##Collection集合
1、Collection集合是单列集合
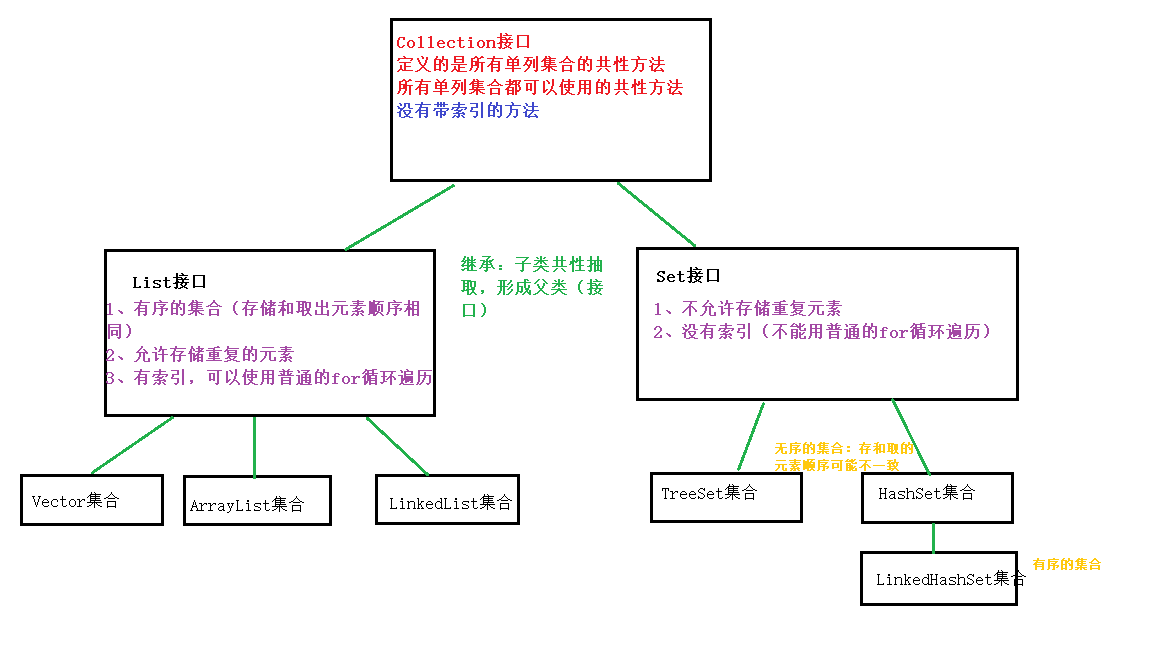
2、Collection是所有单列集合最顶层的接口,定义了所有单列集合的共性方法
任意的单列集合都可以使用Collection接口中的方法
* 1、public boolean add(E e);把指定对象添加到当前集合中。
* 2、public void clear();移除此 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。
* 3、public boolean remove(E e);把给定对象在集合中删除。
* 4、public boolean contains(E e);看指定元素是否包含在集合中。
* 5、public boolean isEmpty(E e);看集合中元素是否为空。
* 6、public int size();返回集合中元素的个数。
* 7、public Object[] toArray();返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。
代码示例:
package Collection.CommonMethod.demo01; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; /* * java.util.Collection接口 * 所有单列集合最顶层的接口,里面定义了所有单列集合的共性方法 * 任意的单列集合都可以使用Collection接口中的方法 * 1、public boolean add(E e);把指定对象添加到当前集合中。 * 2、public void clear();移除此 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。 * 3、public boolean remove(E e);把给定对象在集合中删除。 * 4、public boolean contains(E e);看指定元素是否包含在集合中。 * 5、public boolean isEmpty(E e);看集合中元素是否为空。 * 6、public int size();返回集合中元素的个数。 * 7、public Object[] toArray();返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。 * * */ public class Demo01Collection { public static void main(String[] args) { //可以用多态创建集合 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>(); /*public boolean add(E e);把指定对象添加到当前集合中。 返回值是一个bollean值,一般都返回true,所以不用接收 */ boolean b1 = coll.add("ftj"); coll.add("lxy"); System.out.println(b1); System.out.println(coll); /*public boolean remove(E e);把给定对象在集合中删除。 返回值是一个bollean值,如果集合中存在元素,删除元素,则返回true;反之,false。 */ boolean b2 = coll.remove("ftj"); System.out.println(b2); System.out.println(coll); /*public boolean contains(E e);看指定元素是否包含在集合中。 返回值是一个bollean值,如果集合中存在元素,则返回true,否则,返回false。 */ boolean b3 = coll.contains("lxy"); System.out.println(b3); } }
3、Iterator迭代器:用来遍历集合
1、Iterator是一个接口,我们无法直接使用,需要获取实现类的对象,但是他获取对象的方式比特殊
2、Collection接口中有一个方法,叫iterator(),它返回的就是迭代器的实现类对象 Iterator<E> iterator();
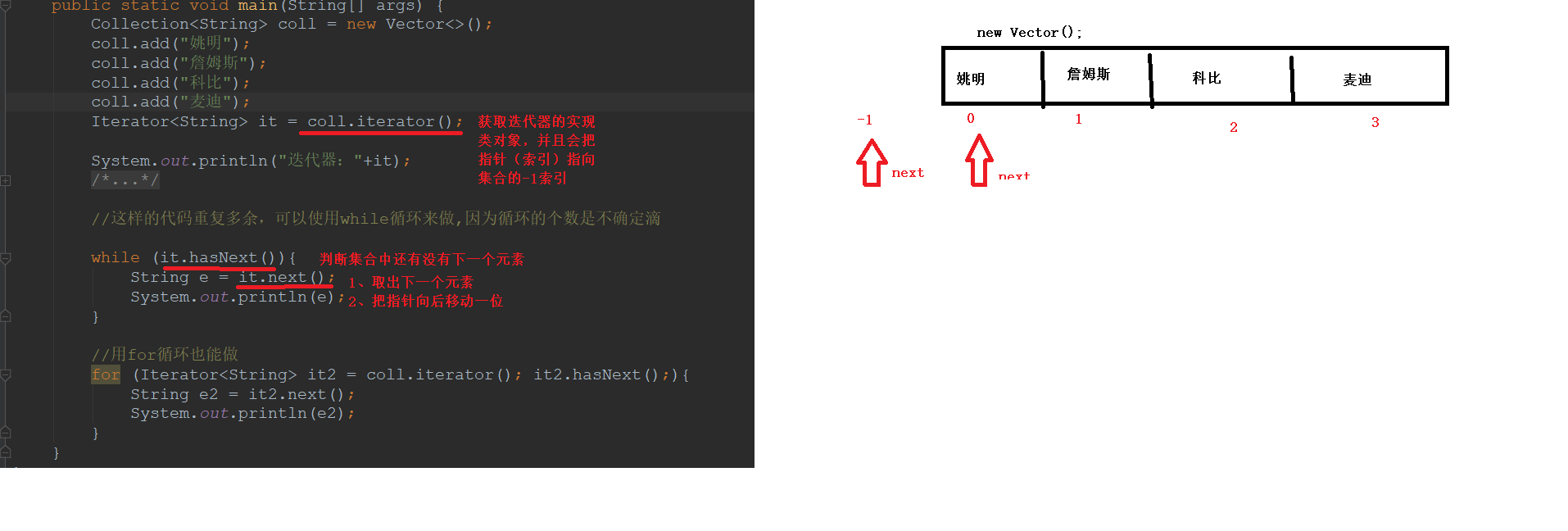
迭代器的使用步骤(重点):
* 1、使用集合中的方法iterator(),获取迭代器的实现类对象,使用Iterator接口接收(多态)
* 2、使用Iterator接口中的方法hasNext判断还有没有下一个元素
* 3、使用Iterator接口中的方法next取出集合中的下一个元素
代码示例:
public class Demo01Iterator { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> coll = new Vector<>(); coll.add("姚明"); coll.add("詹姆斯"); coll.add("科比"); coll.add("麦迪"); Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator(); System.out.println("迭代器:"+it); /*boolean b1 = it.hasNext(); System.out.println(b1); String next1 = it.next(); System.out.println(next1); boolean b2 = it.hasNext(); System.out.println(b2); String next2 = it.next(); System.out.println(next2); boolean b3 = it.hasNext(); System.out.println(b3);*/ //这样的代码重复多余,可以使用while循环来做,因为循环的个数是不确定滴 while (it.hasNext()){ String e = it.next(); System.out.println(e); } //用for循环也能做 for (Iterator<String> it2 = coll.iterator(); it2.hasNext();){ String e2 = it2.next(); System.out.println(e2); } } }
迭代器工作原理:
4、for Each
增强for循环:底层也是使用迭代器,使用for循环的格式,简化迭代器的书写。他是JDK1.5之后的新特性
* public interface Iterable<T>实现这个接口允许对象成为 "foreach" 语句的目标。
* 所有单列集合都可以使用增强for
* 作用:用来遍历集合和数组
* 格式:
* for(集合/数组的数据类型 变量名: 集合名/数组名){
* sout(变量名);
* }
代码示例:
package Collection.CommonMethod.demo03; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * 增强for循环:底层也是使用迭代器,使用for循环的格式,简化迭代器的书写 * JDK1.5之后的新特性 * public interface Iterable<T>实现这个接口允许对象成为 "foreach" 语句的目标。 * 所有单列集合都可以使用增强for * * 作用:用来遍历集合和数组 * 格式: * for(集合/数组的数据类型 变量名: 集合名/数组名){ * sout(变量名); * } */ public class Demo01forEach { public static void main(String[] args) { demo02(); } //使用增强for循环遍历集合 private static void demo02() { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("姚明"); list.add("易建联"); for (String s : list) { System.out.println(s); } } //使用增强for循环遍历数组 private static void demo01() { int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5}; for (int i : arr) { System.out.println(i); } } }
That which doesn't kill me makes me stronger!


