03-树2 List Leaves (25 分)
03-树2 List Leaves (25 分)
Given a tree, you are supposed to list all the leaves in the order of top down, and left to right.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in the tree -- and hence the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1. Then N lines follow, each corresponds to a node, and gives the indices of the left and right children of the node. If the child does not exist, a "-" will be put at the position. Any pair of children are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line all the leaves' indices in the order of top down, and left to right. There must be exactly one space between any adjacent numbers, and no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8 1 - - - 0 - 2 7 - - - - 5 - 4 6
Sample Output:
4 1 5
主要思路:
数据结构:静态数组结点,每一个结点保存着左右节点的序号;
数据操作:
一、构建树,返回根结点序号;
二、层序遍历树:使用队列保存结点;
C语言代码实现:
#include <stdlib.h> #define MAXSIZE 10 #define Null -1 typedef int Tree; typedef struct TreeNode TreeList; struct TreeNode{ int left; int right; int flag; }T[MAXSIZE]; int isFirst = 1; #define ERROR -1 typedef int ElemType; typedef int Position; typedef struct QNode* Queue; typedef struct QNode{ ElemType*data; Position front; Position rear; int maxSize; }; Queue CreateQueue(int maxSize){ Queue Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(struct QNode)); Q->data = (ElemType*)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*maxSize); Q->front = 0; Q->rear = 0; Q->maxSize = maxSize; return Q; } void DestroyQueue(Queue Q) { if (Q) { if(Q->data){ free(Q->data); } free(Q); } } int IsFullQueue(Queue Q){ return (Q->front == (Q->rear + 1) % Q->maxSize); } void Enqueue(Queue Q, ElemType item) { if (IsFullQueue(Q)) { return; } Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % Q->maxSize; Q->data[Q->rear] = item; } int IsEmptyQueue(Queue Q){ return ( Q->front == Q->rear ); } ElemType Dequeue(Queue Q){ if (IsEmptyQueue(Q)){ return ERROR; } Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % Q->maxSize; return Q->data[Q->front]; } Tree BuildTree(int nSize){ int *check = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*nSize); for(int i = 0; i < nSize; i++){ check[i] = 0; } char l,r; for(int i = 0; i < nSize; i++){ scanf("%c %c\n", &l, &r); if(l == '-'){ T[i].left = Null; } else{ T[i].left = l - '0'; check[T[i].left] = 1; } if(r == '-'){ T[i].right = Null; } else{ T[i].right = r - '0'; check[T[i].right] = 1; } T[i].flag = 0; } int head = 0; for(int i = 0; i < nSize; i++){ if(check[i] == 0){ head = i; break; } } return head; } void Print(int i){ if(isFirst){ printf("%d", i); isFirst = 0; } else{ printf(" %d", i); } } //层序遍历 BFS void LevelTraverse(Tree root, int nSize){ Queue Q = CreateQueue(nSize+1); Enqueue(Q, root); do{ Tree parent = Dequeue(Q); if(T[parent].left == Null && T[parent].right == Null){ Print(parent); } if(T[parent].left != Null){ Enqueue(Q, T[parent].left); } if(T[parent].right != Null){ Enqueue(Q, T[parent].right); } }while(!IsEmptyQueue(Q)); } int main(){ int N; scanf("%d\n", &N); Tree root = BuildTree(N); LevelTraverse(root, N); return 0; }
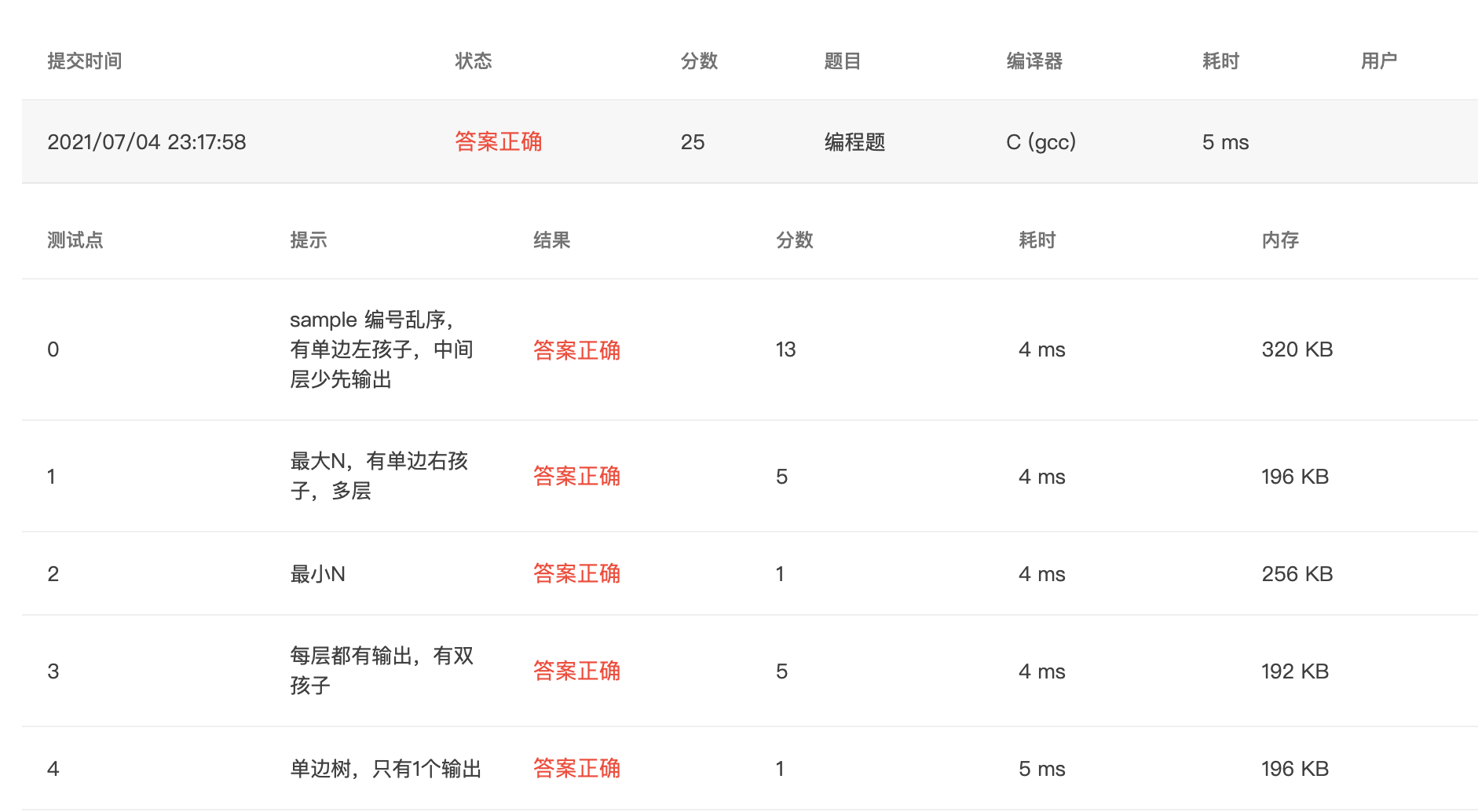
提交结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号