数据结构 第四章 串及子串查找 kmp
串:通常指字符串
S = "Hello world"
s="" 字符串长度为0,称为空串
k=" " 空格串,里面字符串的元素为空格 ascii 码为0x20
串是以字符为数据元素的线性表,是线性表 的一个特例。
其物理结构分类 参考 数据结构 第二章 线性表
操作函数:
构造析构、赋值操作: Assign()、赋值操作:Copy()、判空:IsEmpty()、长度:Size()、清空:Clear()、拼接 Concat()、取得子串SubString(pos,len)、定位操作:Index()\size_t find (constchar* s, size_t pos = 0) const;、比较操作 Compare()
字符集{GB2312、unicode、UTF-8、UTF-16} --> 二进制转为显示器字体
存储时,使用字符集F(x),显示时,则使用字符集F(x)来显示,如果选用其他字符集,则可能导致乱码。
串使用链式存储,为了存储一个字节,使用前后两个指针,32位及占8字节,64位机占16字节,这样导致存储密度低;改造方法,每个结点存储多个字节。
例如:
struct Node{
char data[128];
struct Node* pProir;
struct Node* pNext;
}
【字符串定位\查找操作 】
定位操作:size_t find (constchar* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
在主串中查找 模式串 s的位置,主串中不含该模式串,则返回 -1;
主串:被查找的串,如F = "Hello world"; 子串:主串中肯定存在的串 C=“Hello”; 模式串:任意字符串,M=“Fello” , M=“ABC” , M=“Hello”
查找方法分类:
【朴素算法】最好 O(m) 最坏O(n*m) 平均:O(n*m) n为主串长度 m为 模式串 长度
图解如下:
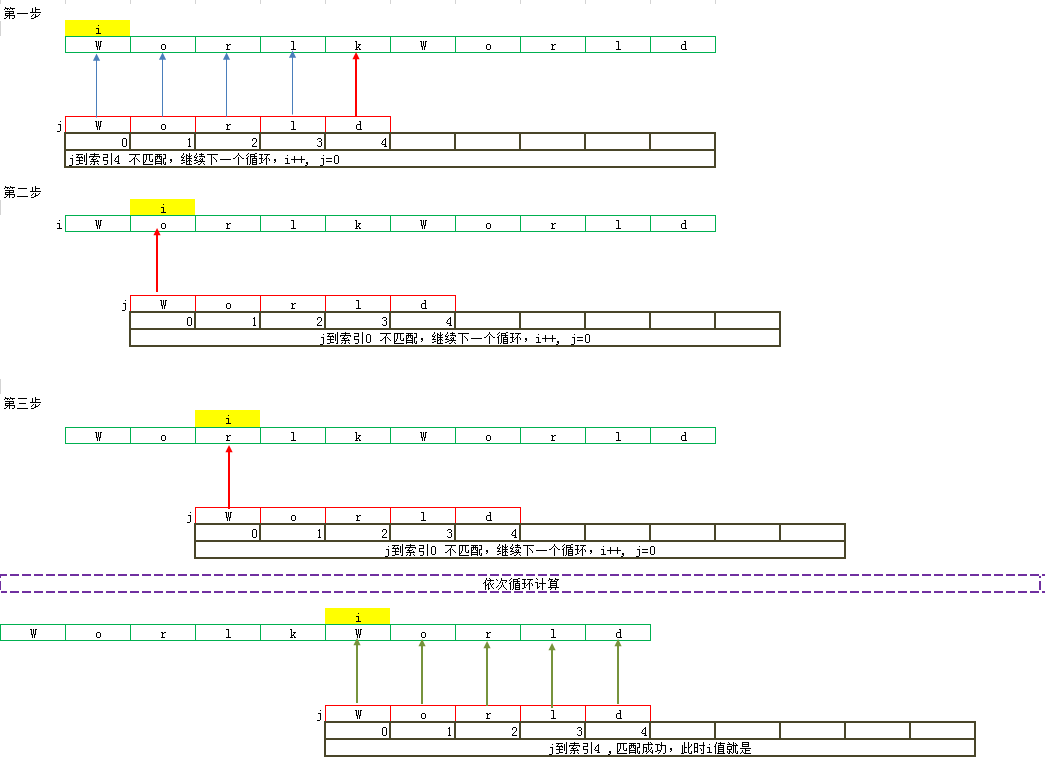
流程图:
【KMP算法】
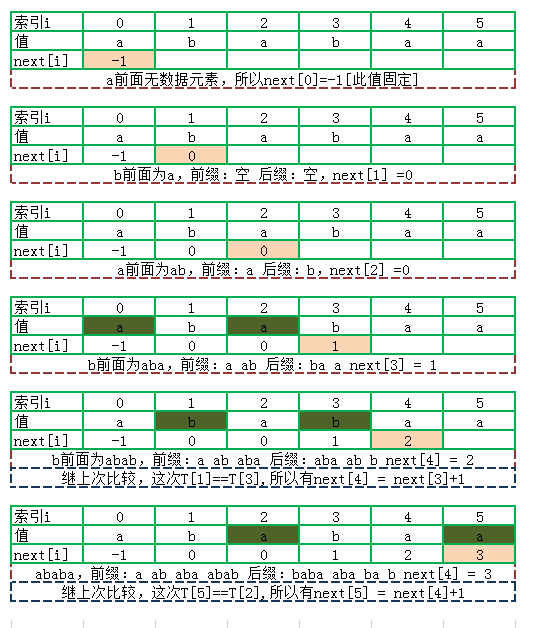
串的前缀、后缀:
S = abcab
前缀:包含第一个字符,且不包含最后一个字符的子串, a ab abc abca
后缀:包含第最后一个字符,且不包含第一个字符的子串,b ab cab bcab
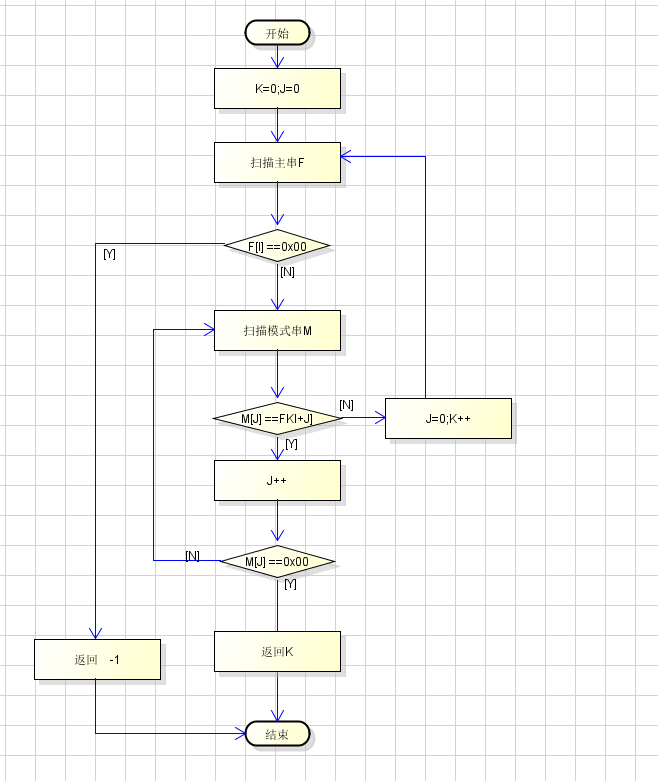
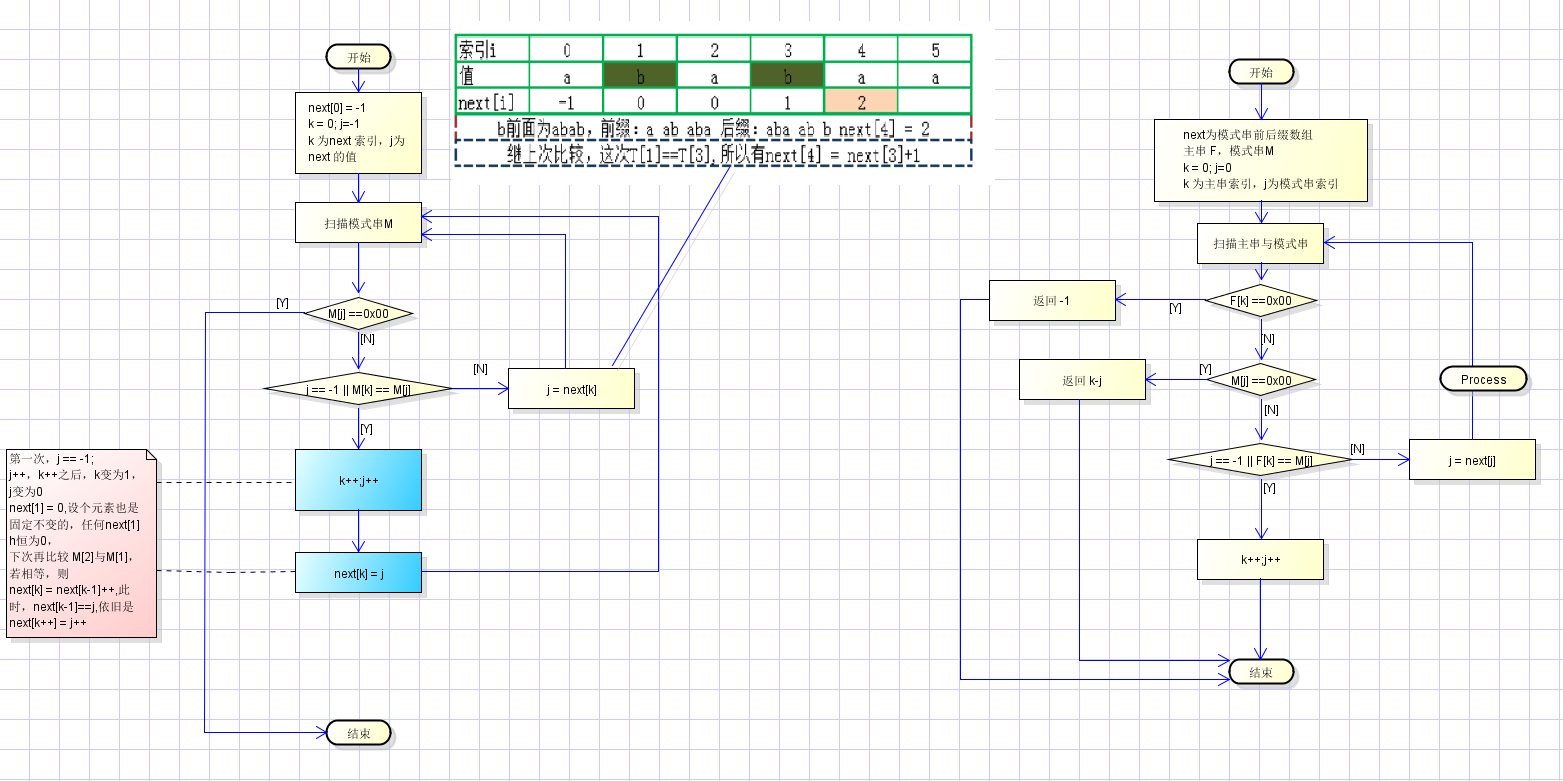
kmp的思想:主串指针/索引 不回溯,只回溯模式串。
模式串的回溯数组指定为 next 数组,即 模式串的子串的 最长公共前后缀。
求next 数组的过程:
kmp 匹配过程:F = babababababaaabababababa M=ababaa

流程图:
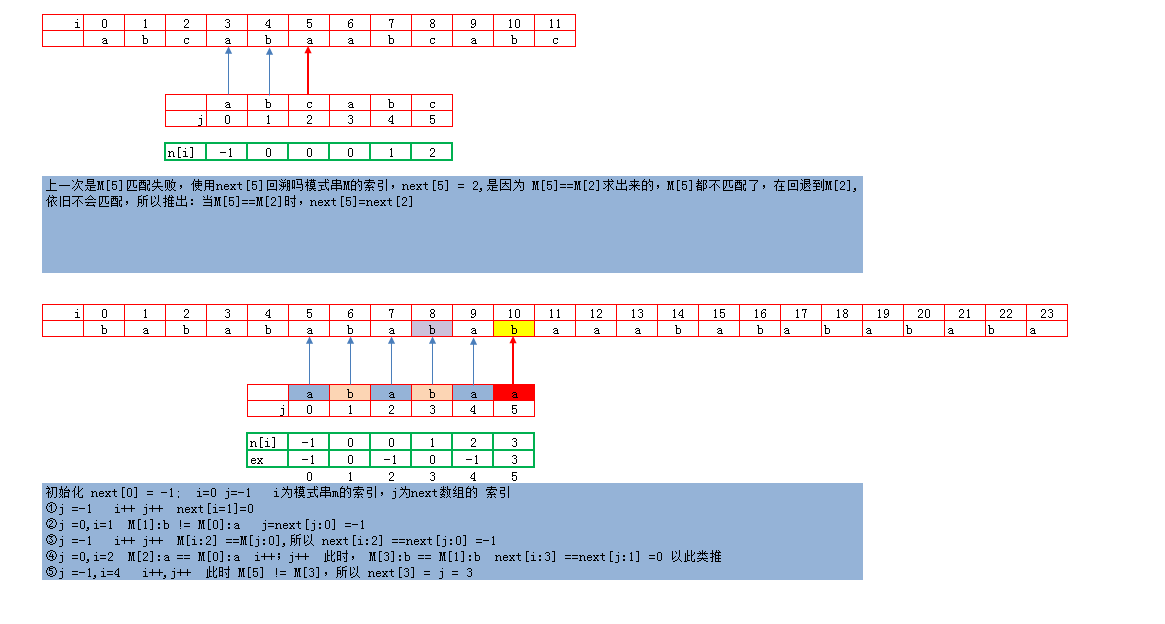
【KMP算法优化】
原理过程:
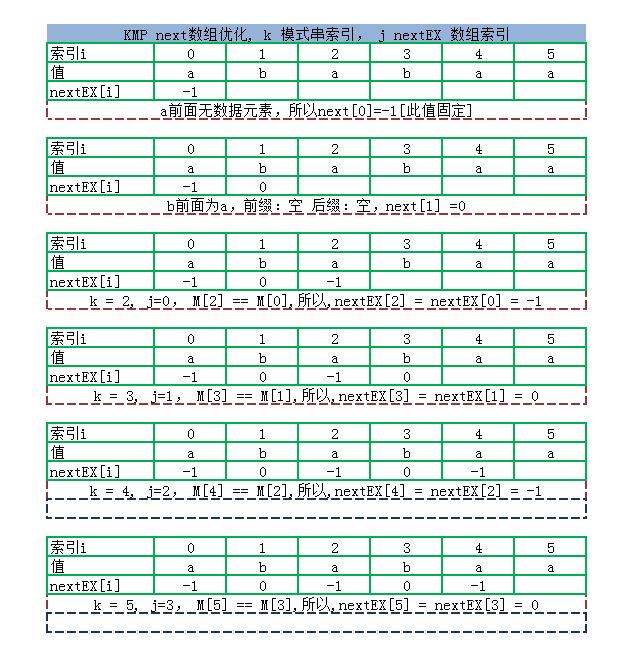
求优化的next 数组的过程:
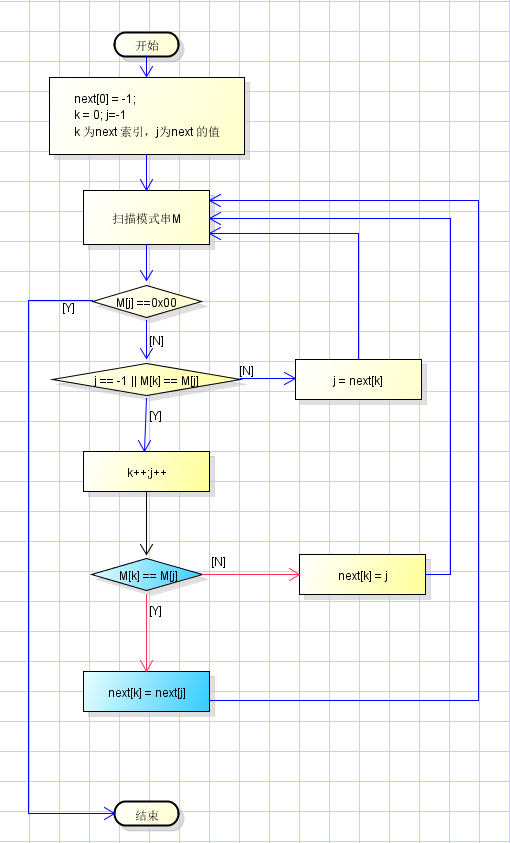
流程图:
【类图】
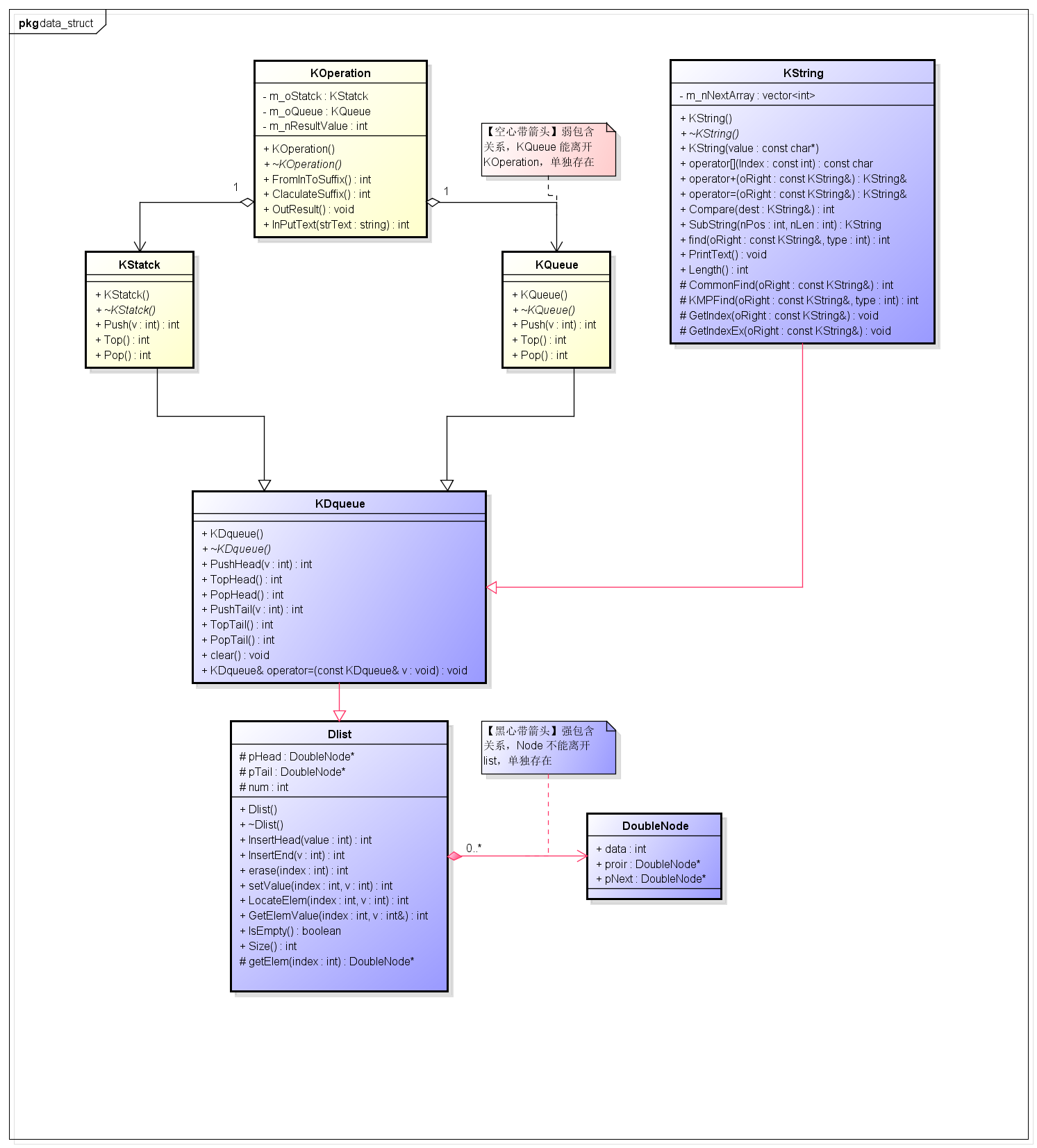
【代码】
KString.h
#ifndef DATA_STRUCT_K_STRING_H
#define DATA_STRUCT_K_STRING_H
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
#include "KDqueue.h"
class KString : public KDqueue
{
private:
vector<int> m_nNextArray;
protected:
/**
* 朴素查找
*/
int CommonFind(KString& oRight);
/**
* KMP 查找
* type 1-KMP查找,使用GetIndex()
* type 2-KMP优化查找,使用GetIndexEx()
*/
int KMPFind(KString& T, int type);
/**
* 取得模式串最大前后缀的值
*/
void GetIndex(KString& T);
/**
* 取得模式串最大前后缀的值
*/
void GetIndexEx(KString& T);
public:
/**
* 构造函数
*/
KString();
/**
* 析构函数
*/
virtual ~KString();
/**
* 构造函数
*/
KString(const char* value);
/**
* 拷贝构造函数
*/
KString(const KString& oRight);
/**
* 取得索引所对应的元素
*/
const char operator[](const int Index);
/**
* 字符串拼接
*/
KString& operator+(const KString& oRight);
/**
* 字符串拼接
*/
KString& operator=(const KString& oRight);
/**
* 字符串比较 src > dest 1 src == dest 0 src < dest -1
*/
int Compare(KString dest);
/**
* 取得子字符串
* nPos 子串在主串索引的起始值
* nLen 子串的长度
*/
KString SubString(int nPos, int nLen);
/**
* 查找子字符串
* type 0-朴素查找
* type 1-KMP查找
* type 2-KMP优化查找
*
*/
int find(KString& oRight, int type=2);
// 打印数据
void PrintText();
// 字符串长度
int Length();
void SetNextArray(int i);
void ClearNextArray();
};
#endif
KString.cpp
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
#include "KString.h"
KString::KString()
:m_nNextArray(8192)
{
}
KString::KString(const KString& oRight)
: m_nNextArray(8192)
{
m_nNextArray.clear();
for (auto v : oRight.m_nNextArray)
{
m_nNextArray.push_back(v);
}
this->pHead->pNext = oRight.pHead->pNext;
oRight.pHead->pNext->pProir = this->pHead;
this->pTail->pProir = oRight.pTail->pProir;
oRight.pTail->pProir->pNext = this->pTail;
this->num = oRight.num;
oRight.pHead->pNext = oRight.pTail;
oRight.pTail->pProir = oRight.pHead;
}
KString::~KString()
{
}
KString::KString(const char* value)
:m_nNextArray(8192)
{
if (nullptr == value)
{
return;
}
int i = 0;
while (value[i] != '\0')
{
PushTail(value[i]);
i++;
}
PushTail('\0');
}
const char KString::operator[](const int Index)
{
int value = 0;
GetElemValue(Index, value);
return value;
}
KString& KString::operator+(const KString& oRight)
{
if (this == &oRight)
{
return *this;
}
if (oRight.pHead->pNext == oRight.pTail)
{
return *this;
}
if (this->pHead->pNext != this->pTail)
{
DoubleNode* temp = this->pTail->pProir;
temp->pProir->pNext = pTail;
pTail->pProir = temp->pProir;
delete temp;
}
this->pTail->pProir->pNext = oRight.pHead->pNext;
oRight.pHead->pNext->pProir = this->pTail->pProir;
this->pTail->pProir = oRight.pTail->pProir;
oRight.pTail->pProir->pNext = this->pTail;
this->num += oRight.num;
oRight.pHead->pNext = oRight.pTail;
oRight.pTail->pProir = oRight.pHead;
return *this;
}
KString& KString::operator=(const KString& oRight)
{
if (this == &oRight)
{
return *this;
}
KDqueue::operator=(oRight);
m_nNextArray.clear();
for (auto v : oRight.m_nNextArray)
{
m_nNextArray.push_back(v);
}
return *this;
}
int KString::Compare(KString dest)
{
int i = 0;
while ((*this)[i] != 0 && dest[i] != 0)
{
if ((*this)[i] > dest[i])
{
return 1;
}
else if ((*this)[i] < dest[i])
{
return -1;
}
i++;
}
return this->num - dest.num;
}
KString KString::SubString(int nPos, int nLen)
{
KString temp;
if (nPos >= this->Length())
{
return temp;
}
char chTemp[65336];
int i = 0;
for (; i < nLen; i++)
{
if ((*this)[nPos+i] == 0x00)
{
break;
}
chTemp[i] = (*this)[nPos + i];
}
chTemp[i] = 0x00;
return temp;
}
int KString::find(KString& oRight, int type)
{
if (0 == type)
{
return CommonFind(oRight);
}
if (1 == type || 2 == type)
{
return KMPFind(oRight, type);
}
return 0;
}
// 朴素查找
int KString::CommonFind(KString& oRight)
{
int i = 0;
for (; i < this->Length(); i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (; j < oRight.Length(); j++)
{
if ((*this)[i+j] == oRight[j])
{
continue;
}
break;
}
if (j == oRight.Length())
{
return i;
}
}
if (i == this->Length())
{
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int KString::KMPFind(KString& T, int type)
{
//根据模式串T,初始化next数组,next 中的内容是 索引+1 = 下一次需要对比的那个数据的索引
if (1 == type)
{
GetIndex(T);
}
else if (2 == type)
{
GetIndexEx(T);
}
else
{
}
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < this->Length() && j < T.Length()) {
//j==0:代表模式串的第一个字符就和当前测试的字符不相等;S[i-1]==T[j-1],如果对应位置字符相等,两种情况下,指向当前测试的两个指针下标i和j都向后移
if (j == -1 || (*this)[i] == T[j]) {
i++;
j++;
}
else{
j = m_nNextArray[j];//如果测试的两个字符不相等,i不动,j变为当前测试字符串的next值
}
}
if (j == T.Length()) {//如果条件为真,说明匹配成功
return i - j; // -1说明返回数组下标
}
return -1;
}
void KString::GetIndex(KString& T)
{
m_nNextArray.clear();
m_nNextArray.resize(8192);
int i = 0;
m_nNextArray[0] = -1;
int j = -1;
while (i < T.Length()-1) {
if (j == -1 || T[i] == T[j]) {
i++;
j++;
m_nNextArray[i] = j;
}
else{
j = m_nNextArray[j];
}
}
}
void KString::GetIndexEx(KString& T)
{
m_nNextArray.clear();
m_nNextArray.resize(8192);
m_nNextArray[0] = -1;
int i = 0;
int j = -1;
while (i < T.Length() - 1) {
if (j == -1 || T[i] == T[j]) {
i++;
j++;
if (T[i] != T[j]) {
m_nNextArray[i] = j;
}
else{
m_nNextArray[i] = m_nNextArray[j];
}
}
else{
j = m_nNextArray[j];
}
}
}
// 打印数据
void KString::PrintText()
{
DoubleNode* Elem = pHead->pNext;
while (Elem != pTail)
{
if (Elem->data == 0x00)
{
break;
}
cout << (char)Elem->data;
Elem = Elem->pNext;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 字符串长度
int KString::Length()
{
return num-1;
}
void KString::SetNextArray(int i)
{
m_nNextArray.push_back(i);
}
void KString::ClearNextArray()
{
m_nNextArray.clear();
}
测试函数
void TestString_20210202()
{
KString F("googlogoooglegoogle");
KString strMain;
// 赋值运算符重载 测试
strMain = F;
strMain.PrintText();
char IndexValue = strMain[5];
cout << IndexValue << endl;
cout << strMain.Compare("googlp") << endl;
KString AddString = strMain + "123";
AddString.PrintText();
strMain = KString("googlogoooglegoogle");
KString ModeString("google");
// 原生字符串 打印
cout << R"(strMain.find("google",0) )" << strMain.find(ModeString, 0) << endl;
cout << R"(strMain.find("google",1) )" << strMain.find(ModeString, 1) << endl;
cout << R"(strMain.find("google",2) )" << strMain.find(ModeString, 2) << endl;
}
【思维图】
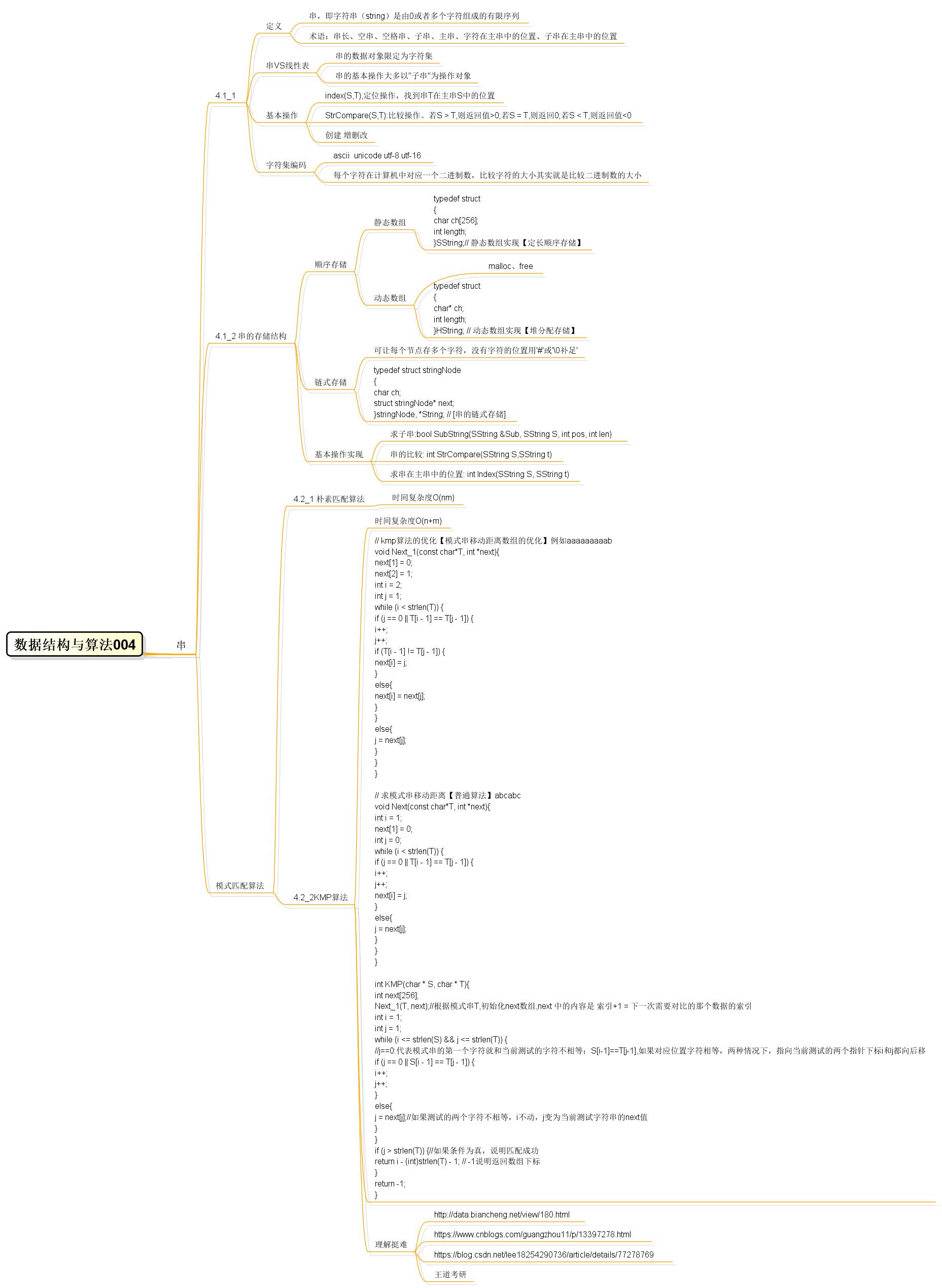
结束




