2018-2019-2 20175211 实验四《Android程序设计》实验报告
一、实验内容及步骤
1、Android Studio的安装测试
- 要求:
- 参考http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6371315.html#SECANDROID,安装 Android Stuidio
- 完成Hello World, 要求修改res目录中的内容,Hello World后要显示自己的学号,自己学号前后一名同学的学号,提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图没有学号要扣分
- 学习Android Stuidio调试应用程序
安装Android Studio
- 从官网上下载,一步一步跟着安装就行了
- 点击下图标志配置虚拟手机来测试代码

Android基础知识(参考:Android Developer Docs)
-
应用组件是 Android 应用的基本构建基块。每个组件都是一个不同的点,系统可以通过它进入您的应用。共有四种不同的应用组件类型
- Activity 表示具有用户界面的单一屏幕
- Services 服务是一种在后台运行的组件,用于执行长时间运行的操作或为远程进程执行作业
- Broadcast receivers 内容提供程序管理一组共享的应用数据
- Content providers 广播接收器是一种用于响应系统范围广播通知的组件
-
启动组件
四种组件类型中的三种 — Activity、服务和广播接收器 — 通过名为 Intent 的异步消息进行启动。Intent 会在运行时将各个组件相互绑定(您可以将 Intent 视为从其他组件请求操作的信使),无论组件属于您的应用还是其他应用。 -
清单文件
在 Android 系统启动应用组件之前,系统必须通过读取应用的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件(“清单”文件)确认组件存在。 您的应用必须在此文件中声明其所有组件,该文件必须位于应用项目目录的根目录中。
Android Studio基本使用(参考:项目概览)
Android Studio界面和Idea基本一致,左侧是项目的文件结构目录

我们主要使用的文件在app目录下
- manifests
存放清单文件 - java
存放java代码,我们编写的代码放在第一个文件夹下 - res
存放各种资源,基本上是xml文件

修改代码
要输出我们自己的学号可以直接去res->layout->activity_main.xml修改。创建项目的时候,默认有一个居中的TextView组件,内容是helloworld,我们增加自己的文本,结果如下
运行截图
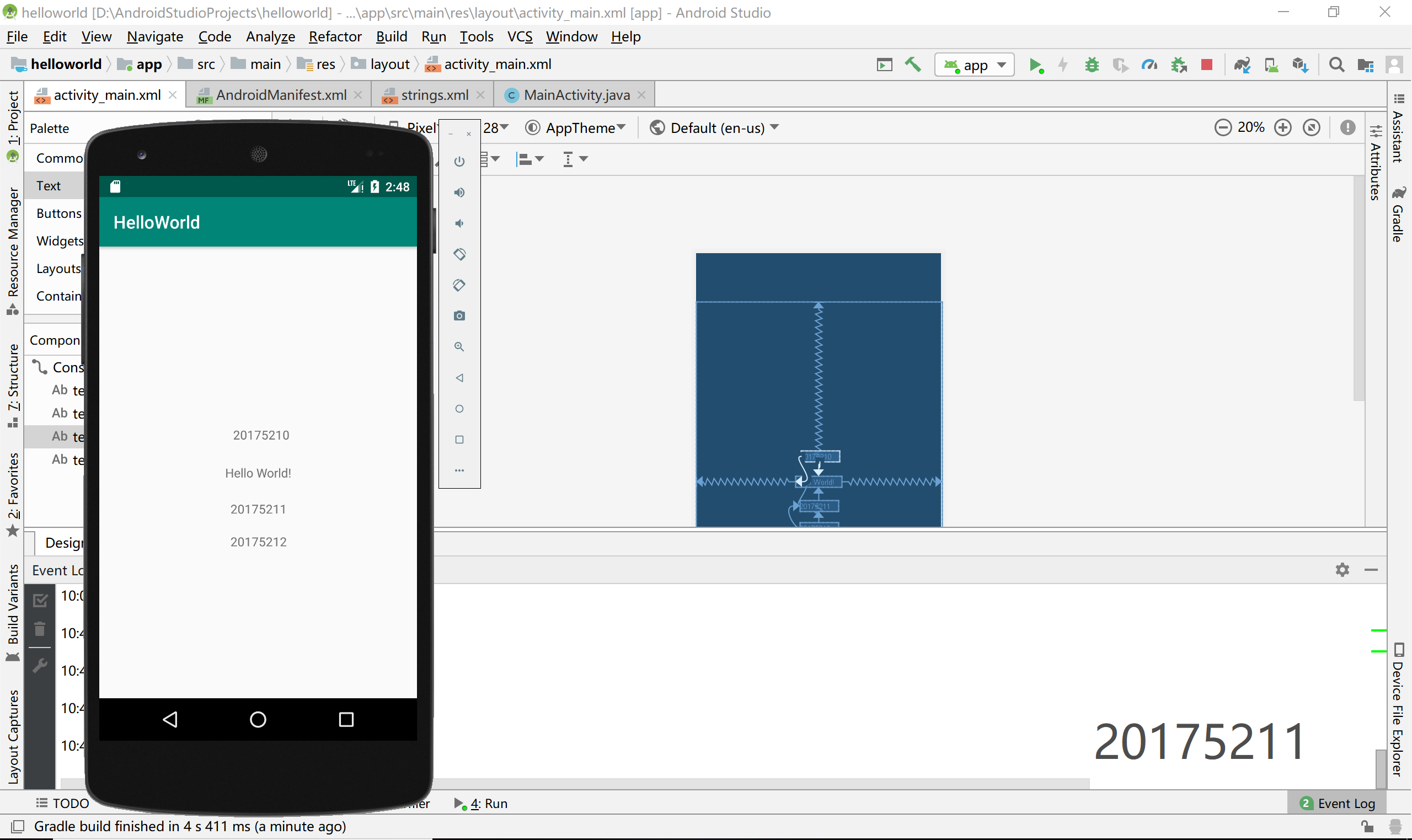
2、Activity测试
- 要求:
- 构建项目,运行教材相关代码
- 创建 ThirdActivity, 在ThirdActivity中显示自己的学号,修改代码让MainActivity启动ThirdActivity
- 提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分
Activity基本知识(参考:Introduction to Activities)
- Activity生命周期
onCreate()在系统创建活动时触发。必须在此处调用setContentView()以定义活动用户界面的布局。onCreate()完成后,接下来回调的永远是onStart()onStart()onCreate()退出时,活动进入开始状态onResume()系统在活动开始与用户交互之前调用此回调。应用程序的大多数核心功能都是在该onResume()方法中实现的。onPause()当活动失去焦点并进入暂停状态时, 系统会调用。例如,当用户点击“后退”或“最近”按钮时,会出现此状''态。onStop()当活动不再对用户可见时, 系统会调用。onRestart()当处于“已停止”状态的活动即将重新启动时,系统将调用此回调onDestroy()系统在销毁活动之前调用此回调

- 声明activity
在清单文件中如下声明
<manifest ... >
<application ... >
<activity android:name=".ExampleActivity" />
...
</application ... >
...
</manifest >
MainActivity代码
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnTouchListener {
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView tv1 = findViewById(R.id.textView1);
tv1.setOnTouchListener(this);
TextView tv2 = findViewById(R.id.textView2);
tv2.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View arg0, MotionEvent event) {
if (arg0.getId()==(R.id.textView1)){
Intent intent = new Intent(this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
if (arg0.getId()==(R.id.textView2)){
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ThirdActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
return true;
}
}
TextView对象可以调用setOnTouchListener方法开启监听,当用户按下该对象时触发onTouch事件。用if语句判断用户触发的是哪个事件,跳转到不同的页面。
运行截图


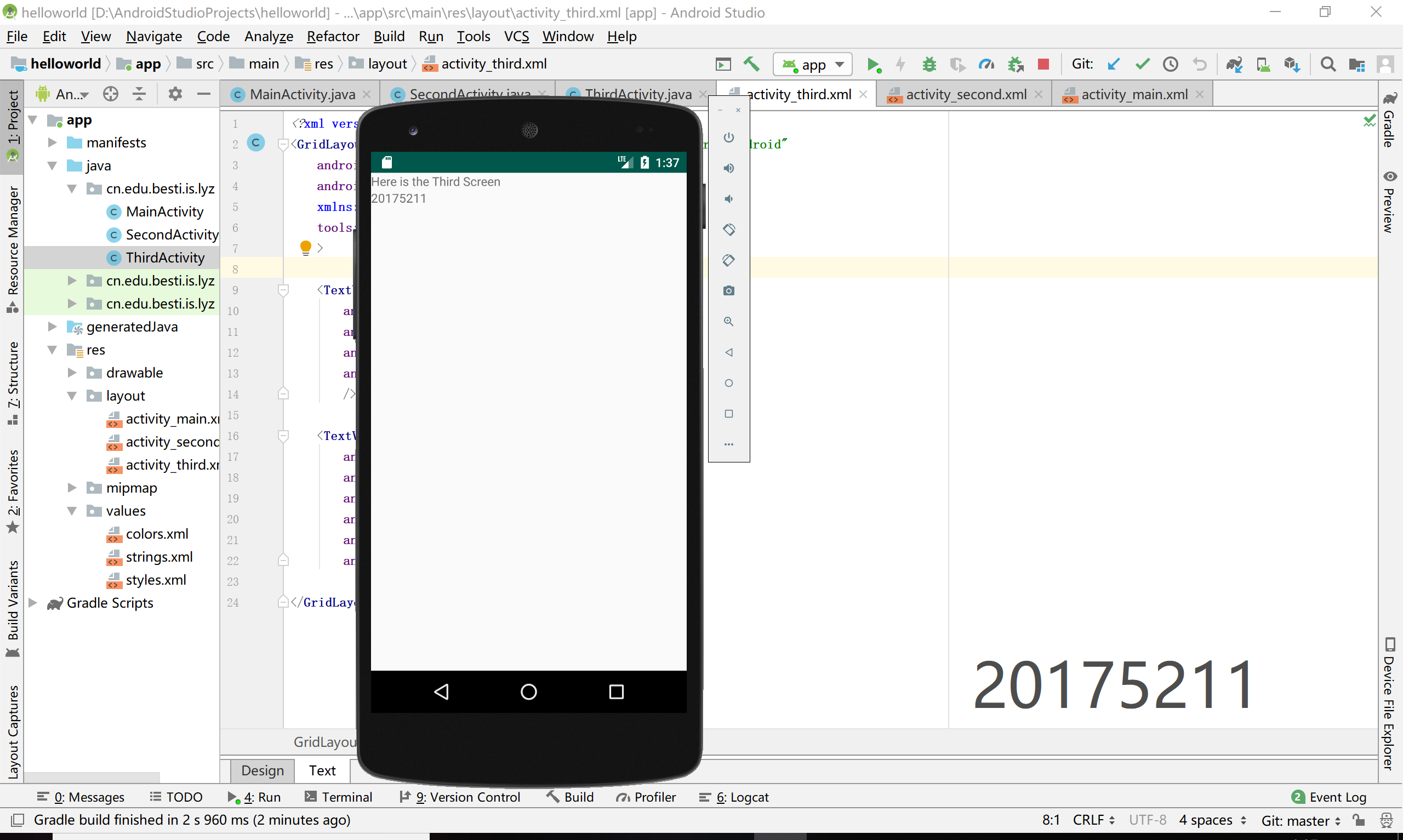
3、UI测试
- 要求:
- 修改代码让Toast消息中显示自己的学号信息
- 提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分
Toast基本知识
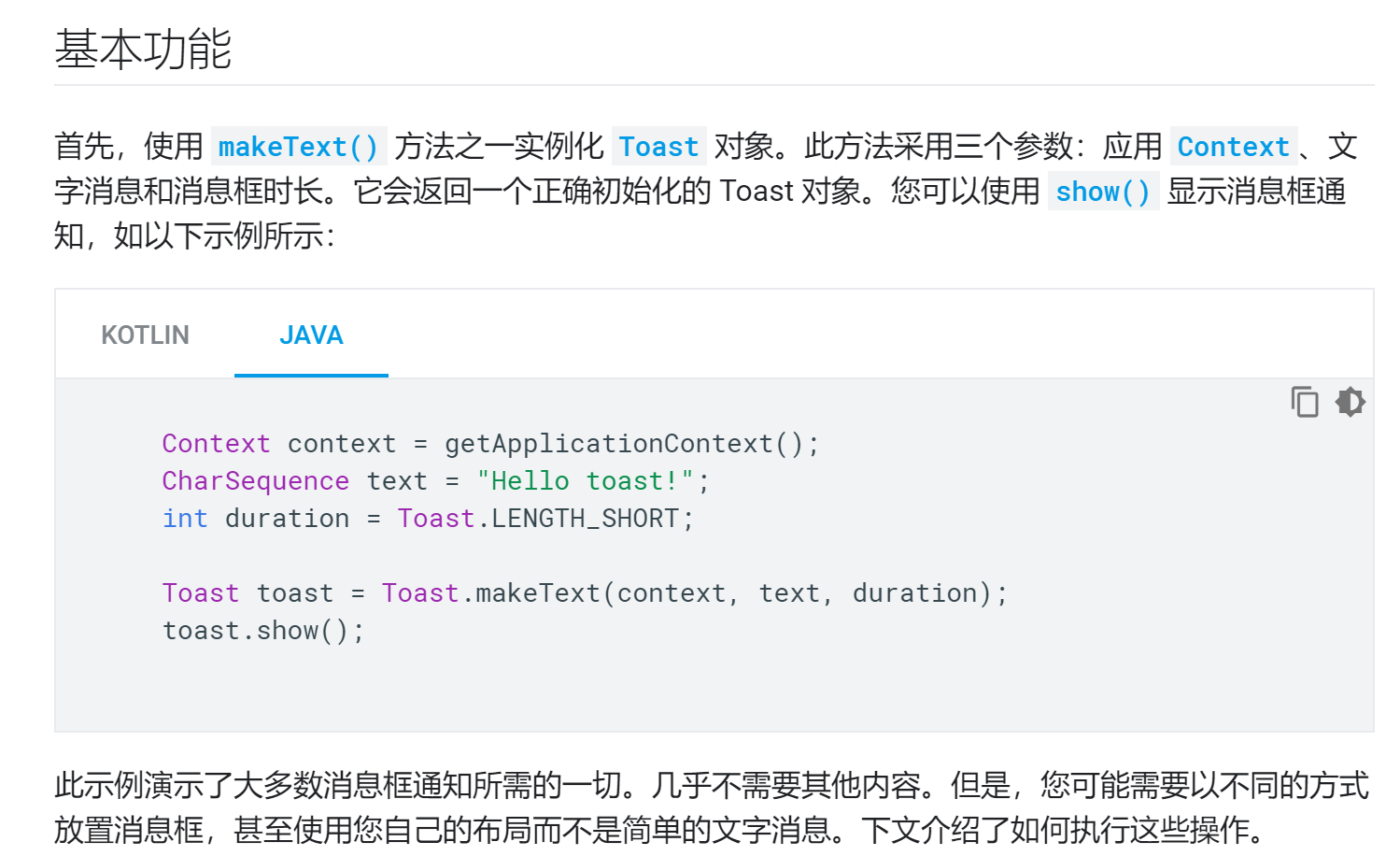
MainActivity代码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Context context = getApplicationContext();
CharSequence text = "I am ... 20175211(响指)!";
int duration = Toast.LENGTH_SHORT;
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(context, text, duration);
toast.show();
}
}
运行截图
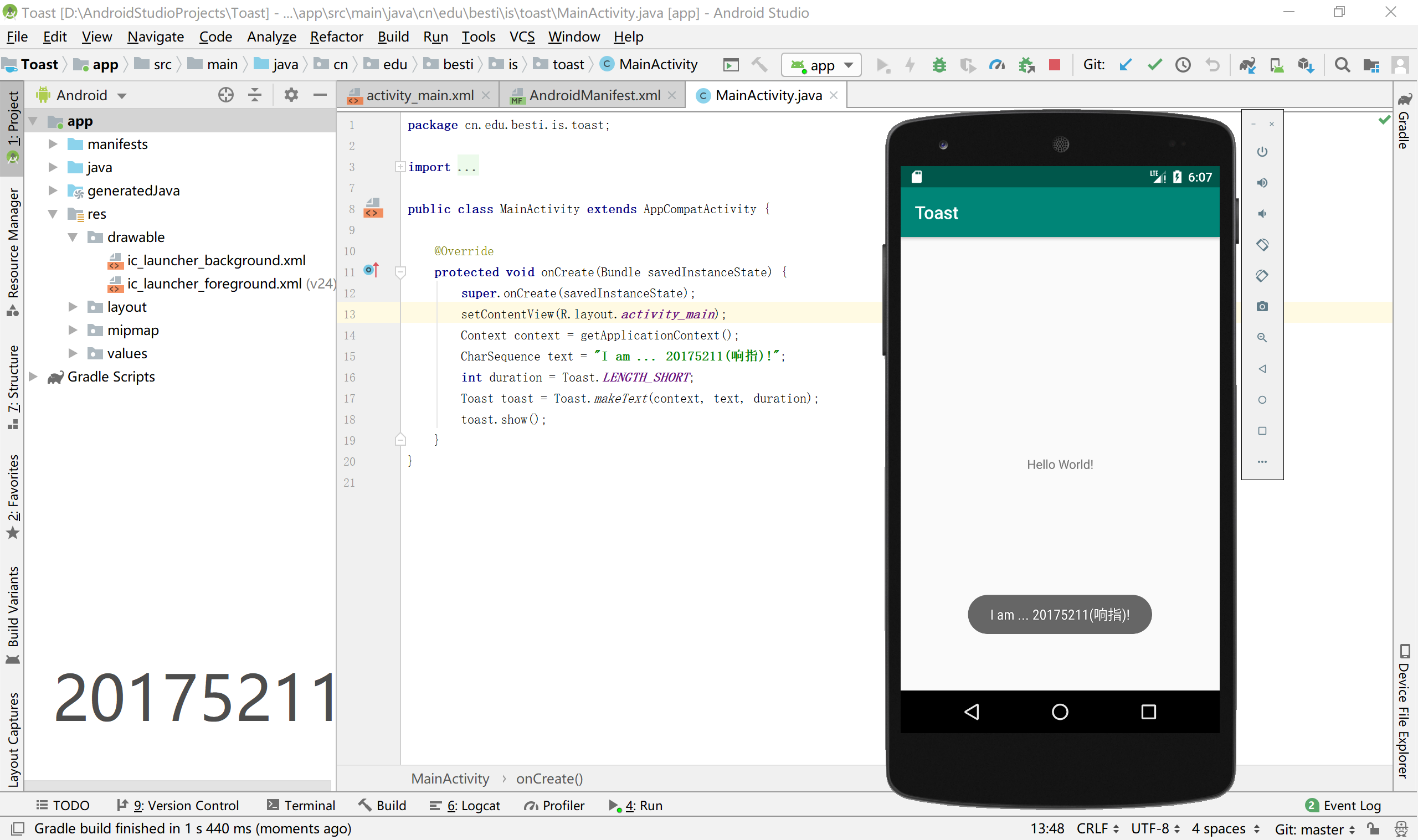
4、布局测试
- 要求
- 修改布局让P290页的界面与教材不同
- 提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分
Layout基本知识(参考:布局资源)
- 档案位置
res/layout/filename.xml
文件名将用作资源ID。 - 句法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ViewGroup
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@[+][package:]id/resource_name"
android:layout_height=["dimension" | "match_parent" | "wrap_content"]
android:layout_width=["dimension" | "match_parent" | "wrap_content"]
[ViewGroup-specific attributes] >
<View
android:id="@[+][package:]id/resource_name"
android:layout_height=["dimension" | "match_parent" | "wrap_content"]
android:layout_width=["dimension" | "match_parent" | "wrap_content"]
[View-specific attributes] >
<requestFocus/>
</View>
<ViewGroup >
<View />
</ViewGroup>
<include layout="@layout/layout_resource"/>
</ViewGroup>
-
内容
ViewGroup
其他View元素的容器<View>
单个UI组件,通常称为“小部件”。不同种类的View对象包括TextView, Button,和CheckBox。- 属性:
- android:id
资源ID。元素的唯一资源名称,可用于View从应用程序获取对该元素的引用。详细了解下面的价值android:id。 - android:layout_height
维度或关键字。必填。元素的高度,作为维度值(或 维度资源)或关键字("match_parent"或"wrap_content")。请参阅下面的有效值。 - android:layout_width
维度或关键字。必填。元素的宽度,维度值(或 维度资源)或关键字("match_parent"或"wrap_content")。
- android:id
- 属性:
-
Value for android:id
对于ID值,通常应使用以下语法形式:"@+id/name",+表示这是一个新的资源ID。aapt工具将在R.java类中创建一个新的资源整数(如果它尚不存在)。例如
<TextView android:id="@+id/nameTextbox"/>
该nameTextbox名称现在是附加到此元素的资源ID。然后,您可以参考TextViewJava中与ID关联的内容:
TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.nameTextbox);
此代码返回TextView对象。 -
Value for android:layout_height and android:layout_width
高度和宽度值可以使用Android支持的任何 维度单位(px,dp,sp,pt,in,mm)或以下关键字表示:

布局文件activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="2dp"
android:paddingRight="2dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/choose"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:gravity="center|top"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/cancelButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:text="@string/cancel"
android:layout_marginEnd="30dp" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/saveButton"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:text="@string/save"
android:layout_marginStart="30dp" />
</LinearLayout>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_marginTop="150dp"
android:padding="4dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/choose"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:src="@android:drawable/ic_btn_speak_now"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/filter_button_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/image"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/filerButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:text="@string/filter"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/shareButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/share" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/deleteButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:text="@string/delete" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
运行截图
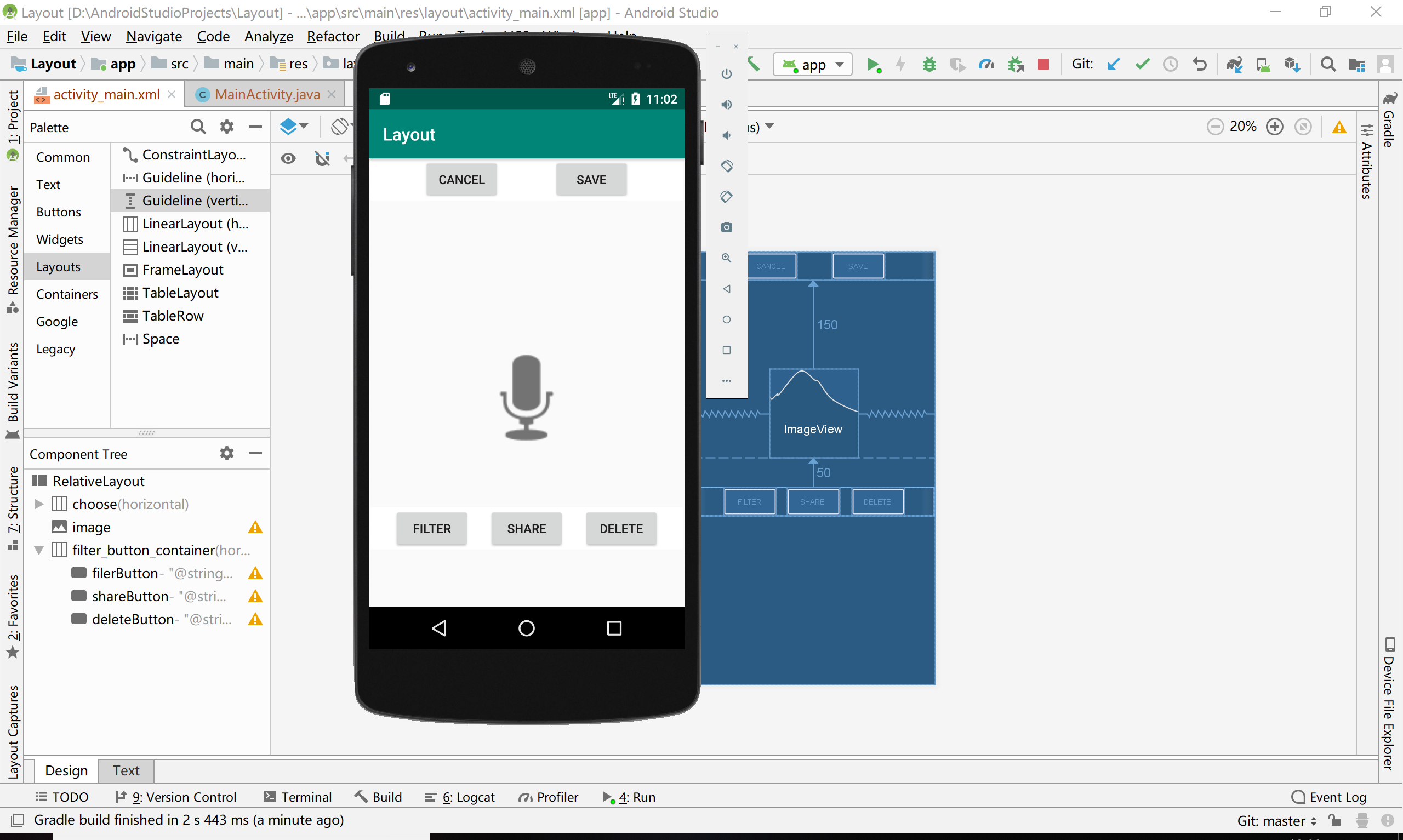
5、事件处理测试
- 要求
- 运行教材本章相关代码并截图
监听器
- Android是基于事件的。使用活动中的一个视图进行的用户交互,可能会触发一个事件,包括点击、长按、触碰和按键等等
- 要让程序响应某一个事件,需要为该事件编写一个监听器。也就是要实现嵌入在android.view.View类中的一个接口。比如OnClickListener接口的onClick()方法
MainActivity
package cn.edu.besti.is.multicolorclock;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
int counter = 0;
int [] colors = {Color.BLACK, Color.BLUE, Color.CYAN,
Color.DKGRAY, Color.GRAY, Color.GREEN, Color.LTGRAY,
Color.MAGENTA, Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.YELLOW };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void changeColor(View view) {
if (counter == colors.length) {
counter = 0;
}
view.setBackgroundColor(colors[counter++]);
}
}
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<AnalogClock
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="90dp"
android:onClick="changeColor"/>
</RelativeLayout>
运行截图

二、问题及解决方法
问题1:安装中一系列问题
(1)一开始我打算将Android Studio安装在虚拟机中,开启AVD时报错如下图
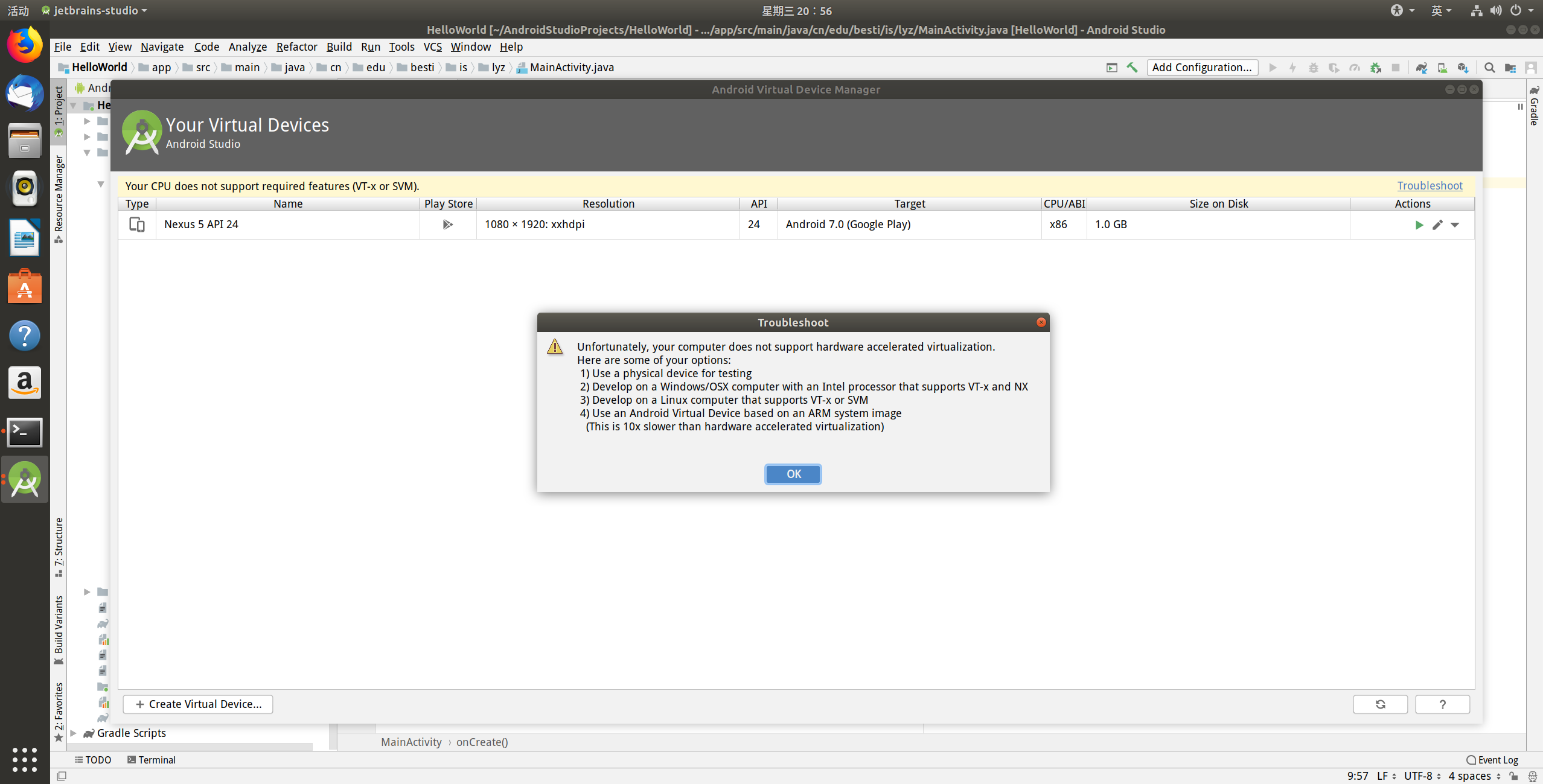
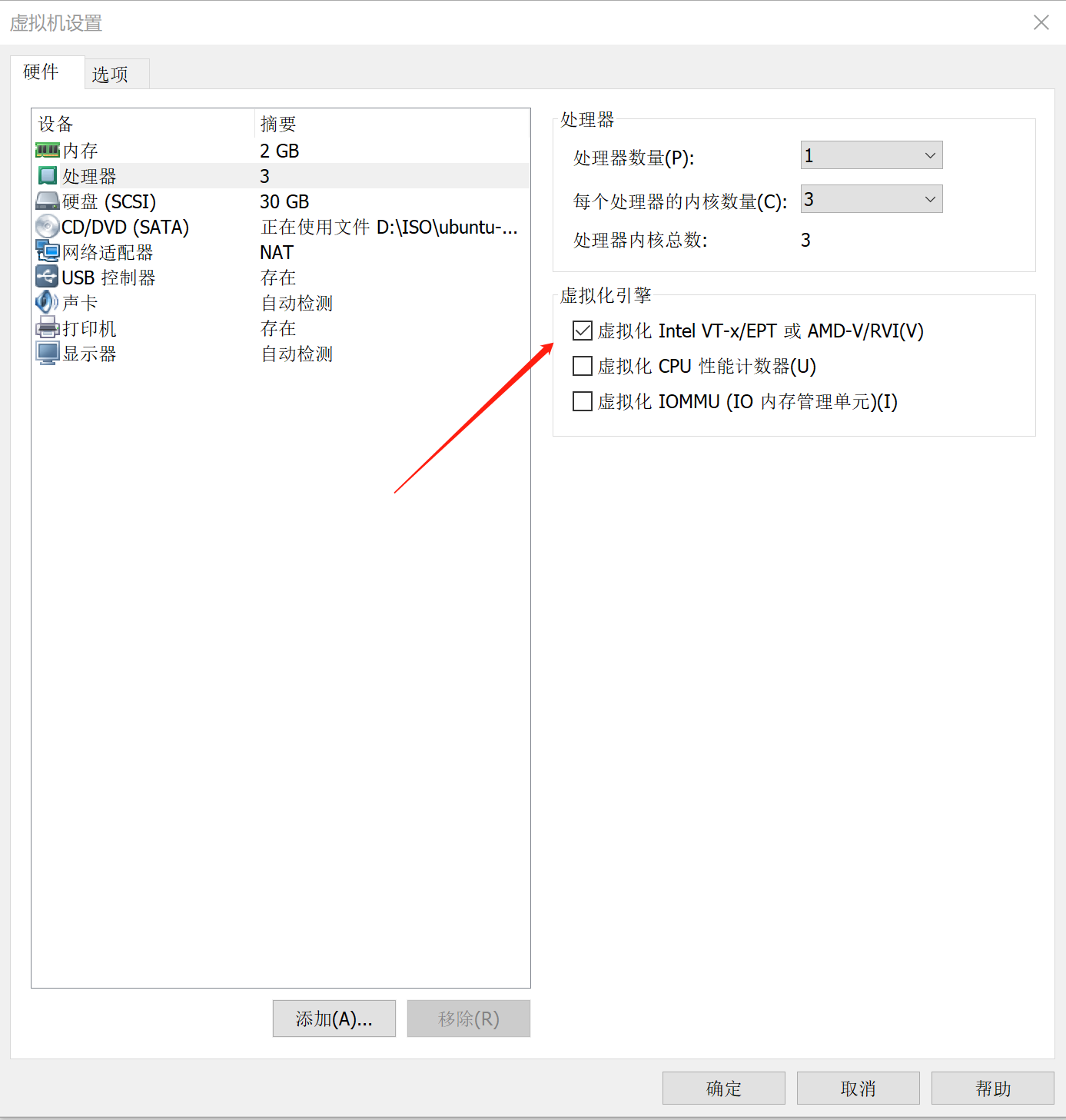
解决:问题出在虚拟机没有开启虚拟化。AVD本质上也是一个虚拟机,只有宿主机开启虚拟化技术才可以创建虚拟机,所以在VMware更改设置
(2)接下来报错如下
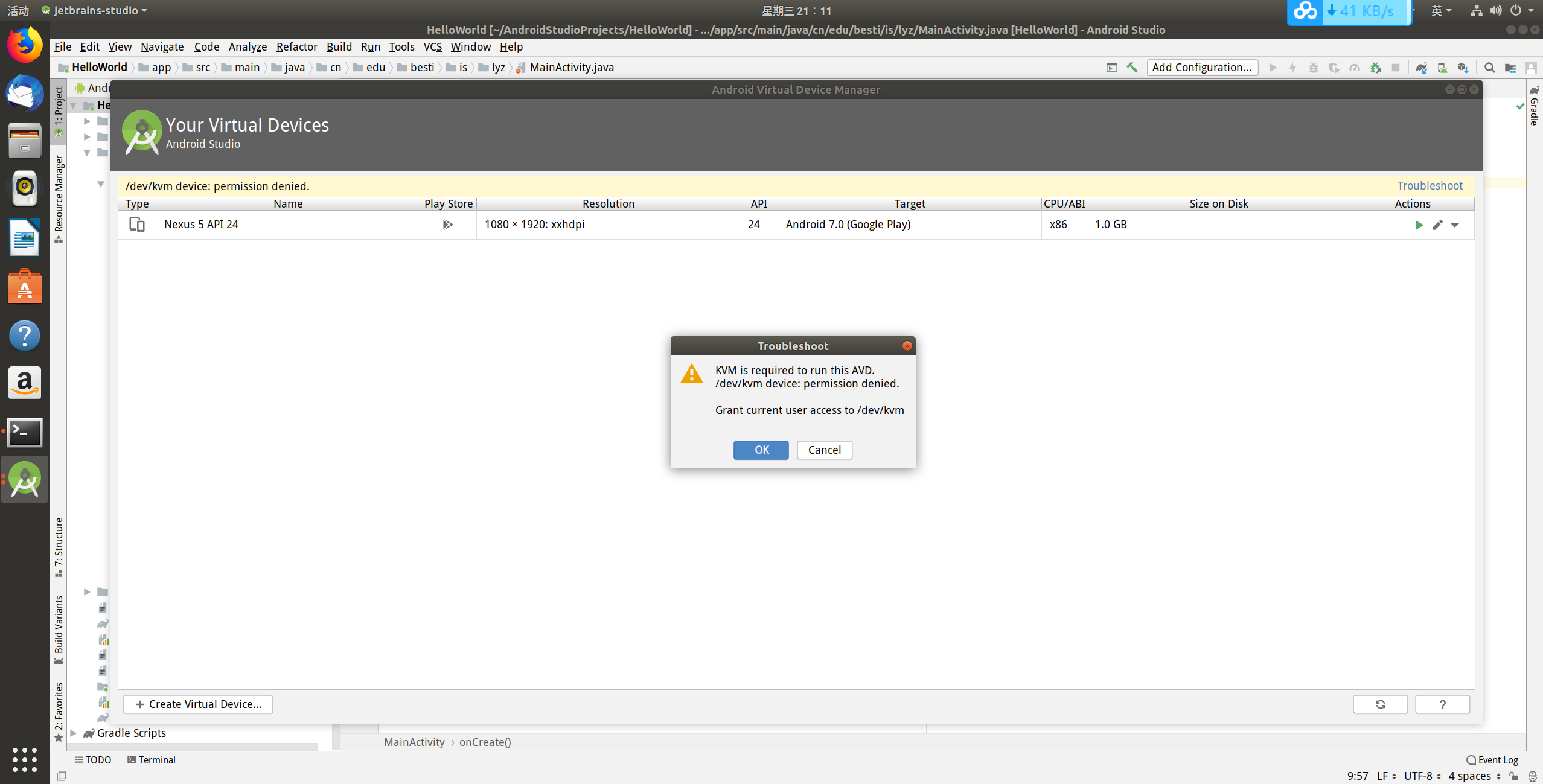
解决:问题出在当前用户权限不够,无法使用/dev/kvm目录,改权限就行了
(3)你以为这样就结束了吗?不,还有问题。创建虚拟机需要大概8个G的空间,我在虚拟机上做哪里给你找8个G?
解决(并没有):更改配置文件,将创建的虚拟手机内存改为2G。但是改完以后,点击运行,配置文件里那个数字又变成了默认的大小。我一气之下把配置文件改成了只读,Android Studio直接告诉我无法写入文件,报错。。。你运行个AVD为什么要改配置文件啊?在baidu、google均无果后,我屈服了,在主机里下了个Android Studio。然而此时距离提交还有24小时(* ̄︶ ̄)
问题2:书上讲的也太简要了吧。。就照着打,什么意思都不知道,这做实验有什么意义。。在有限的篇幅里想把什么东西都讲了,结果就是什么都讲不好。。
解决:老办法,看文档去吧,文档真的什么都有。。配合谷歌翻译,味道好极了o( ̄▽ ̄)d
链接:适用于应用开发者的文档
三、代码托管
- 码云链接
Android项目文件比较多,我也不确定什么该传什么不该传。。就把app下的东西都传上去了
四、实验心得体会
做实验、学知识、写代码都还好,做出东西的成就感足以支撑我继续肝下去,但是安装软件遇到问题带来的挫败感真的是。。。卡了我两天,心情奇差。还好最后是安好了。通过这次试验,我对Android开发有了大概的认识,并且有了基础的开发的能力,有点手痒痒想重拾团队项目了,看看时间吧。。


