实验四Android程序设计
实验四《安卓开发基础》一:
1.实验要求:
Android Stuidio的安装测试: 参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十四章:
(1) 参考http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6371315.html#SECANDROID,安装 Android Stuidio;
(2) 完成Hello World, 要求修改res目录中的内容,Hello World后要显示自己的学号,自己学号前后一名同学的学号,提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图没有学号要扣分;
(3)学习Android Stuidio调试应用程序。
实验步骤:
1.下载安装Android Studio,参考老师的博客(http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6824965.html)安装即可。
2.配置和启动模拟器:
(1)启动虚拟机:
(2)新建虚拟机:
选择虚拟机的尺寸:
选择虚拟机系统的版本:
下载一波SDK(我之前没装):
之后完成
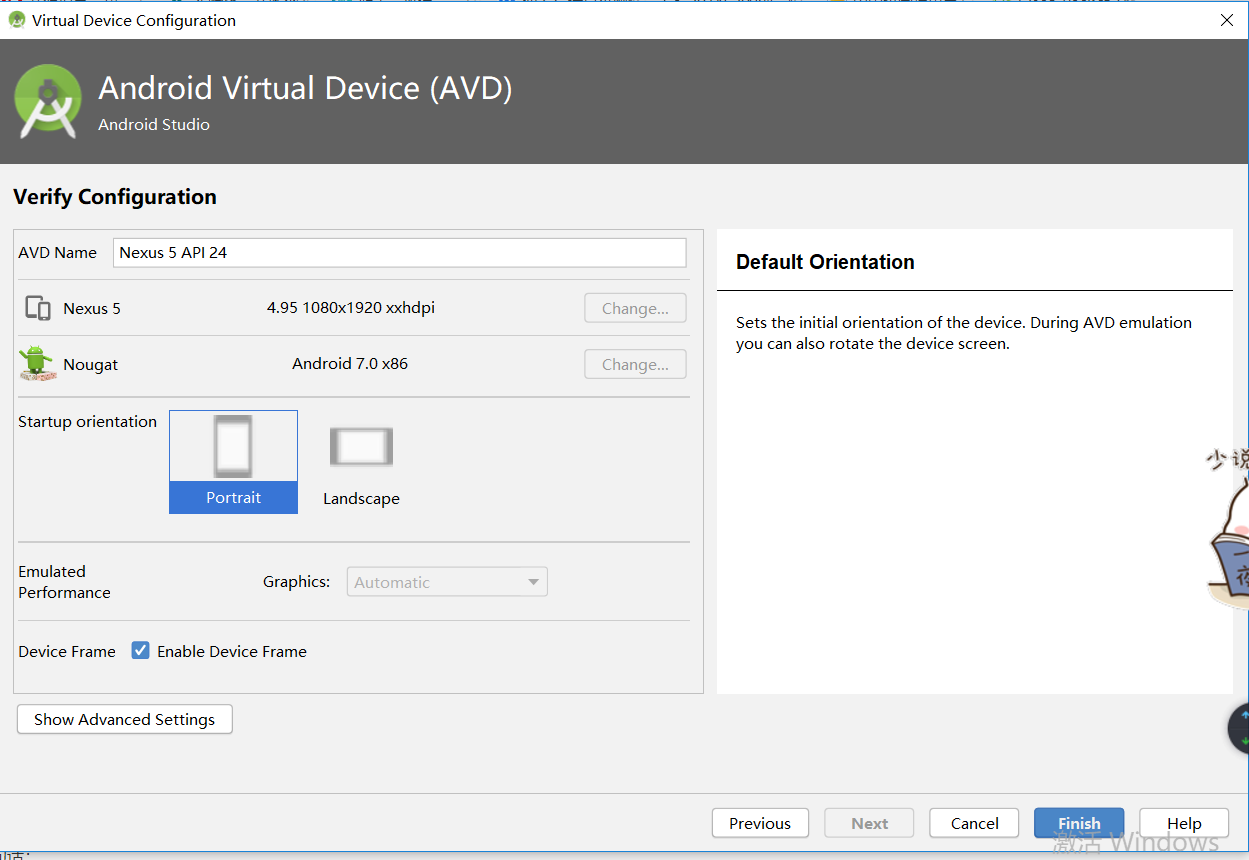
点击绿色箭头按钮启动:
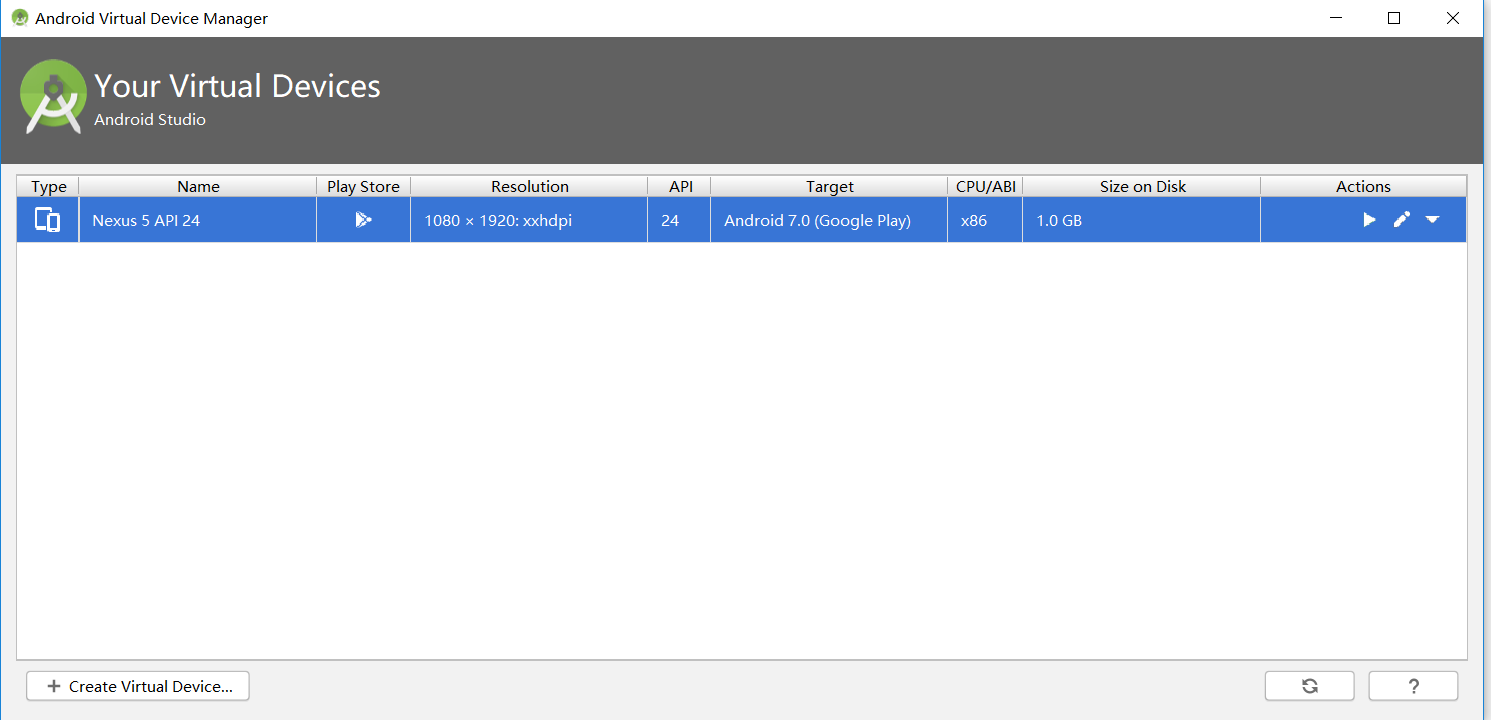
(3)编译项目并运行
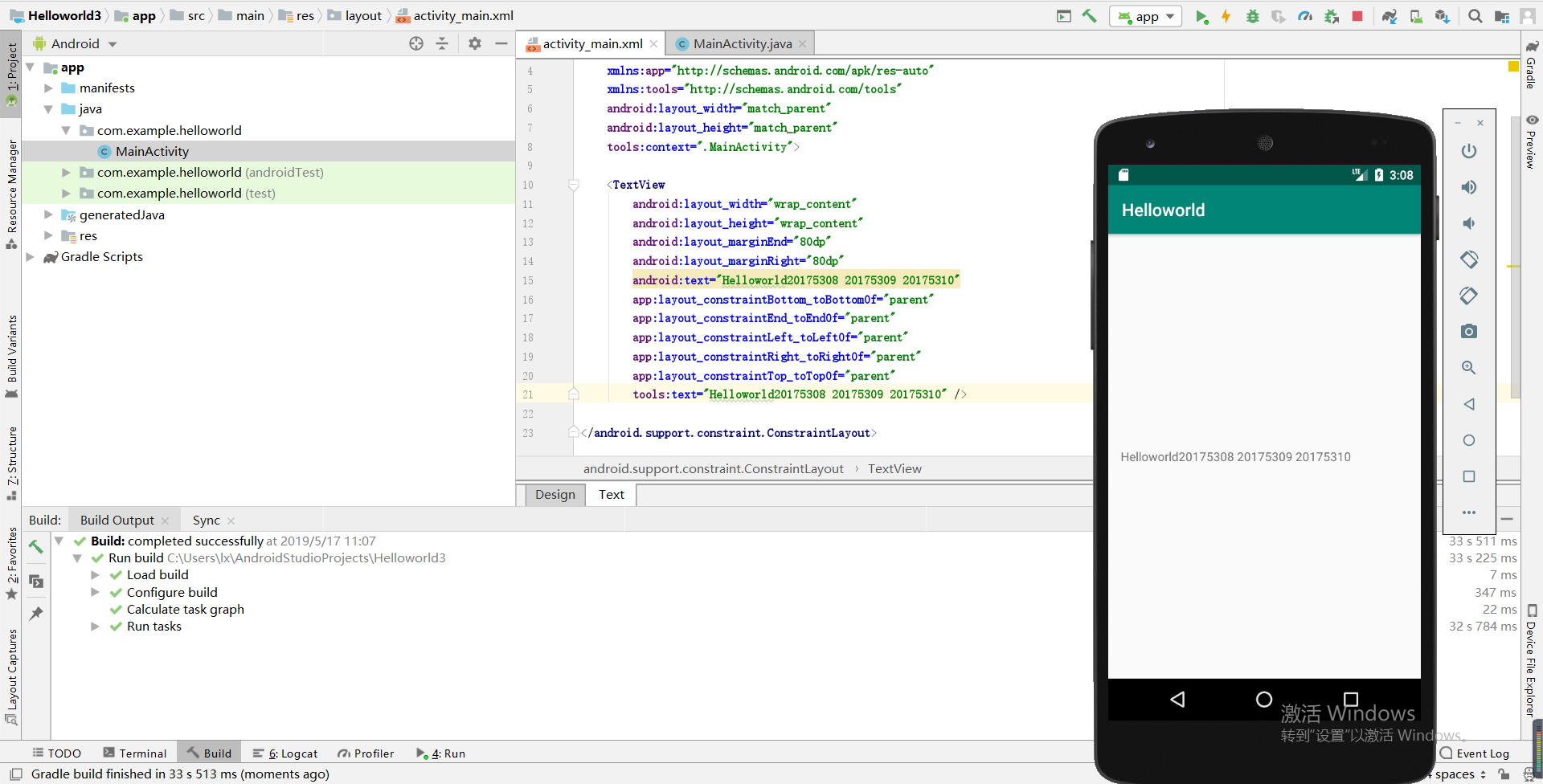
HelloWorld系统自带,修改res中的layout中的activity_main.xml的代码即可。
代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="80dp"
android:layout_marginRight="80dp"
android:text="Hello 20175308 20175309 20175310"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
tools:text="Hello World!20175308 20175309 20175310" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
效果:
实验四《安卓开发基础》二:
1.实验要求:
Activity测试: 参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十五章:
(1)构建项目,运行教材相关代码;
(2)创建 ThirdActivity, 在ThirdActivity中显示自己的学号,修改代码让MainActivity启动ThirdActivity;
(3)提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分。
2.实验步骤:
(1)在activity_main.xml里新加一段代码,总代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="启动另一个activity"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="80dp"
android:layout_marginRight="80dp"
android:text="Hello 20175308 20175309 20175310"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
tools:text="Hello World!20175308 20175309 20175310" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
(2)在MainActivity.class中新加代码创建intent对象,代码:
package com.example.helloworld;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button button1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
button1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(
MainActivity.this, SecondActivityDemo.class); // 创建一个Intent对象
startActivity(intent);
}
})
;}
}
(3)新建活动SecondActivityDemo
建完之后文档下多了两个文件:SecondActivityDemo.class与activity_second_Demo
相应代码如下:
SecondActivityDemo.class
package com.example.helloworld;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class SecondActivityDemo extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_second_demo);
}
}
activity_second_Demo
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="184dp"
android:layout_height="154dp"
android:text="20175105"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="153dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="311dp"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
(4)在app下的manifests下的AndroidMainfest.xml注册:
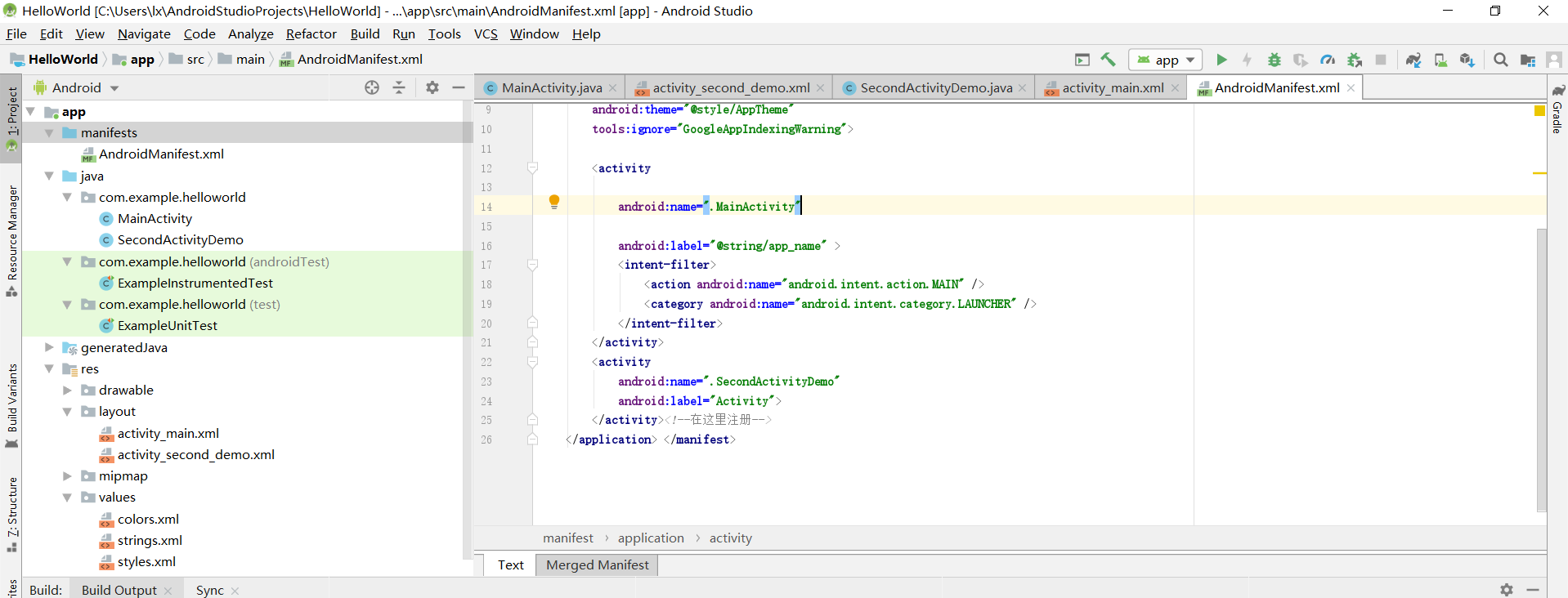
代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
package="com.example.helloworld" >
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme"
tools:ignore="GoogleAppIndexingWarning">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name=".SecondActivityDemo"
android:label="Activity">
</activity><!--在这里注册-->
</application> </manifest>
(5)运行结果截图:
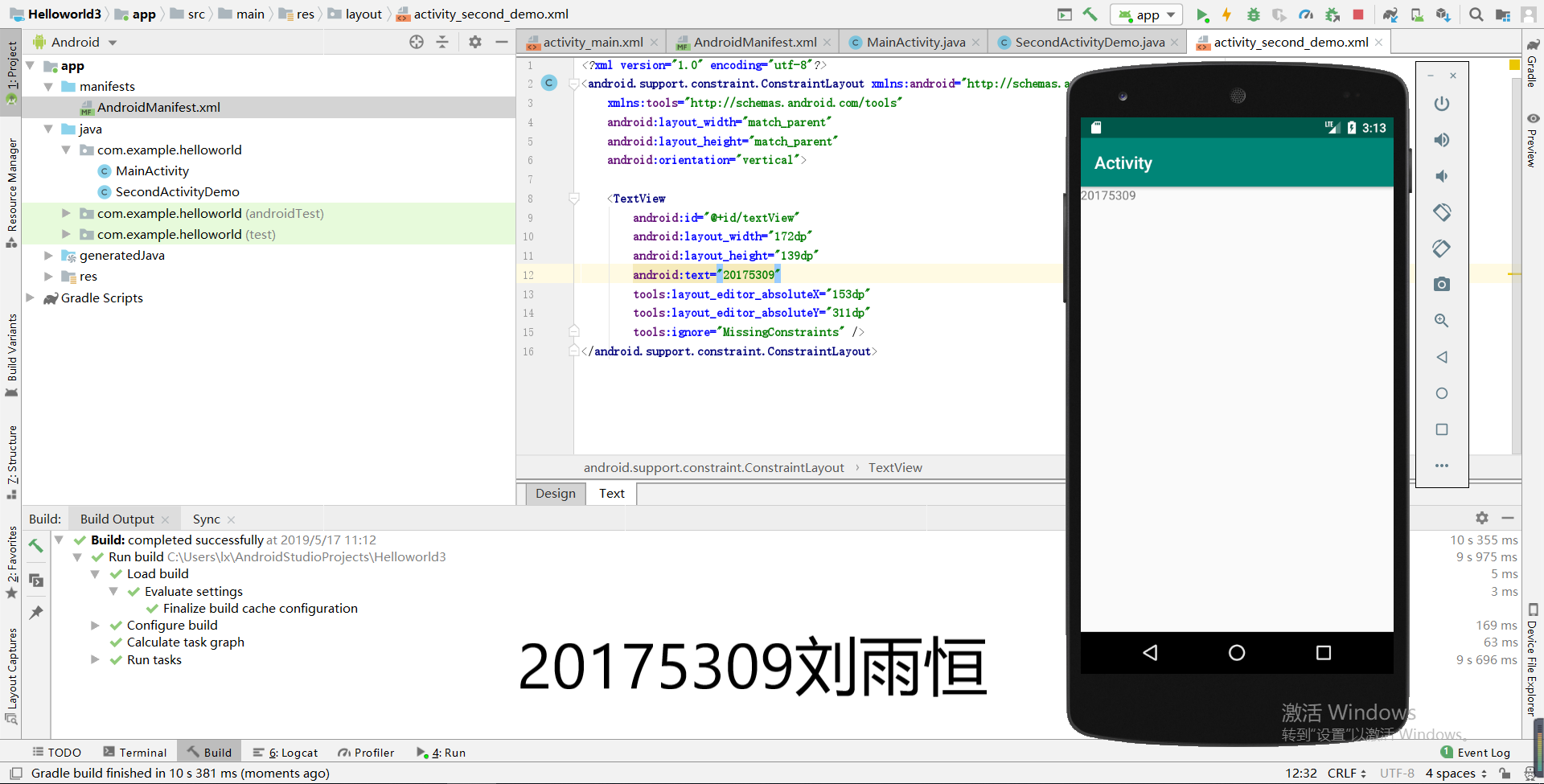
实验四《安卓开发基础》三:
1.实验要求:
UI测试: 参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十六章:
(1)构建项目,运行教材相关代码;
(2)修改代码让Toast消息中显示自己的学号信息;
(3)提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分。
2.实验步骤:
(1)对MainActivity.java中的代码进行修改:
①引入方法import android.widget.Toast;
②快速调用Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "20175309!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
代码如下:
package com.example.helloworld;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button button1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "20175309!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
button1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(
MainActivity.this, SecondActivityDemo.class); // 创建一个Intent对象
startActivity(intent);
}
})
;}
}
(2)效果截图:
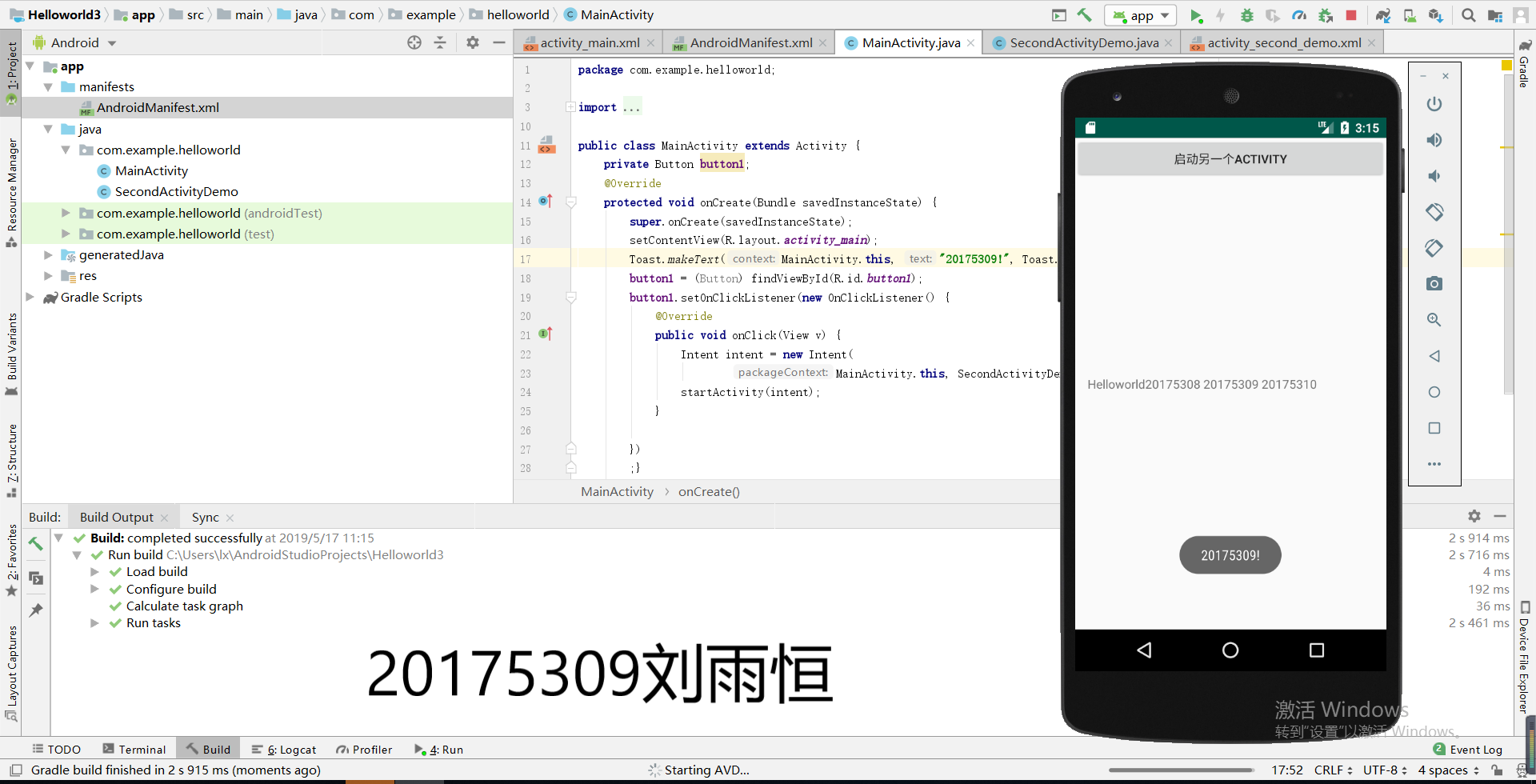
实验四《安卓开发基础》四:
1.实验要求:
布局测试: 参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十七章:
(1)构建项目,运行教材相关代码;
(2)修改布局让P290页的界面与教材不同;
(3)提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分。
2.实验步骤:
(1)本来改代码改的比较头痛,在同学的帮助下,提醒我直接手动操作
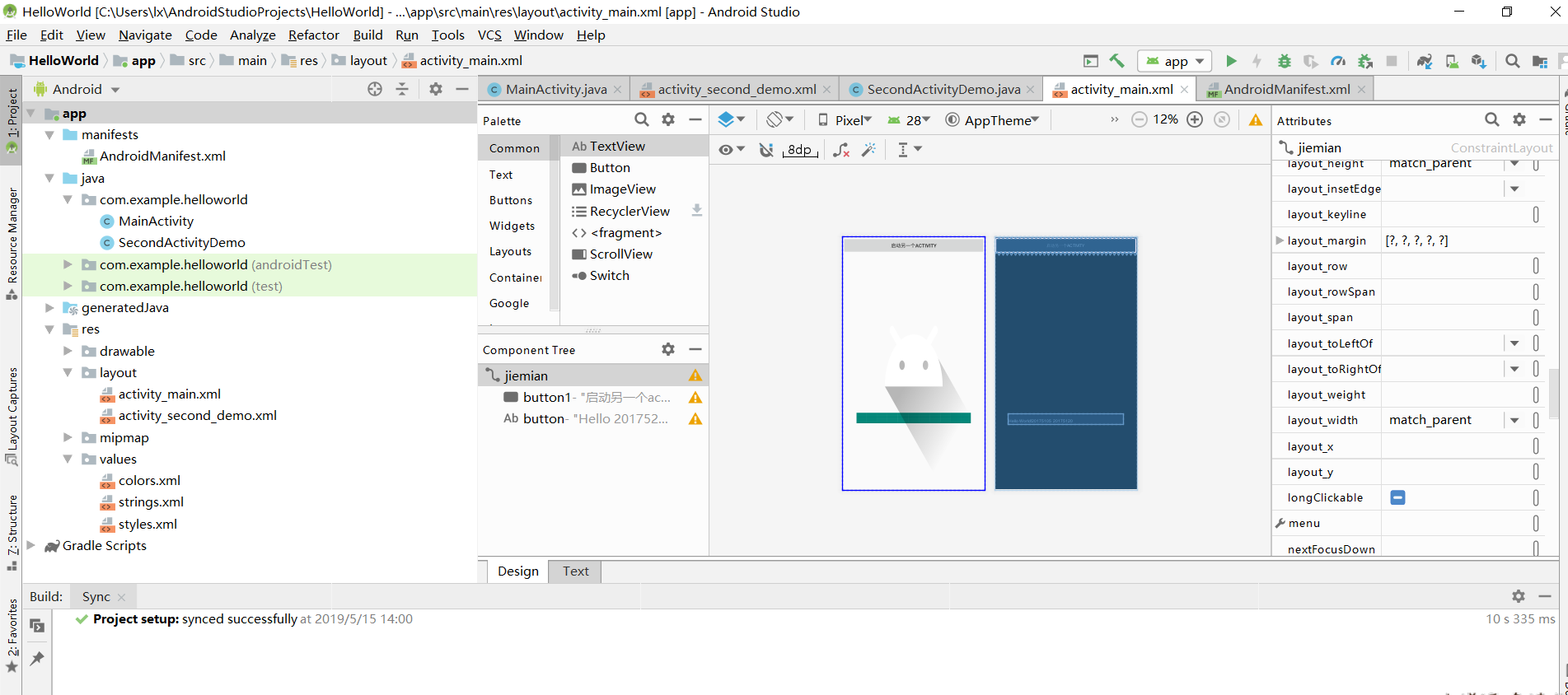
(2)效果截图:
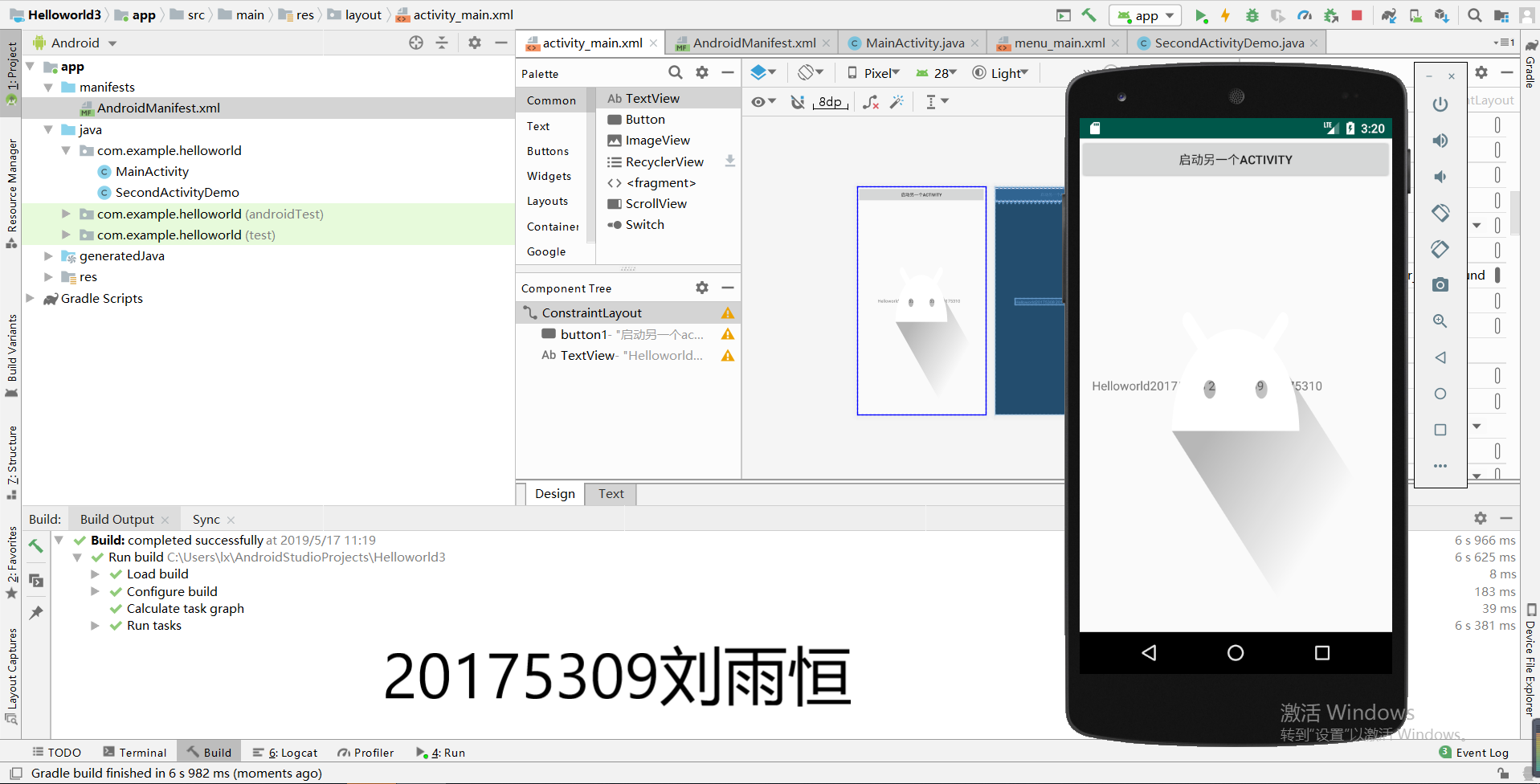
实验四《安卓开发基础》五:
1.实验要求:
事件处理测试: 参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十八章:
(1)构建项目,运行教材相关代码;
(2)提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分。
2.实验步骤:
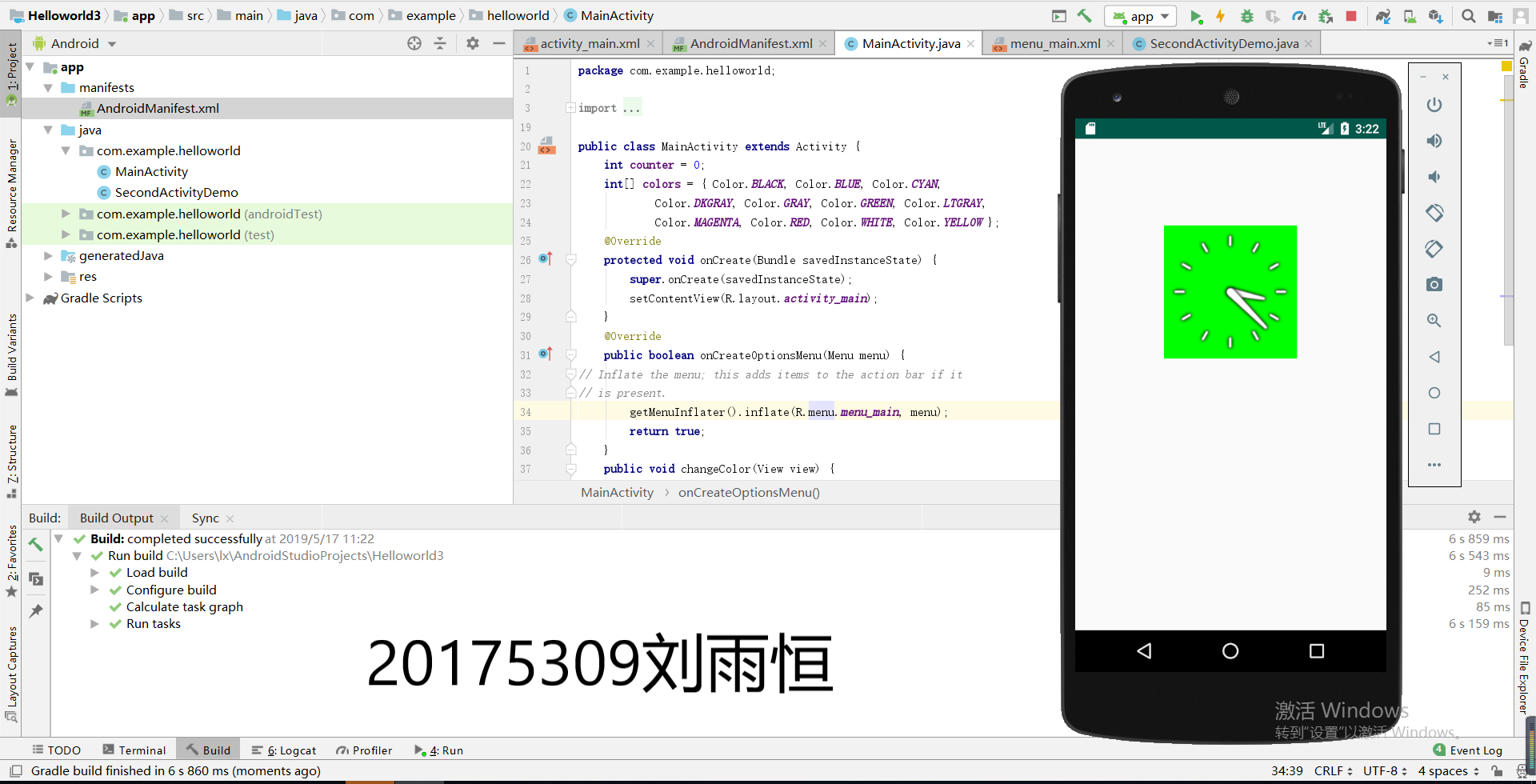
功能描述------在点击屏幕后,时钟背景颜色发生改变
(1)改写MainActivity下的代码如下:
package com.example.helloworld;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AnalogClock;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AnalogClock;
import com.example.helloworld.R;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
int counter = 0;
int[] colors = { Color.BLACK, Color.BLUE, Color.CYAN,
Color.DKGRAY, Color.GRAY, Color.GREEN, Color.LTGRAY,
Color.MAGENTA, Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.YELLOW };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it
// is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
public void changeColor(View view) {
if (counter == colors.length) {
counter = 0;
}
view.setBackgroundColor(colors[counter++]);
}
}
(2)改写activity_main下的代码如下:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="10dp"
android:paddingLeft="10dp"
android:paddingRight="10dp"
android:paddingTop="10dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/analogClock1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="90dp"
android:onClick="changeColor"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
运行效果截图:
码云链接
实验感想:
一直用手机都是iOS系统的,对安卓了解不是很深,只是单纯的觉得安卓开发的平台很开放,现在一看的确,连我这样的都可以试一试,这使我对安卓开发产生了浓厚的兴趣。
话说,我特好奇IOS开发的过程到底是什么样,因为IOS上应用除了从app store下载之外就很难使用了,无法上架的应用即便能使用一阵子之后也会不合格,所以特别好奇IOS的开发会不会比安卓难很多。




