数据结构 第二章 线性表
概念:
具有相同数据类型的数据元素的有限序列。
表示:L = (A1,A2,A3,...AN),N为表长 其中 A1称为表头,AN为表尾, A2是A3的前驱,A3是A2的后继。

链表的基本操作: 创建 销毁 判空 增删改查
函数名称及作用,实际可以用其他名称,这里只作为举例;
【创建】InitList(&L):初始化表,构造一个空的线性表,分配内存空间。
【销毁】DestroyList(&L): 销毁线性表,并释放线性表所占的内存空间。
【增】InsertList(&L, i,e):在表中的第 i个位置上插入指定的元素e。
【删】DeleteList(&L, i,&e):删除表L中第i 个位置的元素,并且将删除元素的值赋值给e。
【改】SetList(&L, i,e):在表中的第 i个位置修改为元素 e,一般不使用。
【查】LocateElem(L,i,e):按值查找。
【查】GetElem(L,i):按索引查找。
物理结构划分:
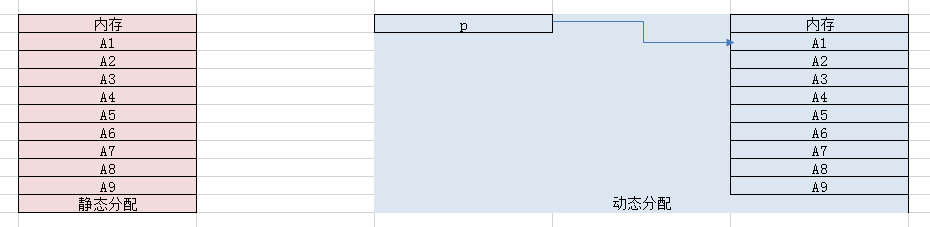
【顺序表】
以数组的形式存储。
指针步长:
void test_array_202101121057()
{
int a[5][6];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
a[i][j] = i * 10 + j;
}
}
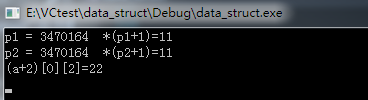
int(*p)[6];
p = a;
int* p1 = a[1];
int* p2 = &a[1][0];
printf("p1 = %d *(p1+1)=%d\n", p1, *(p1 + 1));
printf("p2 = %d *(p2+1)=%d\n", p2, *(p2 + 1));
printf("(a+%d)[%d][%d]=%d\n", 2,0,2,(a+2)[0][2]); // a的步长为跳转一行
}
【动态链表】=【单链表】+【双链表】
以指针的形式动态建立数据的存储单元。


链表插入方法:头插法、尾插法
【头插则是将新节点链接到链表的头结点的后面】
以单链表为例:
current->next=head->next;//新节点的指针域指向*头结点的指针域原来指向的节点(即第一个节点)
head->next=current;//头节点的指针域指向新节点,新节点变为第一个节点。
【尾插则是将新节点链接到链表的尾部】
以单链表为例:
tail->next=current;//原链表尾节点指针域指向新节点
tail=current;//尾指针指向新链接的新节点,新节点变链表的尾节点(尾指针始终指向尾节点)
【静态链表】
以结构体数组的形式存在。
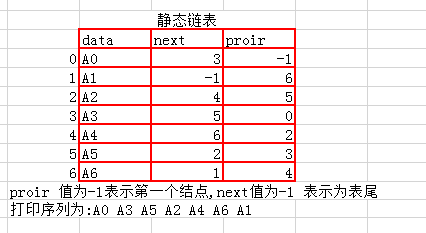
特点:
节省内存
不支持随机存储,使用比较少
应用:
FAT(文件配置表)
【循环链表】
表尾指向表头,表头指向表尾

顺序表与链表的比较:
顺序表,随机存取效率高,存储密度高,但是扩容差 ,;中间插入\删除数据,可能移动大量数据,效率低。
链表:冗余信息较多,存储密度低,随机存储效率低,扩容性好;中间插入/删除 数据,效率高。
【代码实现】
Dlist.h
#pragma once
using DoubleNode = struct _dNode
{
int data;
struct _dNode* pProir;
struct _dNode* pNext;
};
// 双向链表
class Dlist
{
public:
// init 放到构造函数中
Dlist();
// destroy 放到析构函数中
virtual ~Dlist();
// 前插数据
int InsertHead(int value);
// 后插数据
int InsertEnd(int value);
// 删除元素
int erase(int index);
// 设定元素值
int setValue(int index, int value);
// 查找从Index 后面值为value的元素的索引
int LocateElem(int index, int value);
// 查找从Index 的值
int GetElemValue(int index, int& value);
// 判断链表是否为空
bool IsEmpty();
protected:
// 取得下标为 index 的元素
DoubleNode* getElem(int index);
private:
DoubleNode* pHead;// 表头
DoubleNode* pTail;// 表尾
int num;// 元素的个数
};
Dlist.cpp
#include "Dlist.h"
Dlist::Dlist()
{
pHead = new DoubleNode{0, nullptr, nullptr};// 表头
pTail = new DoubleNode{0, nullptr, nullptr};// 表尾
pHead->pNext = pTail;
pTail->pProir = pHead;
num = 0;// 元素的个数
}
Dlist::~Dlist()
{
while (pHead->pNext !=nullptr)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = pHead->pNext;
pHead->pNext = Elem->pNext;
delete Elem;
}
delete pHead;
}
// 前插数据
int Dlist::InsertHead(int value)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = new DoubleNode{value, nullptr, nullptr};
num++;
Elem->pNext = pHead->pNext;
Elem->pProir = pHead;
pHead->pNext = Elem;
Elem->pNext->pProir = Elem;
return 0;
}
// 后插数据
int Dlist::InsertEnd(int value)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = new DoubleNode{value, nullptr, nullptr};
num++;
Elem->pProir = pTail->pProir;
Elem->pNext = pTail;
Elem->pProir->pNext = Elem;
pTail->pProir = Elem;
return 0;
}
// 取得下标为 index 的元素
DoubleNode* Dlist::getElem(int index)
{
if ((index >= num) || nullptr == pHead)
{
return nullptr;
}
// 第0号元素
DoubleNode* Elem = pHead->pNext;
// 找到指定元素
while (index >= 1)
{
Elem = Elem->pNext;
index--;
}
return Elem;
}
// 删除元素
int Dlist::erase(int index)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = getElem(index);
if (nullptr == Elem)
{
return -1;
}
// 修改指针链
Elem->pProir->pNext = Elem->pNext;
Elem->pNext->pProir = Elem->pProir;
// 删除结点
delete Elem;
// 计数减一
num--;
return 0;
}
// 设定元素值
int Dlist::setValue(int index, int value)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = getElem(index);
if (nullptr == Elem)
{
return -1;
}
Elem->data = value;
return 0;
}
// 查找从Index 后面值为value的元素的索引
int Dlist::LocateElem(int index, int value)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = getElem(index);
if (nullptr == Elem)
{
return -1;
}
int retIndex = index;
do
{
if (Elem->data == value)
{
break;
}
retIndex++;
} while (nullptr != (Elem = Elem->pNext));
if (retIndex == num)
{
retIndex = -1;
}
// 函数值返回
return retIndex;
}
// 查找从Index 的值
int Dlist::GetElemValue(int index,int& value)
{
DoubleNode* Elem = getElem(index);
if (nullptr == Elem)
{
return -1;
}
value = Elem->data;
return 0;
}
// 判断链表是否为空
bool Dlist::IsEmpty()
{
return num = 0 ? true : false;
}
测试函数:
void test_Dlist_20210113()
{
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Dlist* dlist = new Dlist();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
dlist->InsertHead(a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int v = 0;
dlist->GetElemValue(i, v);
cout << v << " ";
}
delete dlist;
cout << endl;
dlist = new Dlist();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
dlist->InsertEnd(a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int v = 0;
dlist->GetElemValue(i, v);
cout << v << " ";
}
delete dlist;
cout << endl;
dlist = new Dlist();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
dlist->InsertHead(a[i]);
}
dlist->erase(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int v = 0;
if (0 != dlist->GetElemValue(i, v))
{
continue;
}
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
bool isempty = dlist->IsEmpty();
if (isempty)
{
cout << "空 ";
}
else
{
cout << "非空 ";
}
cout << endl;
delete dlist;
dlist = new Dlist();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
dlist->InsertHead(a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
dlist->erase(0);
}
isempty = dlist->IsEmpty();
if (isempty)
{
cout << "空 ";
}
else
{
cout << "非空 ";
}
cout << endl;
dlist->InsertEnd(6);
dlist->InsertEnd(7);
dlist->InsertEnd(8);
dlist->InsertEnd(9);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int v = 0;
if (0 != dlist->GetElemValue(i, v))
{
continue;
}
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
isempty = dlist->IsEmpty();
if (isempty)
{
cout << "空 ";
}
else
{
cout << "非空 ";
}
cout << endl;
delete dlist;
}
【内容总结】

结束




