C++模板之Vector与STL初探
STL源码初步接触
STL = Standard Template Library,直译过来是:标准模板库,是惠普实验室开发的一系列软件的统称。从根本上说,STL是一些“容器”的集合,这些“容器”有list,vector,set,map等,STL也是算法和其他一些组件的集合。这里的“容器”和算法的集合指的是世界上很多聪明人很多年的杰作。STL的目的是标准化组件,这样就不用重新开发,可以使用现成的组件。STL现在是C++的一部分,因此不用额外安装什么。STL所实现的,是依据泛型思维架设起来的一个概念结构。说了这么多还是不知道STL是个什么东东,今天只是初接触这个概念,感觉很高深的样子,先这样理解吧,STL就是一个仓库,一个存放各种工具的仓库。它的工具分为六大类(六大组件) :
容器(containers):各种数据结构,如Vector,list,deque,set,map,用来存放底层数据。一般有序列式(下面要写的Vector就是个这种)、关联式等。
算法(algorithms):各种常用算法如:sort,search,copy,erase……
迭代器(iterator):扮演容器与算法之间的胶合剂,是所谓的“泛型指针”,共5种类型,以及他们的衍生变化。所有的STL容器都附带有自己专属的迭代器。原生指针也是一种迭代器。
仿函数(functor):行为类似函数可作为算法的某种策略。一般函数指针可认为是侠义的仿函数。
配接器(adapter):一种用来修饰容器,或仿函数,或迭代器接口的东西。
配置器(allocators)负责空间配置与管理。配置器是一个实现了动态空间配置、空间管理、空间释放的class template。
因为下面主要是实现Vector的简单操作,所以就再多讲一点它。Vector是动态空间,随着元素的加入,它的内部机制会自行扩充空间以容纳新元素。因此Vector的运用对于内存的合理运用与运用得灵活性有很大的帮助。Vector维护的是一个连续的空间,无论元素的型别为何,普通指针都可以作为Vector的迭代器而满足所有必要条件。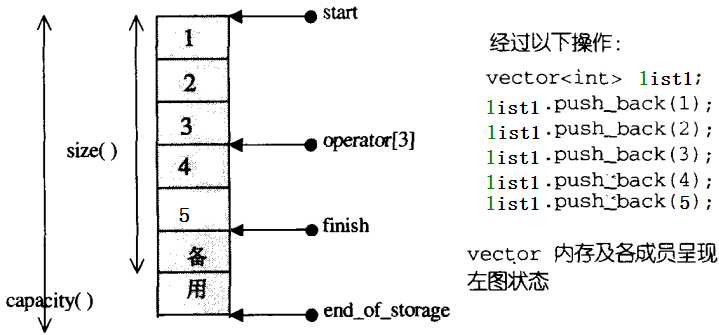
Vector 的简单实现:
1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<assert.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 using namespace std; 6 template<class T> 7 class Vector 8 { 9 public: 10 typedef T* Iterator; 11 typedef const T* Citerator; 12 public: 13 Vector() 14 :start(NULL) 15 ,finish(NULL) 16 ,endofstorage(NULL) 17 {} 18 Vector(const Vector<T>& v) 19 //:start(new T[v.endofstorage - v.start]) 20 //, finish(v.finish ) 21 //, endofstorage(v.endofstorage) 22 :start(new T[v.endofstorage - v.start]) 23 , finish(start + (v.finish - v.start)) 24 ,endofstorage(start + (v.endofstorage - v.start)) { 25 my_memcopy(start, v.start, sizeof(T)*(v.endofstorage - v.start)); 26 } 27 //向Vector中存入size个元素 28 Vector(Citerator array, size_t size) 29 :start(new T[size]) 30 , finish(start) 31 , endofstorage(start + size) { 32 for (size_t index = 0; index < size; ++size) { 33 start[index] = array[index]; finish++; 34 } 35 } 36 Vector<T>&operator=(const Vector<T>& v) { 37 if (this != &v) { 38 Vector<int>tmp(v); 39 swap(tmp); 40 } 41 return *this; 42 } 43 ~Vector(){ 44 if (start) { 45 delete[] start; 46 start = NULL; 47 // delete[] finish; 48 finish = NULL; 49 // delete[] endofstorage; 50 endofstorage = NULL; 51 } 52 } 53 // 返回首元素的迭代器 54 Iterator Begin() { 55 return start; 56 } 57 Citerator Begin()const { 58 return start; 59 } 60 // 获取Vector中最后一个元素的下一个位置 61 Iterator End() { 62 return finish: 63 } 64 Iterator End()const { 65 return finish; 66 } 67 size_t Size()const { 68 return finish - start; 69 } 70 size_t Capacity()const { 71 return endofstorage - start; 72 } 73 bool Empty()const { 74 return finish == start; 75 } 76 T& operator[](size_t index) { 77 return start[index]; 78 } 79 const T& operator[](size_t index)const { 80 return start[index]; 81 } 82 T& At(size_t index) { 83 if ((index <= Size()) && (index >= 0)) 84 return start[index]; 85 } 86 const T& At(size_t index)const { 87 if ((index <= Size()) && (index >= 0)) 88 return start[index]; 89 } 90 // 获取Vector中的第一个元素 91 T& Front() { 92 return srart[0]; 93 } 94 const T& Front()const { 95 return start[0]; 96 } 97 // 获取Vector中的最后一个元素 98 T& Back() { 99 return start[finish - start]; 100 } 101 const T& Back()const { 102 return start[finish - start]; 103 } 104 void PushBack(const T& x) { 105 capacity(); 106 // start[finish - start + 1] = x; 107 start[finish - start] = x; 108 finish++; 109 } 110 void PopBack() { 111 if (!Empty()) { 112 finish--; 113 } 114 } 115 // 在pos位置上插入元素x 116 Iterator Insert(Iterator pos, const T& x) { 117 for (size_t index = Size(); index >= (size_t)(pos - start); index--) { 118 start[index + 1] = start[index]; 119 } 120 *pos = x; 121 finish++; 122 return pos; 123 } 124 // 删除pos位置上面的元素 125 Iterator Erase(Iterator pos) { 126 for (size_t index = (size_t)(pos - start); index < Size(); index++) { 127 start[index] = start[index + 1]; 128 } 129 finish--; 130 return pos; 131 } 132 // 给Vector赋值n个值为x的元素 133 void Assign(size_t n, const T& x) { 134 if (n > endofstorage - start) { 135 finish = start + n; 136 capacity(); 137 for (size_t index = 0; index < n; index++) { 138 start[index] = x; 139 } 140 } 141 else { 142 for (size_t index = 0; index < n; index++) 143 start[index] = x; 144 } 145 finish = start + n; 146 } 147 public: //自己管理 扩容 148 void capacity() { 149 if (finish >= endofstorage) { 150 size_t capacity = 2 * (endofstorage - start) + 3; 151 Iterator tmp = new T[capacity]; // 拷贝元素 152 my_memcopy(tmp, start, sizeof(T)*(endofstorage - start)); 154 size_t ret = finish-start; 155 delete start; 156 start = tmp; 157 finish = start + ret; 158 endofstorage = start + capacity; // /*Iterator pos = start; size_t index = 0; while (pos < endofstprage) temp[index++] = *pos++; deleta[] start; start = temp; finish = start + index; endofstorage = start + capacity;*/ 159 } 160 } 161 void swap(Vector<T>& v) { 162 std::swap(start, v.start); 163 std::swap(finish, v.finish); 164 std::swap(endofstorage, v.endofstorage); 165 } 166 void Print() { 167 for (size_t i = 0; i < Size(); i++) 168 { 169 cout << start[i] << " "; 170 } 171 cout << endl; 172 } 173 void* my_memcopy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t sz) { 174 //assert(!dest || !src); 175 assert(dest != NULL || src != NULL); 176 char* ret = (char*)dest; 177 char* tmp = (char*)src; 178 while (sz--) { 179 *ret = *tmp; 180 ret++; 181 tmp++; 182 } 183 return dest; 184 } 185 private: 186 Iterator start; 187 Iterator finish; 188 Iterator endofstorage; 189 };
其中,注释掉的代码部分是我曾经踩过的坑,下面是部分测试代码
1 #include"vector.h" 2 void Test1() 3 { 4 Vector<int> list1; 5 list1.PushBack(1); 6 list1.PushBack(2); 7 list1.PushBack(3); 8 list1.PushBack(4); 9 list1.PushBack(5); 10 list1.Print(); 11 Vector<int> list2; 12 list2.PushBack(0); 13 list2.PushBack(9); 14 list2.PushBack(8); 15 list2.PushBack(7); 16 list2.PushBack(6); 17 list2.Print(); 18 list1 = list2; 19 list1.Print(); 20 } 21 void Test2() 22 { 23 Vector<int> list1; 24 list1.PushBack(1); 25 list1.PushBack(2); 26 list1.PushBack(3); 27 list1.PushBack(4); 28 list1.PushBack(5); 29 list1.Print(); 30 list1.PopBack(); 31 list1.Print(); 32 list1.Insert(&list1.At(2), 0); 33 list1.Print(); 34 list1.Erase(&list1.At(3)); 35 list1.Print(); 36 } 37 int main() 38 { 39 Test1(); 40 Test2(); 41 getchar(); 42 return 0; 43 }
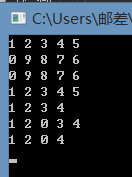
注意:扩容时函数中my_memcpy()函数,它的本质就是值拷贝,当Vector中存放的内置类型时没有任何问题,但是像String类这种问题就无法解决。所以下面给出了另一种写法。
1 /*Iterator pos = start; 2 size_t index = 0; 3 while (pos < endofstprage) 4 temp[index++] = *pos++; 5 deleta[] start; 6 start = temp; 7 finish = start + index; 8 endofstorage = start + capacity;*/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号