AtCoder Beginner Contest 338
AtCoder Beginner Contest 338

ABC 切 ABC,什么实力。
C - Leftover Recipes
Problem Statement
Your refrigerator has \(N\) kinds of ingredients. Let us call them ingredient \(1\), \(\dots\), ingredient \(N\). You have \(Q_i\) grams of ingredient \(i\).
You can make two types of dishes. To make one serving of dish A, you need \(A_i\) grams of each ingredient \(i\) \((1 \leq i \leq N)\). To make one serving of dish B, you need \(B_i\) grams of each ingredient \(i\). You can only make an integer number of servings of each type of dish.
Using only the ingredients in the refrigerator, what is the maximum total number of servings of dishes you can make?
Solution
枚举 A 菜品的数量 \(i\)。那么很显然 B 菜品的数量应当小于等于每一个 \(\left \lfloor \frac {q_j - i \times a_j}{b_j} \right \rfloor\),其中 \(1 \le j \le n\),表示有 \(i \times a_j\) 克的配料给 A,剩下的 \(q_j - i \times a_j\) 给 B。
我们希望在满足上述条件的情况下,总的菜数最多。那么取 \(\min_{j = 1}^n \left \lfloor \frac {q_j - i \times a_j}{b_j} \right \rfloor\) 个 B 菜品是最好的选择。
所以答案为:
将上面的 \(B\) 设为一个很大的数即可,比如 \(10^6\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int n, q[N], a[N], b[N], res;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i ) cin >> q[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i ) cin >> b[i];
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++ i ) {
// i 个 A
int k = 2e9;
bool flg = false;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++ j ) {
if (q[j] < i * a[j]) {
flg = true;
break;
}
if (!b[j]) continue;
k = min(k, (q[j] - i * a[j]) / b[j]);
}
if (flg) break; // 如果这些配料光做 A 菜品都不够了,直接结束
res = max(res, i + k);
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
D - Island Tour
Problem Statement
The AtCoder Archipelago consists of \(N\) islands connected by \(N\) bridges. The islands are numbered from \(1\) to \(N\), and the \(i\)-th bridge (\(1\leq i\leq N-1\)) connects islands \(i\) and \(i+1\) bidirectionally, while the \(N\)-th bridge connects islands \(N\) and \(1\) bidirectionally. There is no way to travel between islands other than crossing the bridges.
On the islands, a tour that starts from island \(X_1\) and visits islands \(X_2, X_3, \dots, X_M\) in order is regularly conducted. The tour may pass through islands other than those being visited, and the total number of times bridges are crossed during the tour is defined as the length of the tour.
More precisely, a tour is a sequence of \(l+1\) islands \(a_0, a_1, \dots, a_l\) that satisfies all the following conditions, and its length is defined as \(l\):
- For all \(j\ (0\leq j\leq l-1)\), islands \(a_j\) and \(a_{j+1}\) are directly connected by a bridge.
- There are some \(0 = y_1 < y_2 < \dots < y_M = l\) such that for all \(k\ (1\leq k\leq M)\), \(a_{y_k} = X_k\).
Due to financial difficulties, the islands will close one bridge to reduce maintenance costs. Determine the minimum possible length of the tour when the bridge to be closed is chosen optimally.
Solution
我们令 \(v_i\) 表示在第 \(i\) 座桥爆炸时,完成旅行的最短路程。我们希望在线性或线性对数的复杂度下求出所有的 \(v_i\),那么 \(\min v_i\) 即为答案。
可以发现,在整个旅程 \(x_1 \to x_2 \to \dots \to x_m\) 中,我们可以把它看成若干个小旅途 \(x_1 \to x_2, x_2 \to x_2, \dots, x_{m - 1} \to x_m\),因为它们之间是相互独立的。
那么最终 \(v_i = \sum v_i'\),表示每个小旅程的长度之和。
因此考虑对于一个小旅程 \(x_j \to x_{j + 1}\)。如果不爆炸的话会有两条路径,例如:
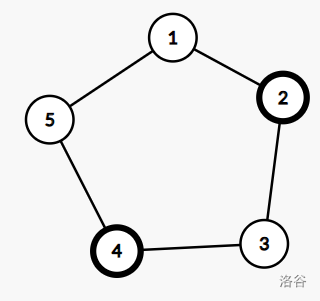
在 \(x_j = 2\),$x_{j + 1} = $4 时,有两条路径:
- \(S_1\):\(2 \to 1 \to 5 \to 4\),长度为 \(4\);
- \(S_2\):\(2 \to 3 \to 4\),长度为 \(3\)。
那么如果把 \(2 \to 1\) 或 \(1 \to 5\) 或 \(5 \to 4\) 炸了,这个小旅程的长度为 \(3\)。剩下的情况,如果把 \(2 \to 3\) 或 \(3 \to 4\) 炸了,这个小旅程的长度为 \(4\)。
也就是 \(v_1' = v_4' = v_5' = 3\),\(v_2' = v_3' = 4\)。
那么如果暴力计算每个小旅程和每个爆炸的桥,时间复杂度是不优的。可以发现每次修改 \(v\) 都是连续的一段,所以可以在差分数组上单点修改,最后求差分数组的前缀和即可。
Code
注意区间修改时可能会出现 \(\dots, v_{n - 1}, v_n, v_1, v_2, \dots\) 的情况。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
int n, m, a[N];
long long s[N];
int dis(int l, int r) {
if (l <= r) return r - l;
return r - l + n;
}
void add(int l, int r, int d) {
if (l <= r) {
s[l] += d;
s[r] -= d;
}
else {
s[l] += d;
s[n + 1] -= d;
s[0] += d;
s[r] -= d;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++ i )
add(a[i], a[i + 1], dis(a[i + 1], a[i])),
add(a[i + 1], a[i], dis(a[i], a[i + 1]));
long long res = 1e18;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i )
res = min(res, s[i] += s[i - 1]);
cout << res;
return 0;
}
E - Chords
Problem Statement
There are \(2N\) points placed at equal intervals on a circle, numbered \(1\) to \(2N\) in a clockwise direction starting from a certain point.
There are also \(N\) chords on the circle, with the \(i\)-th chord connecting points \(A_i\) and \(B_i\). It is guaranteed that all the values \(A_1,\dots,A_N,B_1,\dots,B_N\) are distinct.
Determine whether there is an intersection between the chords.
Solution
首先我们保证 \(a_i < b_i\)。若不满足先把它们交换。
然后圆拆开成一条链。一张官方题解的图示:

可以发现,如果两条线 \(x, y\) 有交叉,那么一定有 \(a_x < a_y < b_x < b_y\)。
枚举 \(x\),然后找是否存在一个 \(y\) 满足以上条件。
如果我们令 \(c_i\) 表示在 \(a_x = i\) 时 \(b_x\) 的值。由于 \(a_i, b_i\) 这总共 \(2n\) 个数互不相同,所以 \(c_i\) 是唯一确定的。那么上面的问题其实就是:
是否存在一个 \(a_x < j < b_x\),使得 \(c_j > b_x\)。
这是经典问题。我们只需要求这个区间内的最大值,然后判断是否大于 \(b_x\) 即可。也就是判断:
这就是静态区间求最大值的问题。ST 表即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 400010, M = 25;
int n, a[N], b[N];
int st[N][M];
int query(int l, int r) {
if (l > r) return -2e9;
int k = log2(r - l + 1);
return max(st[l][k], st[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i ) {
cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
if (a[i] > b[i]) swap(a[i], b[i]);
st[a[i]][0] = max(st[a[i]][0], b[i]);
}
for (int j = 1; j < M; ++ j )
for (int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= 2 * n; ++ i )
st[i][j] = max(st[i][j - 1], st[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i )
if (query(a[i] + 1, b[i] - 1) > b[i])
return puts("Yes"), 0;
puts("No");
return 0;
}


