第四周课程总结&实验报告
一、实验目的
(1) 掌握类的定义,熟悉属性、构造函数、方法的作用,掌握用类作为类型声明变量和方法返回值;
(2) 理解类和对象的区别,掌握构造函数的使用,熟悉通过对象名引用实例的方法和属性;
(3) 理解static修饰付对类、类成员变量及类方法的影响。
二、实验内容
- 写一个名为Rectangle的类表示矩形。其属性包括宽width、高height和颜色color,width和height都是double型的,而color则是String类型的。
要求该类具有:
(1) 使用构造函数完成各属性的初始赋值
(2) 使用get…()和set…()的形式完成属性的访问及修改
(3) 提供计算面积的getArea()方法和计算周长的getLength()方法
Rectangle
package test;
public class Rectangle {
private double width;
private double height;
private String color;
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Rectangle (double width, double height, String color) {
this.setColor(color);
this.setHeight(height);
this.setWidth(width);
}
public void getArea(){
double area = 0;
area = this.height*this.width;
System.out.println("矩形的面积为:"+area);
}
public void getZhouchang() {
double Zhouchang = 0;
Zhouchang = this.height + this.width;
System.out.println("矩形的周长为:"+Zhouchang);
}
public void getYanse() {
String Yanse = "red";
System.out.println("矩形的颜色为:"+Yanse);
}
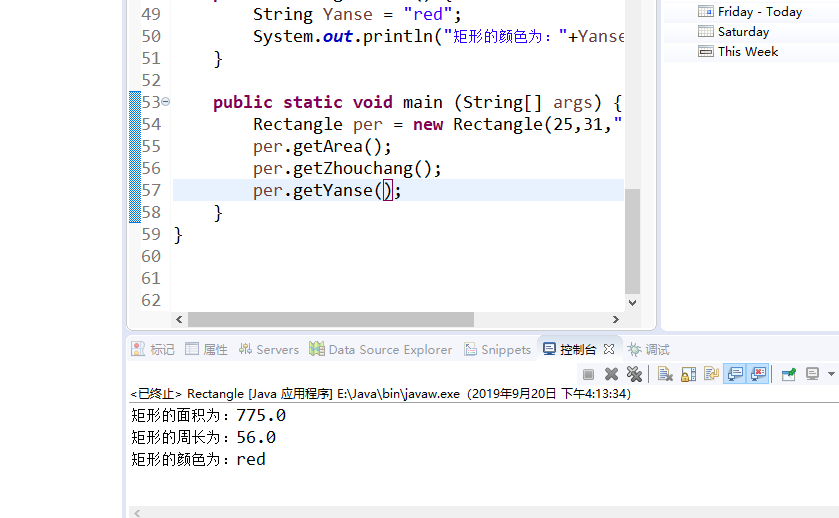
public static void main (String[] args) {
Rectangle per = new Rectangle(25,31,"red");
per.getArea();
per.getZhouchang();
per.getYanse();
}
}
- 银行的账户记录Account有账户的唯一性标识(11个长度的字符和数字的组合),用户的姓名,开户日期,账户密码(六位的数字,可以用0开头),当前的余额。
银行规定新开一个账户时,银行方面提供一个标识符、账户初始密码123456,客户提供姓名,开户时客户可以直接存入一笔初始账户金额,
不提供时初始余额为0。定义该类,并要求该类提供如下方法:存款、取款、变更密码、可以分别查询账户的标识、姓名、开户日期、当前余额等信息。
Bank
package test;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Bank {
private String id;
private String name;
private Date createTime;
private String code;
private double balance;
public Bank(String id, String name, double balance) {
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
this.balance=balance;
this.createTime=new Date();
this.code="123456";
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
this.balance+=balance;
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
this.balance-=amount;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date time) {
createTime = time;
}
public void changecode() {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入新密码:");
String code = sc.nextLine();
this.code = code;
sc.close();
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
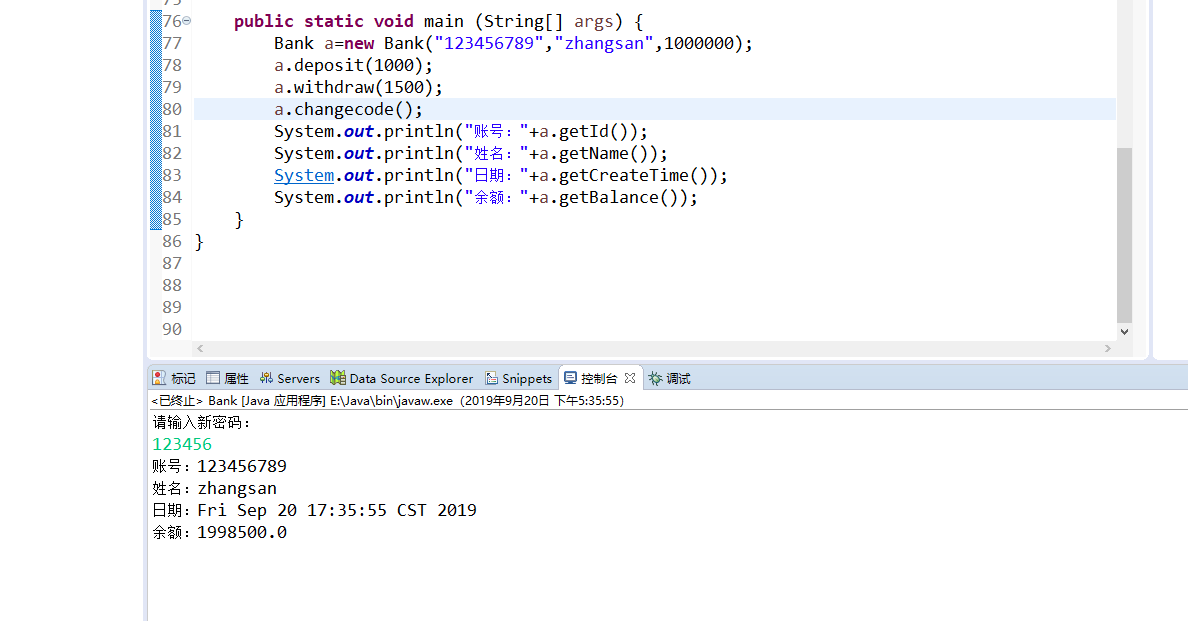
public static void main (String[] args) {
Bank a=new Bank("123456789","zhangsan",1000000);
a.deposit(1000);
a.withdraw(1500);
a.changecode();
System.out.println("账号:"+a.getId());
System.out.println("姓名:"+a.getName());
System.out.println("日期:"+a.getCreateTime());
System.out.println("余额:"+a.getBalance());
}
}
学习总结
*学习了一些String类常用操作方法。
(1).字符串的连接
public String concat(String str)
该方法的参数为一个String类对象,作用是将参数中的字符串str连接到原来字符串的后面.
(2).求字符串的长度
public int length()
返回字串的长度,这里的长度指的是字符串中Unicode字符的数目.
(3).求字符串中某一位置的字符
public char charAt(int index)
该方法在一个特定的位置索引一个字符串,以得到字符串中指定位置的字符.值得注意的是,在字符串中第一个字符的索引是0,第二个字符的索引是1,依次类推,最后一个字符的索引是length()-1.
(4).public boolean equals(Object anObject)
该方法比较两个字符串,和Character类提供的equals方法相似,因为它们都是重载Object类的方法.该方法比较当前字符串和参数字符串,在两个字符串相等的时候返回true,否则返回false.
(5).public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
该方法和equals方法相似,不同的地方在于,equalsIgnoreCase方法将忽略字母大小写的区别.
(6).public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
该方法从当前字符串中取出一个子串,该子串从beginIndex位置起至endIndex-1为结束.子串返的长度为endIndex-beginIndex.
(7).public int indexOf(int ch)
该方法用于查找当前字符串中某一个特定字符ch出现的位置.该方法从头向后查找,如果在字符串中找到字符ch,则返回字符ch在字符串中第一次出现的位置;如果在整个字符串中没有找到字符ch,则返回-1.
(8).public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
该方法和第一种方法类似,不同的地方在于,该方法从fromIndex位置向后查找,返回的仍然是字符ch在字符串第一次出现的位置. 等等
*包的概念
包是使用多个类或接口时,为了避免名称重复而采用的一种措施。
包的主要目的时实现程序的分割保存,这样既便于开发且方便维护。



