20192307 2020-2021-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验八报告
20192307 2020-2021-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验八报告
- 课程:《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》
- 班级: 1923
- 姓名: 常万里
- 学号: 20192307
- 实验教师:王志强老师
- 实验日期:2020年12月4日
- 必修/选修: 必修
一、实验内容
- 1.参考教材PP16.1,完成链树LinkedBinaryTree的实现(getRight,contains,toString,preorder,postorder)
用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的LinkedBinaryTree进行测试,提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息- 2.基于LinkedBinaryTree,实现基于(中序,先序)序列构造唯一一棵二㕚树的功能,比如给出中序HDIBEMJNAFCKGL和后序ABDHIEJMNCFGKL,构造出附图中的树
用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的功能进行测试,提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息- 3.自己设计并实现一颗决策树
- 4.输入中缀表达式,使用树将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并输出后缀表达式和计算结果
二、实验过程及结果
(一)链树LinkedBinaryTree的实现
BinaryTree.java
//*******************************************************************
// Java Foundations
//
// Defines the interface to a binary tree collection.
//*******************************************************************
package javafoundations;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author Shape Of My Heart
*/
public interface BinaryTree<T> extends Iterable<T>
{
// Returns the element stored in the root of the tree.
public T getRootElement();
// Returns the left subtree of the root.
public BinaryTree<T> getLeft();
// Returns the right subtree of the root.
public BinaryTree<T> getRight();
// Returns true if the binary tree contains an element that
// matches the specified element and false otherwise.
public boolean contains (T target);
// Returns a reference to the element in the tree matching
// the specified target.
public T find (T target);
// Returns true if the binary tree contains no elements, and
// false otherwise.
public boolean isEmpty();
// Returns the number of elements in this binary tree.
public int size();
// Returns the string representation of the binary tree.
@Override
public String toString();
// Returns a preorder traversal on the binary tree.
public ArrayList<T> preorder();
// Returns an inorder traversal on the binary tree.
public ArrayList<T> inorder();
// Returns a postorder traversal on the binary tree.
public ArrayList<T> postorder();
// Performs a level-order traversal on the binary tree.
public ArrayList<T> levelorder();
}
LinkedBinaryTree.java
//*******************************************************************
// Java Foundations
//
// Implements a binary tree using a linked representation.
//*******************************************************************
package javafoundations;
import javafoundations.exceptions.ElementNotFoundException;
import javafoundations.exceptions.EmptyCollectionException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class LinkedBinaryTree<T> implements BinaryTree<T> {
protected BTNode<T> root;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates an empty binary tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public LinkedBinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates a binary tree with the specified element as its root.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public LinkedBinaryTree(T element) {
root = new BTNode<>(element);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates a binary tree with the two specified subtrees.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public LinkedBinaryTree(T element, LinkedBinaryTree<T> left,
LinkedBinaryTree<T> right) {
root = new BTNode<>(element);
root.setLeft(left.root);
root.setRight(right.root);
}
public static void inOrder(BTNode tree) {
if (tree == null) {
} else {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.print() + " ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// The following methods are left as programming projects.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// public LinkedBinaryTree<T> getRight() { }
// public boolean contains (T target) { }
// public boolean isEmpty() { }
// public String toString() { }
// public Iterator<T> preorder() { }
// public Iterator<T> postorder() { }
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the element stored in the root of the tree. Throws an
// EmptyCollectionException if the tree is empty.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public T getRootElement() {
if (root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get root operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
}
return root.getElement();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the left subtree of the root of this tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public LinkedBinaryTree<T> getLeft() {
if (root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get left operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
}
LinkedBinaryTree<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree<>();
result.root = root.getLeft();
return result;
}
@Override
public BinaryTree<T> getRight() {
if (root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get right operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
}
LinkedBinaryTree<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree<>();
result.root = root.getRight();
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(T target) {
return root.find(target) != null;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the element in this binary tree that matches the
// specified target. Throws a ElementNotFoundException if the
// target is not found.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public T find(T target) {
BTNode<T> node = null;
if (root != null) {
node = root.find(target);
}
if (node == null) {
throw new ElementNotFoundException("Find operation failed. "
+ "No such element in tree.");
}
return node.getElement();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the number of elements in this binary tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public int size() {
int result = 0;
if (root != null) {
result = root.count();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
@Override
public ArrayList<T> preorder() {
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
root.preorder(iter);
}
return iter;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Populates and returns an iterator containing the elements in
// this binary tree using an inorder traversal.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public ArrayList<T> inorder() {
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
root.inorder(iter);
}
return iter;
}
@Override
public ArrayList<T> postorder() {
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
root.postorder(iter);
}
return iter;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Populates and returns an iterator containing the elements in
// this binary tree using a levelorder traversal.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public ArrayList<T> levelorder() {
LinkedQueue<BTNode<T>> queue = new LinkedQueue<>();
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.enqueue(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BTNode<T> current = queue.dequeue();
iter.add(current.getElement());
if (current.getLeft() != null) {
queue.enqueue(current.getLeft());
}
if (current.getRight() != null) {
queue.enqueue(current.getRight());
}
}
}
return iter;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Satisfies the Iterable interface using an inorder traversal.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public BTNode<Character> construct(char[] pre, char[] in) {
if (pre.length == 0 || in.length == 0) {
return null;
}
BTNode<Character> tree = new BTNode<>(pre[0]);
int index = search(0, in.length, in, tree.getElement());
tree.setLeft(construct(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, index + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(in, 0, index)));
tree.setRight(construct(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, index + 1, pre.length),
Arrays.copyOfRange(in, index + 1, in.length)));
return tree;
}
public int search(int start, int end, char[] inOrders, char data) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (data == inOrders[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public void preOrder(BTNode<T> Tree) {
System.out.print(Tree.getElement() + " ");
BTNode<T> leftTree = Tree.left;
if (leftTree != null) {
preOrder(leftTree);
}
BTNode<T> rightTree = Tree.right;
if (rightTree != null) {
preOrder(rightTree);
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return null;
}
}
测试代码
package javafoundations;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class LinkedBinaryTreeTest extends TestCase {
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> a = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(1);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> b = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(2);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> c = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(3,a,b);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> d = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(4);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> e = new LinkedBinaryTree<Integer>(5,c,d);
LinkedBinaryTree f = new LinkedBinaryTree();
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> x1 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(20);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> x2 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(23);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> x3 = new LinkedBinaryTree<Integer>(18,x1,x2);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> x4 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(7);
LinkedBinaryTree<Integer> x5 = new LinkedBinaryTree<Integer>(7,x3,x4);
@Test
public void testSize() {
assertEquals(3,c.size());
assertEquals(5,e.size());
}
public void testInorder() {
assertEquals("[1, 3, 2, 5, 4]",e.inorder().toString());
assertEquals("[1, 3, 2]",c.inorder().toString());
}
public void testPreorder() {
assertEquals("[5, 1, 3, 2, 4]",e.preorder().toString());
assertEquals("[3, 1, 2]",c.preorder().toString());
}
public void testPostorder() {
assertEquals("[1, 3, 2, 4, 5]",e.postorder().toString());
assertEquals("[1, 2, 3]",c.postorder().toString());
assertEquals("[20, 18, 23, 7, 7]",x5.postorder().toString());
}
public void testLevelorder() {
assertEquals("[5, 3, 4, 1, 2]",e.levelorder().toString());
assertEquals("[3, 1, 2]",c.levelorder().toString());
}
public void testContains() {
assertTrue(e.contains(5));
assertFalse(a.contains(6));
}
public void testIsEmpty() {
assertFalse(a.isEmpty());
assertTrue(f.isEmpty());
}
}
实验测试截图
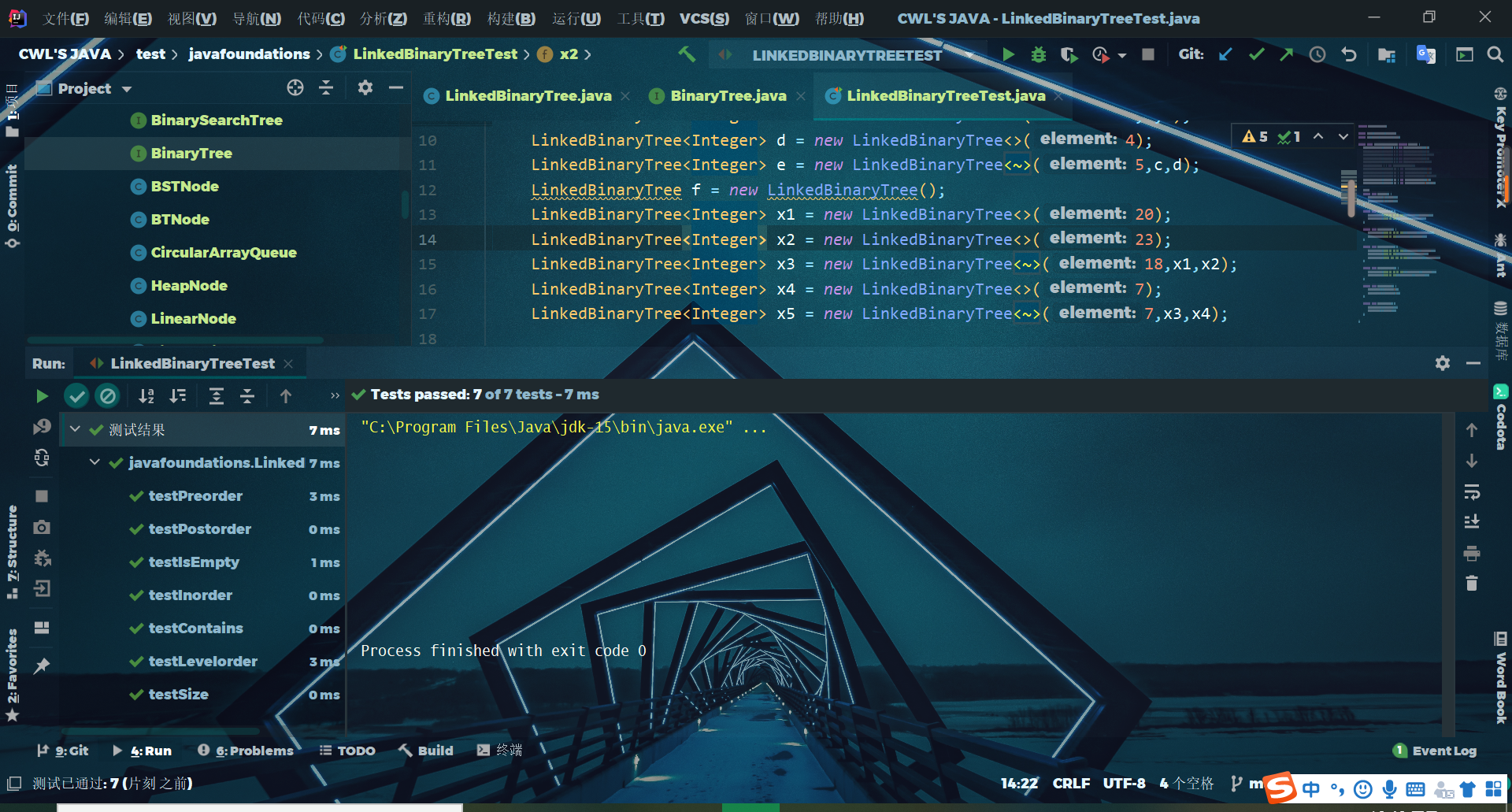
(二)构造唯一一棵二㕚树的功能
//*******************************************************************
// LinkedBinaryTree.java Java Foundations
//
// Implements a binary tree using a linked representation.
//*******************************************************************
package javafoundations;
import javafoundations.exceptions.ElementNotFoundException;
import javafoundations.exceptions.EmptyCollectionException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class LinkedBinaryTree<T> implements BinaryTree<T> {
protected BTNode<T> root;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates an empty binary tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public LinkedBinaryTree() {
root = null;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates a binary tree with the specified element as its root.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public LinkedBinaryTree(T element) {
root = new BTNode<>(element);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Creates a binary tree with the two specified subtrees.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public LinkedBinaryTree(T element, LinkedBinaryTree<T> left,
LinkedBinaryTree<T> right) {
root = new BTNode<>(element);
root.setLeft(left.root);
root.setRight(right.root);
}
public static void inOrder(BTNode tree) {
if (tree == null) {
} else {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.print() + " ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// The following methods are left as programming projects.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// public LinkedBinaryTree<T> getRight() { }
// public boolean contains (T target) { }
// public boolean isEmpty() { }
// public String toString() { }
// public Iterator<T> preorder() { }
// public Iterator<T> postorder() { }
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the element stored in the root of the tree. Throws an
// EmptyCollectionException if the tree is empty.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public T getRootElement() {
if (root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get root operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
}
return root.getElement();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the left subtree of the root of this tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public LinkedBinaryTree<T> getLeft() {
if (root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get left operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
}
LinkedBinaryTree<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree<>();
result.root = root.getLeft();
return result;
}
@Override
public BinaryTree<T> getRight() {
if (root == null) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get right operation "
+ "failed. The tree is empty.");
}
LinkedBinaryTree<T> result = new LinkedBinaryTree<>();
result.root = root.getRight();
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(T target) {
return root.find(target) != null;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the element in this binary tree that matches the
// specified target. Throws a ElementNotFoundException if the
// target is not found.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public T find(T target) {
BTNode<T> node = null;
if (root != null) {
node = root.find(target);
}
if (node == null) {
throw new ElementNotFoundException("Find operation failed. "
+ "No such element in tree.");
}
return node.getElement();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Returns the number of elements in this binary tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public int size() {
int result = 0;
if (root != null) {
result = root.count();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
@Override
public ArrayList<T> preorder() {
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
root.preorder(iter);
}
return iter;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Populates and returns an iterator containing the elements in
// this binary tree using an inorder traversal.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public ArrayList<T> inorder() {
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
root.inorder(iter);
}
return iter;
}
@Override
public ArrayList<T> postorder() {
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
root.postorder(iter);
}
return iter;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Populates and returns an iterator containing the elements in
// this binary tree using a levelorder traversal.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public ArrayList<T> levelorder() {
LinkedQueue<BTNode<T>> queue = new LinkedQueue<>();
ArrayList<T> iter = new ArrayList<>();
if (root != null) {
queue.enqueue(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BTNode<T> current = queue.dequeue();
iter.add(current.getElement());
if (current.getLeft() != null) {
queue.enqueue(current.getLeft());
}
if (current.getRight() != null) {
queue.enqueue(current.getRight());
}
}
}
return iter;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Satisfies the Iterable interface using an inorder traversal.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public BTNode<Character> construct(char[] pre, char[] in) {
if (pre.length == 0 || in.length == 0) {
return null;
}
BTNode<Character> tree = new BTNode<>(pre[0]);
int index = search(0, in.length, in, tree.getElement());
tree.setLeft(construct(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, index + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(in, 0, index)));
tree.setRight(construct(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, index + 1, pre.length),
Arrays.copyOfRange(in, index + 1, in.length)));
return tree;
}
public int search(int start, int end, char[] inOrders, char data) {
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
if (data == inOrders[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public void preOrder(BTNode<T> Tree) {
System.out.print(Tree.getElement() + " ");
BTNode<T> leftTree = Tree.left;
if (leftTree != null) {
preOrder(leftTree);
}
BTNode<T> rightTree = Tree.right;
if (rightTree != null) {
preOrder(rightTree);
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return null;
}
}
测试代码
package NBE131;/*
\* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
\* User: Shape Of My Heart
\* Date: 2020/12/4
\* Time: 8:59
\* Besides,some of the best things in life are total mistakes.
\* Description:
\**/
import javafoundations.BTNode;
import javafoundations.LinkedBinaryTree;
/**
* @author Shape Of My Heart
*/
public class LBTTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedBinaryTree<Character> t = new LinkedBinaryTree<>();
BTNode<Character> tree;
char[] pre = {'A','B','D','H','I','E','J','M','N','C','F','G','K','L'};
char[] in = {'H','D','I','B','E','M','J','N','A','F','C','K','G','L'};
tree = t.construct(pre,in);
System.out.println("前序遍历");
t.preOrder(tree);
System.out.println("\n中序遍历");
LinkedBinaryTree.inOrder(tree);
System.out.println("\n层序遍历");
System.out.println(t);
}
}
测试代码运行截图

(三)决策树
BackPainExpert.java
package NBE131;//********************************************************************
// Java Foundations
//
// Represents a simple expert system for back pain diagnosis.
//********************************************************************
import javafoundations.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Shape Of My Heart
*/
public class BackPainExpert
{
private final LinkedBinaryTree<String> tree;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Sets up the diagnosis question tree.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public BackPainExpert()
{
String e1 = "Did the pain occur after a blow or jolt?";
String e2 = "Do you have a fever?";
String e3 = "Do you have difficulty controlling your arms or legs?";
String e4 = "Do you have persistent morning stiffness?";
String e5 = "Do you have a sore throat or runny nose?";
String e6 = "Do you have pain or numbness in one arm or leg?";
String e7 = "Emergency! You may have damaged your spinal cord.";
String e8 = "See doctor if pain persists.";
String e9 = "You may have an inflammation of the joints.";
String e10 = "See doctor to address symptoms.";
String e11 = "You may have a respiratory infection.";
String e12 = "You may have a sprain or strain.";
String e13 = "You may have a muscle or nerve injury.";
LinkedBinaryTree<String> n2, n3, n4, n5, n6, n7, n8, n9,
n10, n11, n12, n13;
n8 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e8);
n9 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e9);
n4 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e4, n8, n9);
n10 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e10);
n11 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e11);
n5 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e5, n10, n11);
n12 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e12);
n13 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e13);
n6 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e6, n12, n13);
n7 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e7);
n2 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e2, n4, n5);
n3 = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e3, n6, n7);
tree = new LinkedBinaryTree<>(e1, n2, n3);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Follows the diagnosis tree based on user responses.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public void diagnose()
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedBinaryTree<String> current = tree;
System.out.println ("So, you're having back pain.");
while (current.size() > 1)
{
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
if ("N".equalsIgnoreCase(scan.nextLine())) {
current = current.getLeft();
} else {
current = (LinkedBinaryTree<String>) current.getRight();
}
}
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
}
}
BackPainAnalyzer.java
package NBE131;//********************************************************************
// Java Foundations
//
// Demonstrates the use of a binary tree.
//********************************************************************
public class BackPainAnalyzer
{
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
// Asks questions of the user to diagnose a medical problem.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------
public static void main (String[] args)
{
BackPainExpert expert = new BackPainExpert();
expert.diagnose();
}
}
测试代码运行截图

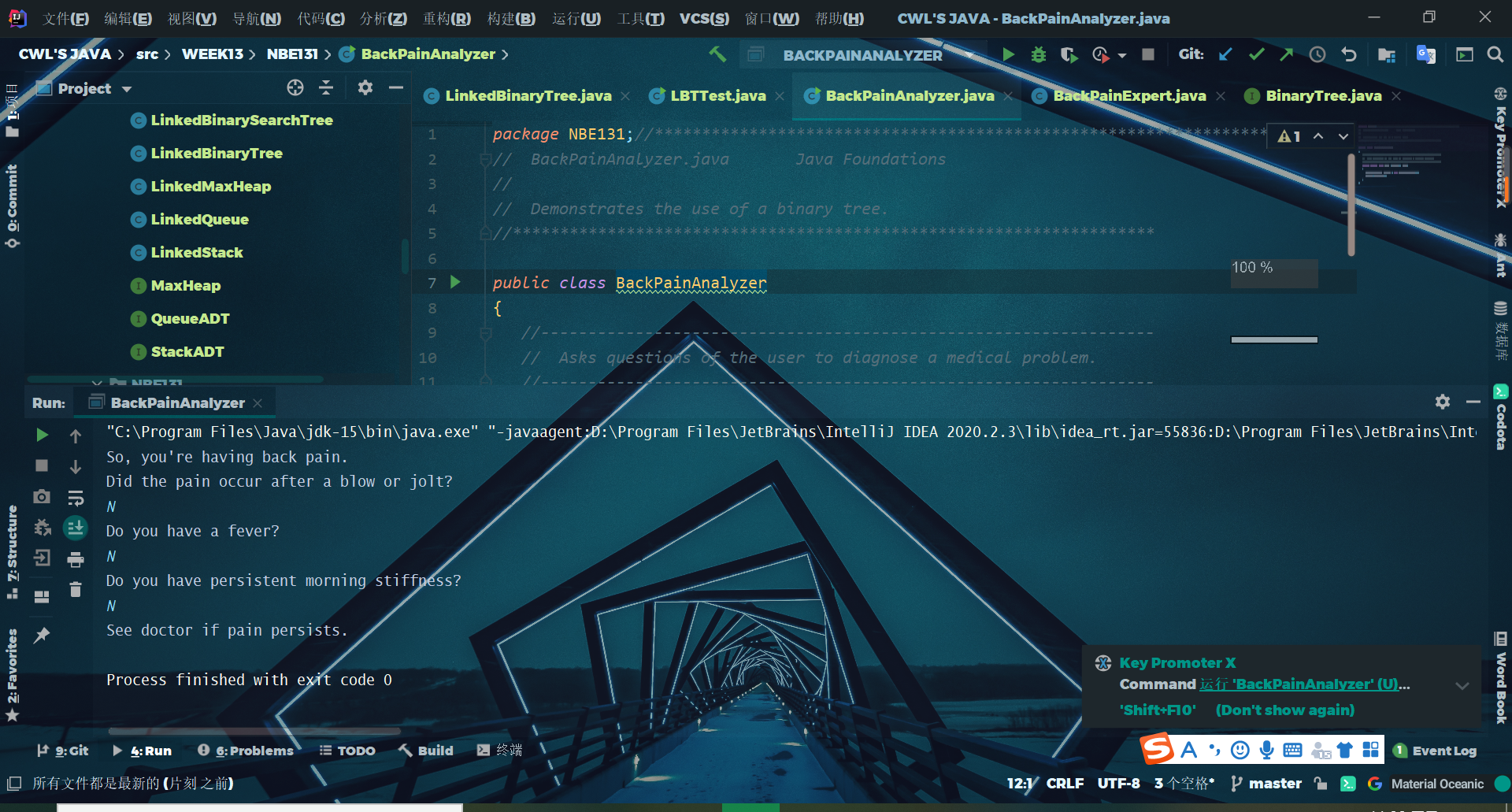
(四)输入中缀表达式,使用树将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
排序测试代码
package NBE131;/*
\* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
\* User: Shape Of My Heart
\* Date: 2020/12/4
\* Time: 9:02
\* Besides,some of the best things in life are total mistakes.
\* Description:
\**/
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @author Shape Of My Heart
*/
public class Fix {
static Stack<Character> op = new Stack<>();
public static Float getv(char op, Float f1, Float f2) {
if (op == '+') {
return f2 + f1;
} else if (op == '-') {
return f2 - f1;
} else if (op == '*') {
return f2 * f1;
} else if (op == '/') {
return f2 / f1;
} else {
return (float) -0;
}
}
public static float calrp(String rp) {
Stack<Float> v = new Stack<>();
char[] arr = rp.toCharArray();
for (char ch : arr) {
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
v.push((float) (ch - '0'));
} else {
v.push(getv(ch, v.pop(), v.pop()));
}
}
return v.pop();
}
public static String getrp(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
StringBuilder out = new StringBuilder();
for (char ch : arr) {
if (ch == ' ') {
continue;
}
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
out.append(ch);
continue;
}
if (ch == '(') {
op.push(ch);
}
if (ch == '+' || ch == '-') {
while (!op.empty() && (op.peek() != '(')) {
out.append(op.pop());
}
op.push(ch);
continue;
}
if (ch == '*' || ch == '/') {
while (!op.empty() && (op.peek() == '*' || op.peek() == '/')) {
out.append(op.pop());
}
op.push(ch);
continue;
}
if (ch == ')') {
while (!op.empty() && op.peek() != '(') {
out.append(op.pop());
}
op.pop();
}
}
while (!op.empty()) {
out.append(op.pop());
}
return out.toString();
}
}
测试代码
package NBE131;/*
\* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
\* User: Shape Of My Heart
\* Date: 2020/12/4
\* Time: 9:05
\* Besides,some of the best things in life are total mistakes.
\* Description:
\**/
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Shape Of My Heart
*/
public class FixTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入表达式:");
String s = scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("后缀表达式为:\n"+Fix.getrp(s));
System.out.println("计算结果为:\n"+ Fix.calrp(Fix.getrp(s)));
}
}
运行结果截图
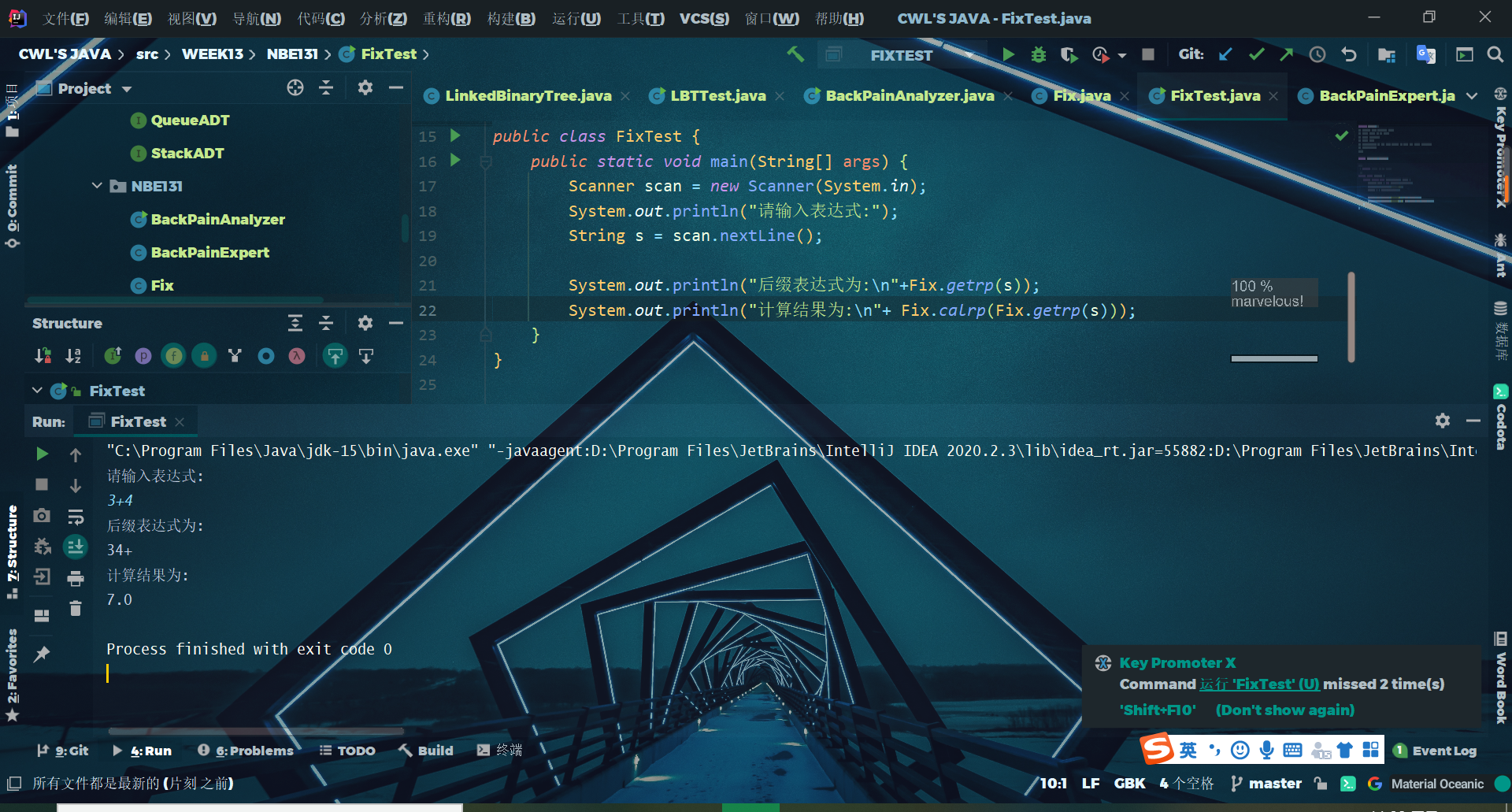
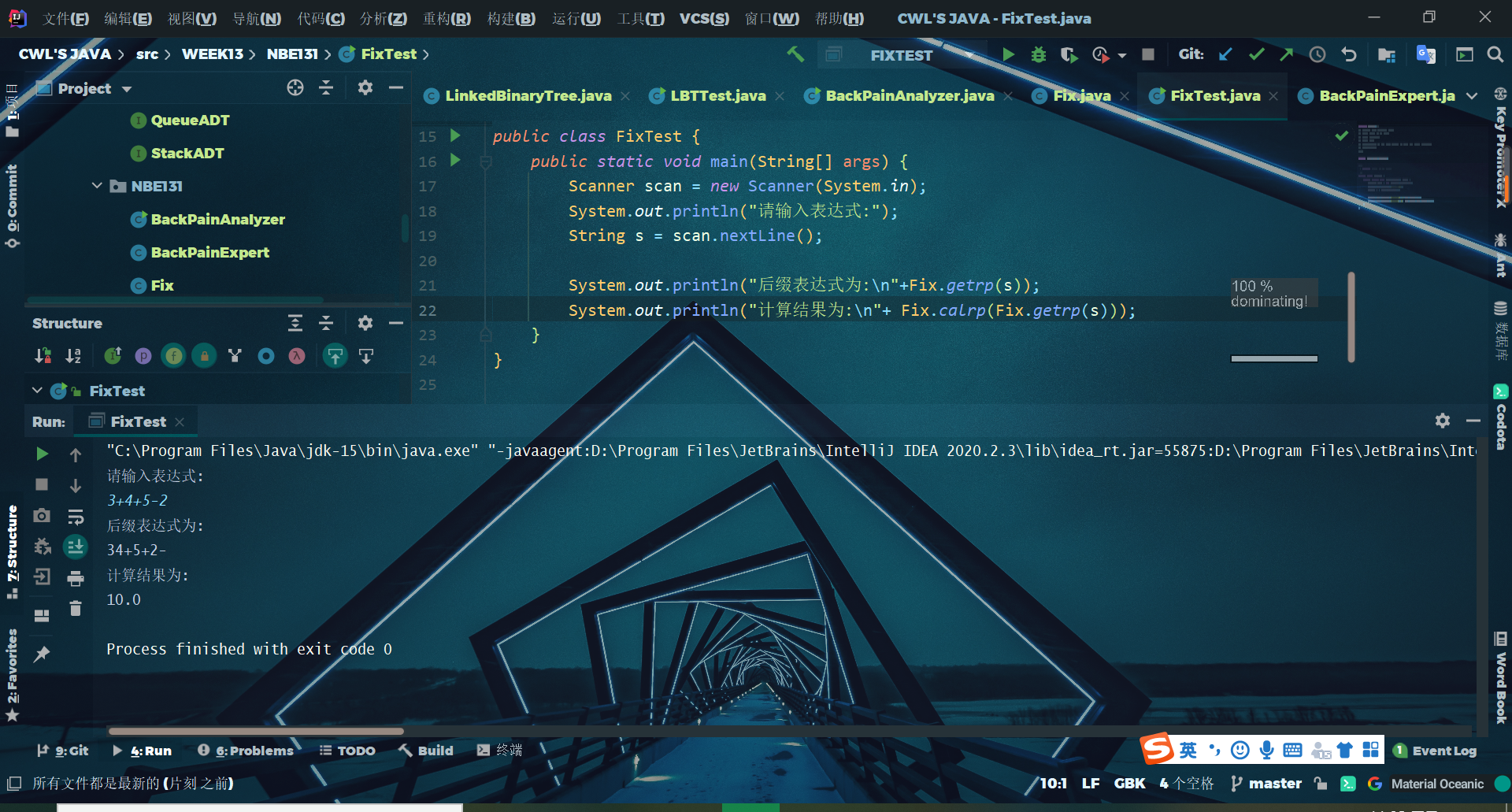
(五)码云仓库地址
三、心得体会
- 在这次实验过程中,我遇到了许多问题,其中既有知识上的漏洞,也有不细心导致的马虎,这一切都补充,完善,丰富,扩展了我的计算机知识体系。在不断修复问题的过程中,我使用了很多方式去查询资料,例如:《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》,博客园平台,CSDN平台,码云平台,知乎app,等。进一步熟悉了Android studio这个平台的使用与运行方式,提高了自己自主学习的能力,为我接下来学习数据结构以及JAVA语言程序设计打下了坚实的基础,并在不断探索的过程中逐步提升了自己。
四、参考资料
- 《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》
- [《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》学习指导]



