out.print(",健康值:"+this.getHealth()); System.out.print(",亲密度"+this.getLove()); } //重写Object 方法 @Override public String toString() { return "Pen [name=" + name + ", health=" + health + ", love=" + love + "]"; } //重写compareTo方法(先比亲密度,在比较名字) /*内部比较器 * 当一个自定义对象实现Comparable并实现compareTo方法时,通过指定具体的比较策略,此时称为内部比较器。 * 比较策略的几种情况 [1]比较策略一般当前对象写在前面,待比较对象也在后面,比较结果默认升序 如果想要降序,改变两个比较对象的位置即可。 [2] 多种比较因素 * */ @Override public int compareTo(Pen a) { if (this.getLove()<a.getLove()){ return -1; }else if(this.getLove()==a.getLove()){ return this.getName().compareTo(a.getName());//string类型写法 }else{ return 1; }//简单写法:return this.getLove()-<a.getLove(); } }
package day03; /**Set接口的实现类常见的有HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet * HashSet * HashSet是Set接口的实现类,底层数据结构是哈希表。 HashSet是线程不安全的(不保证同步) */ import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.TreeSet; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { /*添加自定义对象 如果向HashSet中存储元素时,元素一定要实现hashCode方法和equals方法。 优点:添加、删除、查询效率高;缺点:无序*/ HashSet<Pen> set=new HashSet<Pen>(); Pen d1 = new Pen("大狗",100,0); Pen d2 = new Pen("二狗",100,0); Pen d3 = new Pen("三狗",100,0); Pen d4 = new Pen("三狗",100,0); set.add(d1); set.add(d2); set.add(d3); //未重写前 System.out.println(set.add(d4));输出结果:true System.out.println(set.add(d4));//(在Pen用编译器自动生成重写方法)重写后输出结果:false //(因为哈希表中的hashCode方法和equals方法本质是比较地址,如果想比较元素内容,则要重写两个方法) System.out.println(set.toString()); //输出结果:[Pen [name=二狗, health=100, love=0], Pen [name=大狗, health=100, love=0], Pen [name=三狗, health=100, love=0]] //输出结果没有顺序 /*LinkedHashSet LinkedHashSet是Set接口的实现类,底层数据结构哈希表+链表 哈希表用于散列元素;链表用于维持添加顺序。 如果要添加自定义类的对象元素,也需要重写hashCode和equals方法。*/ LinkedHashSet<Integer> set2= new LinkedHashSet<Integer>(); // 添加的顺序则是元素的顺序(由链表来实现) set2.add(10); set2.add(90); set2.add(20); set2.add(0); set2.add(1); set2.add(11); set2.add(10);//因为上面已有10 ,所以未添加到 System.out.println(set2);//输出结果:[10, 90, 20, 0, 1, 11] LinkedHashSet<Pen> set3= new LinkedHashSet<Pen>(); Pen d5 = new Pen("大狗",100,0); Pen d6 = new Pen("二狗",100,0); Pen d7 = new Pen("三狗",100,0); set3.add(d5); set3.add(d6); set3.add(d7); System.out.println(set3); //输出结果:[Pen [name=大狗, health=100, love=0], Pen [name=二狗, health=100, love=0], Pen [name=三狗, health=100, love=0]] /*1.12TreeSet TreeSet 是Set接口的实现类,底层数据结构是二叉树。 TreeSet 存储的数据按照一定的规则存储。存储规则让数据表现出自然顺序。 根据TreeSet的工作原理,向TreeSet添加自定义元素? 向TreeSet中添加元素时,一定要提供比较策略,否则会出现ClassCastException。 比较策略分两种:内部比较器和外部比较器 内部比较器(在Pen类中) 因为有时候我们不能访问源代码时,就要用到外部比较器 */ TreeSet<Pen> set4=new TreeSet<Pen>(); Pen d8 = new Pen("A",10,5); Pen d9 = new Pen("B",100,5); Pen d10 = new Pen("C",150,1); set4.add(d8); set4.add(d9); set4.add(d10); System.out.println(set4);//(先比亲密度,在比较名字,升序降序可自己调)( 内部比较器(在Pen类中)) //[Pen [name=C, health=150, love=1], Pen [name=A, health=10, love=5], Pen [name=B, health=100, love=5]] //使用外部比较器;需求:按照字符串的长度比较 Len len=new Len(); TreeSet<String> len1 = new TreeSet<String>(len); /*使用匿名内部类优化: * TreeSet<String> len1 = new TreeSet<String>(new Comparator<String>); * public int compare(String o1, String o2) { * // return o1.length() - o2.length(); // 如果长度一样,按照自然顺序 if(o1.length() == o2.length()) { return o1.compareTo(o2); }else { return o1.length() - o2.length(); } } len1.add("banana"); len1.add("coco"); len1.add("apple"); len1.add("apple"); System.out.println(len1);//输出结果:[coco, apple, banana] * */ len1.add("banana"); len1.add("coco"); len1.add("apple"); len1.add("apple"); System.out.println(len1);//输出结果:[coco, apple, banana] } } /*外部比较器 * 当实际开发过程中不知道添加元素的源代码、无权修改别人的代码,此时可以使用外部比较器。 Comparator 位于java.util包中,定义了compare(o1,o2) 用于提供外部比较策略 。 TreeSet接受一个指定比较策略的构造方法,这些比较策略的实现类必须实现Comparator接口。 需求:按照字符串的长度比较 * */ class Len implements Comparator<String>{ @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o1.length() - o2.length(); } }
注意: LinkedHashSet实现类中的方法hashCode和equals方法本质是比较地址,如果要比较内容,则要重写hashCode和equals方法(去掉自定义类中重复内容的对象);
;TreeSet 类中如果以自定义类来作为Key的话,要自己写比较条件(要排序),
哈希表:

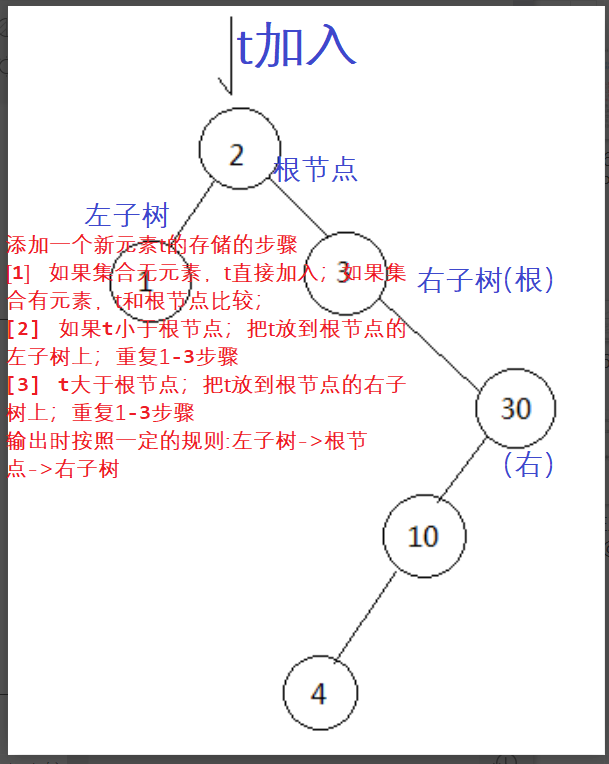
二叉树
package day03; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; /*Collections类 * 此类完全由在 collection 上进行操作或返回 collection 的静态方法组成。 * 它包含在 collection 上操作的多态算法,即“包装器”,包装器返回由指定 collection 支持的新 collection,以及少数其他内容。 也就是说完善 collection */ import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; public class collections { public static void main(String[] args) { // 【1】添加元素( 将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。) ArrayList<String> list =new ArrayList<String>(); Collections.addAll(list,"banana","coco","apple"); System.out.println(list);//输出结果:[banana, coco, apple] // 【2】排序(根据元素的自然顺序 对指定列表按升序进行排序。) Collections.sort(list); System.out.println(list);//输出结果:[apple, banana, coco] //通过指定的排序方法排序(数组的长度) Collections.sort(list,new Comparator<String>() { public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o1.length() - o2.length(); } }); System.out.println(list);//输出结果:[coco, apple, banana] //【3】max/min(默认比较内容大小) String maxStr=Collections.max(list); System.out.println(maxStr);//输出结果:coco(最大值) //重写排序方法 ;通过字符长度来排最大值 maxStr = Collections.max(list,new Comparator<String>() { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return o1.length() - o2.length(); } }); System.out.println(maxStr);//输出结果:banana // 【4】线程安全版本的集合( 返回指定列表支持的同步(线程安全的)列表。) LinkedList<String> list2 = new LinkedList<String>(); List<String> list3 = Collections.synchronizedList(list2); //把list2这个线程不安全的集合转换为线程安全版本 } }



