通过调试对WriteFile()API的钩取
通过调试对WriteFile()API的钩取
0x00 目标与思路
目标:钩取指定的notepad.exe进程writeFile()API函数,对notepad.exe进程的写入的字符保存时保存为大写形式
思路:
1)使用DebugActiveProcess函数使调试器附加到指定进程中。
2)使用WaitForDebugEvent函数取得目标进程的调试信息。
3)更改writeFile()函数api的第一个字节为0xcc,使其进入调试区
4)进入调试去后将writeFile()API的第一个字节恢复原状,因为后面还有用。
5)对notepad输入缓冲区的字符串进行大写转换,并保存到缓冲区。
6)恢复writeFile的EIP信息
7)继续运行调试程序
8)再次写入INT3钩子
0x01实现代码
// hookapi1.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<stdio.h>
LPVOID g_pfWriteFile = NULL;
CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_INFO g_cpdi;
BYTE g_chINT3 = 0xcc, g_chOrgByte = 0;
//被调试进程启动时函数发生作用
BOOL OnCreateProcessDebugEvent(LPDEBUG_EVENT pde)
{
//获取WriteFile()API地址
g_pfWriteFile = GetProcAddress(GetModuleHandleA("kernel32.dll"), "WriteFile");
//将WriteFile()的第一个字节换成INT3即0xcc
//并且添加WriteFile()第一字节的备份,为以后恢复做准备
memcpy(&g_cpdi, &pde->u.CreateProcessInfo, sizeof(CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_INFO));
ReadProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, g_pfWriteFile, &g_chOrgByte, sizeof(BYTE), NULL);
WriteProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, g_pfWriteFile, &g_chINT3, sizeof(BYTE), NULL);
return TRUE;
}
//发生异常启动
//发生异常启动
BOOL OnExceptionDebugEvent(LPDEBUG_EVENT pde)
{
CONTEXT ctx;
PBYTE lpBuffer = NULL;
DWORD dwNumofByteToWrite, dwAddrOfBuffer, i;
PEXCEPTION_RECORD per = &pde->u.Exception.ExceptionRecord;
//判断是否是INT3异常
if (EXCEPTION_BREAKPOINT == per->ExceptionCode)
{
//判断是够否是WriteFile()API的地址
if (g_pfWriteFile == per->ExceptionAddress)
{
//1.脱钩,即将writeFile()的首地址恢复,因为后面的用到该函数
WriteProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, g_pfWriteFile, &g_chOrgByte, sizeof(BYTE), NULL);
//2.获取进程上下文,其实就是获取各个寄存器的值
//获得进程上下文之后就可以获得进程中函数的各个参数值
ctx.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_CONTROL;
GetThreadContext(g_cpdi.hThread, &ctx);
//3.获取WriteFile()的param2以及param3的值
//param2是writeFile()的字符缓冲区地址
//param3是WriteFile()的字符缓冲区大小
ReadProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, (LPVOID)(ctx.Esp + 0x8), &dwAddrOfBuffer, sizeof(DWORD), NULL);
ReadProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, (LPVOID)(ctx.Esp + 0xC), &dwNumofByteToWrite, sizeof(DWORD), NULL);
//4.分配临时缓冲区给存放缓冲区的字符串
lpBuffer = (PBYTE)malloc(dwNumofByteToWrite + 1);
//将新分配的缓冲区的内容清零,以便存放内容
memset(lpBuffer, 0, dwNumofByteToWrite + 1);
//5.复制writeFile()的缓冲区的内容复制到临时缓冲区
ReadProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, (LPVOID)dwAddrOfBuffer, lpBuffer, dwNumofByteToWrite, NULL);
printf("\n### 初始字符串 ###\n%s\n", lpBuffer);
//6.将临时缓冲区的字符串转换成大写
for (i = 0; i < dwNumofByteToWrite; i++)
{
if (0x61 <= lpBuffer[i] && lpBuffer[i] <= 0x7a)
{
lpBuffer[i] -= 0x20;
}
}
printf("\n ****转换后的字符串为###\n%s\n", lpBuffer);
//7.将变换后的字符串复制到WriteFile()的缓冲区
WriteProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, (LPVOID)dwAddrOfBuffer, lpBuffer, dwNumofByteToWrite, NULL);
//8.释放临时缓冲区
free(lpBuffer);
//9.更改EIP指针恢复为WriteFile()的首地址
//由于前面更改WriteFile()的首地址为INT3了,后面执行了INT3指令之后EIP增加了1。所以执行完之后要改回去。
ctx.Eip = (DWORD)g_pfWriteFile;
SetThreadContext(g_cpdi.hThread, &ctx);
//10.继续运行被调试程序
ContinueDebugEvent(pde->dwProcessId, pde->dwThreadId, DBG_CONTINUE);
Sleep(0);
//11.再次写入API钩子
WriteProcessMemory(g_cpdi.hProcess, g_pfWriteFile, &g_chINT3, sizeof(BYTE), NULL);
return TRUE;
}
}
return FALSE;
}
//等待事件发生
void Debugloop()
{
DEBUG_EVENT de;
DWORD dwContinueStatus;
//等待被调试事件发生
while (WaitForDebugEvent(&de,INFINITE))
{
dwContinueStatus = DBG_CONTINUE;
//被调试进程生成或者要附加事件
if (CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_EVENT==de.dwDebugEventCode)
{
OnCreateProcessDebugEvent(&de);
}
else if (EXCEPTION_DEBUG_EVENT==de.dwDebugEventCode)
{
if (OnExceptionDebugEvent(&de))
continue;
}
else if (EXIT_PROCESS_DEBUG_EVENT==de.dwDebugEventCode)
{
//被调试进程终止
break;
}
ContinueDebugEvent(de.dwProcessId, de.dwThreadId, dwContinueStatus);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
DWORD dwPID;
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("\nUSAGE : hookdbg.exe <pid>\n");
return 1;
}
// 将第二个参数转化为long型
dwPID = atoi(argv[1]);
if (!DebugActiveProcess(dwPID))
{
printf("DebugActiveProcess(%d) failed!!!\n"
"Error Code = %d\n", dwPID, GetLastError());
return 1;
}
// 循环等待事件发生
Debugloop();
return 0;
}
编译生成hookapi1.exe文件。将其放入D盘。
0x02 运行查看效果
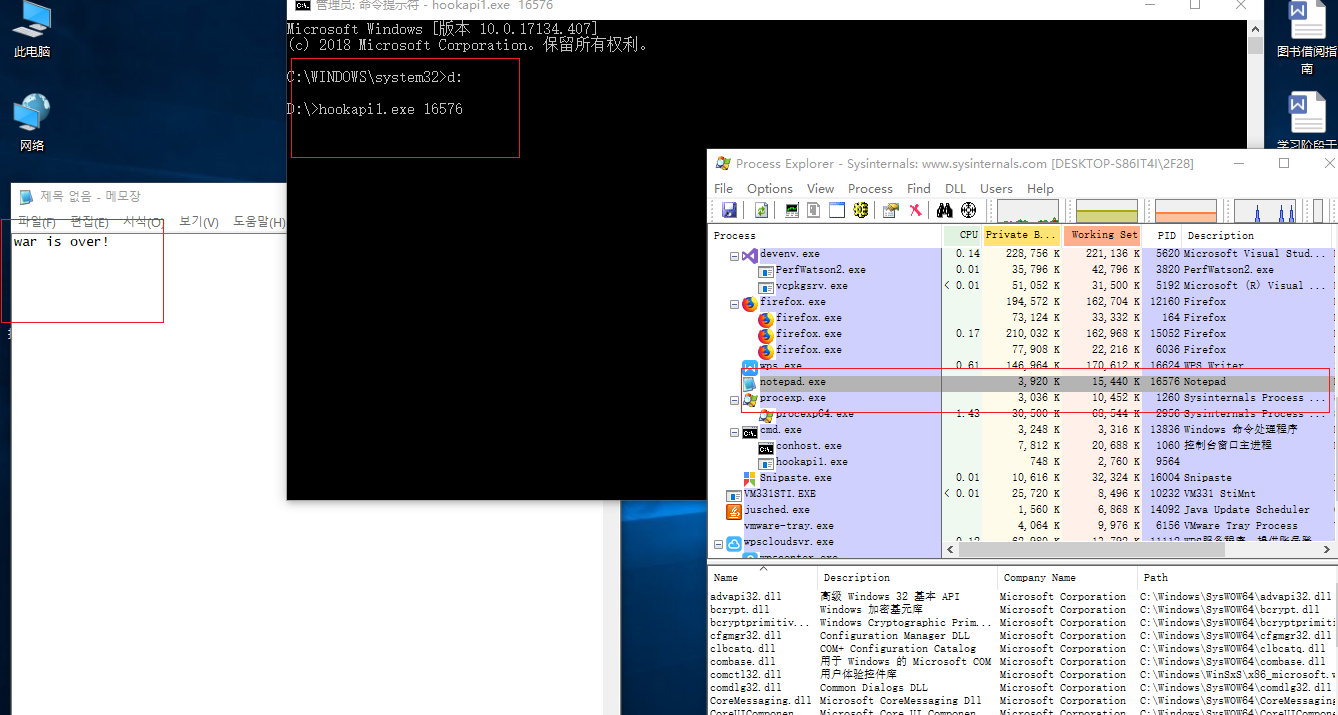
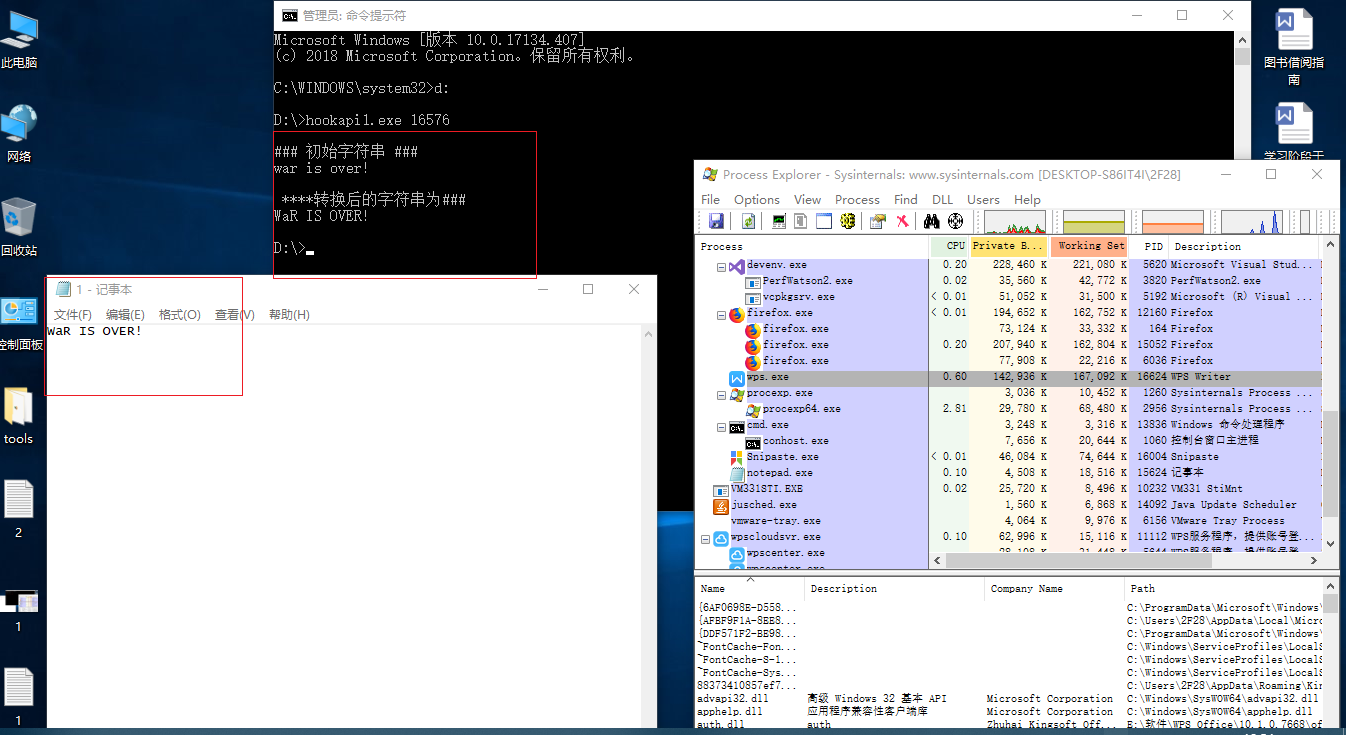
打开notepad.exe,打开processExploer查看notepad.exe的PID,用管理员权限打开cmd,输入hookapi1.exe 16576,向notepad中输入小写的“war is over!”退出并保存为1.text文件。运行结果如下图:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号