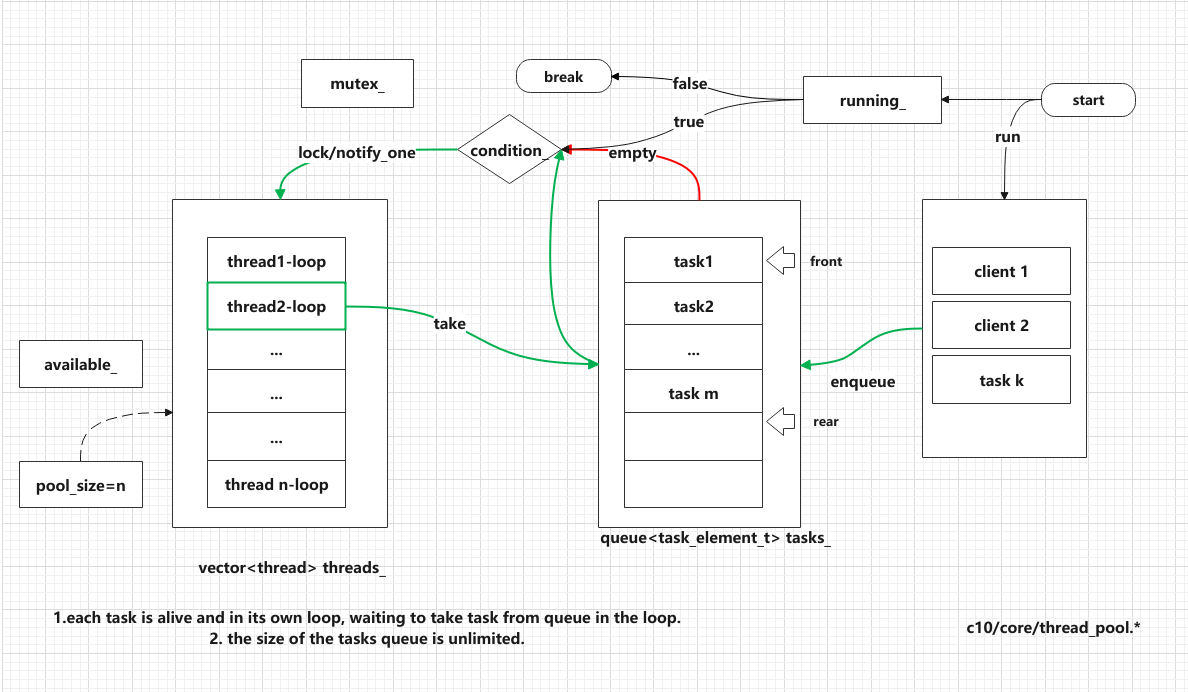
1 #ifndef THREAD_POOL_H 2 #define THREAD_POOL_H 3 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <memory> 7 #include <thread> 8 #include <mutex> 9 #include <condition_variable> 10 #include <future> 11 #include <functional> 12 #include <stdexcept> 13 14 class ThreadPool { 15 public: 16 ThreadPool(size_t); 17 template<class F, class... Args> 18 auto enqueue(F&& f, Args&&... args) 19 -> std::future<typename std::result_of<F(Args...)>::type>; 20 void enqueue(std::function<void()> func); 21 ~ThreadPool(); 22 23 size_t size() const; 24 size_t numAvailable() const; 25 bool inThreadPool() const; 26 void run(std::function<void()> func); 27 private: 28 // need to keep track of threads so we can join them 29 std::vector< std::thread > workers; 30 // the task queue 31 std::queue< std::function<void()> > tasks; 32 // synchronization 33 std::mutex queue_mutex; 34 std::condition_variable condition; 35 bool stop; 36 size_t available_; 37 void main_loop(); 38 };
1 // the constructor just launches some amount of workers 2 inline ThreadPool::ThreadPool(size_t threads) 3 : stop(false) 4 { 5 for(size_t i = 0;i<threads;++i) 6 workers.emplace_back( 7 [this] 8 { 9 while (!this->stop) { 10 std::function<void()> task; 11 12 { 13 std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(this->queue_mutex); 14 this->condition.wait(lock, 15 [this]{ return this->stop || !this->tasks.empty(); }); 16 if(this->stop && this->tasks.empty()) 17 return; 18 task = std::move(this->tasks.front()); 19 this->tasks.pop(); 20 } 21 22 task(); 23 } 24 // 25 std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(this->queue_mutex); 26 while (!this->stop) { 27 while (this->tasks.empty() && !this->stop) { 28 this->condition.wait(lock); 29 } 30 if (this->stop) { 31 break; 32 } 33 34 std::function<void()> task; 35 { 36 task = std::move(this->tasks.front()); 37 this->tasks.pop(); 38 // Decrement count, indicating thread is no longer available. 39 --available_; 40 lock.unlock(); 41 42 // Run the task. 43 try { 44 task(); 45 } catch (const std::exception& e) { 46 LOG(ERROR) << "Exception in thread pool task: " << e.what(); 47 } catch (...) { 48 LOG(ERROR) << "Exception in thread pool task: unknown"; 49 } 50 } 51 lock.lock(); 52 ++available_; 53 } 54 // 55 this->main_loop(); 56 // 57 } 58 ); 59 } 60 61 void ThreadPool::main_loop() {}
1 // add new work item to the pool 2 template<class F, class... Args> 3 auto ThreadPool::enqueue(F&& f, Args&&... args) 4 -> std::future<typename std::result_of<F(Args...)>::type> 5 { 6 using return_type = typename std::result_of<F(Args...)>::type; 7 8 auto task = std::make_shared< std::packaged_task<return_type()> >( 9 std::bind(std::forward<F>(f), std::forward<Args>(args)...) 10 ); 11 12 std::future<return_type> res = task->get_future(); 13 { 14 std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); 15 16 // don't allow enqueueing after stopping the pool 17 if(stop) 18 throw std::runtime_error("enqueue on stopped ThreadPool"); 19 20 tasks.emplace([task](){ (*task)(); }); 21 } 22 condition.notify_one(); 23 return res; 24 } 25 26 // OK 27 void ThreadPool::enqueue(std::function<void()> func) { 28 if (workers.size() == 0) { 29 throw std::runtime_error("No threads to run a task"); 30 } 31 std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); 32 33 // Set task and signal condition variable so that a worker thread will 34 // wake up and use the task. 35 tasks.emplace(std::move(func)); 36 condition_.notify_one(); 37 } 38 39 // the destructor joins all threads #OK 40 inline ThreadPool::~ThreadPool() 41 { 42 { 43 std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); 44 stop = true; 45 } 46 condition.notify_all(); 47 for(std::thread &worker: workers) 48 try { 49 worker.join(); 50 } catch (const std::exception&) { 51 52 } 53 }
1 size_t ThreadPool::size() const { 2 return workers.size(); 3 } 4 5 size_t ThreadPool::numAvailable() const { 6 std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex); 7 return available_; 8 } 9 10 bool ThreadPool::inThreadPool() const { 11 for (auto& thread : workers) { 12 if (thread.get_id() == std::this_thread::get_id()) { 13 return true; 14 } 15 } 16 return false; 17 } 18 #endif



