Java实验报告(实验三)
2015-10-18 23:47 艾鸽 阅读(586) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报
一、实验内容
1. XP基础
2. XP核心实践
3. 相关工具
4.结对同学:20159205 石宇婷
Blog网址:http://home.cnblogs.com/u/20159205syt/
二、实验步骤
(一)敏捷开发与XP
(1)含义:是一种以人为核心、迭代、循序渐进的开发方法。
(2)模式:XP,TDD,CI,FDD,BDD,SCRUM,Feature Team,Domain Model,Extract Activities,Refactor,Pair Programming,Feature List/Product Backlog.
(3)极限编程(eXtreme Programming,XP) 是一种全新而快捷的软件开发方法。
(4)XP准则:沟通,简单,反馈,勇气。
(5)XP活动:编码,测试,倾听,设计。
(二)编码标准
1、包含:具有说明性的名字、清晰的表达式、直截了当的控制流、可读的代码和注释,以及在追求这些内容时一致地使用某些规则和惯用法的重要性。
2、Eclipse中的快捷键使用:
Ctrl+Shift+F或菜单中的source->Format,使代码按Eclipse规定的规范缩进。
初始代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | package cc.openhome;import java.lang.String; public class pracJDB {public static void main(String args) {StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();buffer.append('s');buffer.append("trignBuffer");System.out.println(buffer.charAt(1));System.out.println(buffer.capacity());System.out.println(buffer.indexOf("tring"));System.out.println("buffer=" + buffer.toString());if (buffer.capacity() < 20)buffer.append("1234567");for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length(); i++)System.out.println(buffer.charAt(i));}} |
用Format格式后的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | package cc.openhome;import java.lang.String;public class pracJDB { public static void main(String args) { StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); buffer.append('s'); buffer.append("trignBuffer"); System.out.println(buffer.charAt(1)); System.out.println(buffer.capacity()); System.out.println(buffer.indexOf("tring")); System.out.println("buffer=" + buffer.toString()); if (buffer.capacity() < 20) buffer.append("1234567"); for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length(); i++) System.out.println(buffer.charAt(i)); }} |
(三)结对编程
1、分为:驾驶员(Driver)是控制键盘输入的人。
领航员(Navigator)起到领航、提醒的作用。
2、驾驶员:写设计文档,进行编码和单元测试等XP开发流程。
领航员:审阅驾驶员的文档、驾驶员对编码等开发流程的执行;考虑单元测试的覆盖率;思考是否需要和如何重构;帮助驾驶员解决具体的技术问题。
(四)版本控制
1、版本控制提供项目级的 undo(撤销) 功能。
2、版本控制允许多人在同一代码上工作, 只要遵守一定的控制原则就行。
3、版本控制系统保存了过去所作的修改的历史记录。
4、版本控制系统还支持在主线上开发的同时发布多个软件版本。
5、版本控制也是项目级的时间机器,你可以选择任何一个时间, 精确地查看项目在当时的情况。
6、流行的版本控制工具有CVS,SVN,Git等。
7、实验楼中的git服务:
(1)公开的代码仓库:shiyanlou_cs212
(2)启动实验时,会自动执行git pull,获取课程仓库中的最新代码,存放于/home/shiyanlou/Code目录。
(3)进入到实验环境中修改代码,完成后需要依次执行下述命令即可提交:
$ cd /home/shiyanlou/Code/shiyanlou_cs212
# 修改代码文件
# 添加修改文件
$ git add 所有修改的文件
# 提交到环境中本地代码仓库
$ git commit -m '本次修改的描述'
# push到git.shiyanlou.com,无需输入密码
$ git push
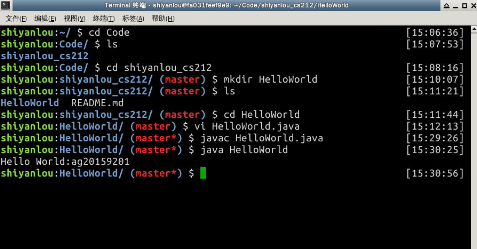
git实验部分我做过,但是由于网速很慢重新刷新时无法再打开,事先没有截图,望老师见谅。
(4)克隆其他用户代码仓库只需要知道对方的仓库链接,我们鼓励在别人代码基础上修改:
$ git clone http://git.shiyanlou.com/[对方的专属用户名]/[课程代码仓库名]
(5)输入git status:查看代码状态;
出现未跟踪的文件,使用git add <file>...:以包含要提交的内容;
使用git commit:git将依据索引库中的内容来进行文件的提交;
使用git push:把代码保存到远程托管服务器中。
(五)重构(Refactor)
1、概念:重构是在不改变软件外部行为的基础上,改变软件内部的结构,使其更加易于阅读、易于维护和易于变更。
2、重构的第一项功能---Rename
可以给类、包、方法、变量改名字。
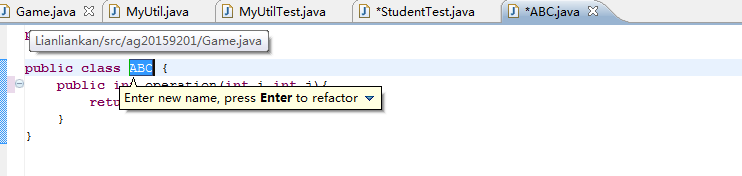
修改方法:用鼠标单击要改的名字,选择Eclipse中菜单中的Refactor->Rename...
初始代码:
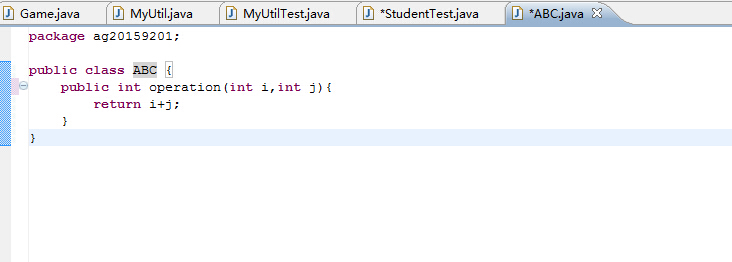
对此代码进行重构:
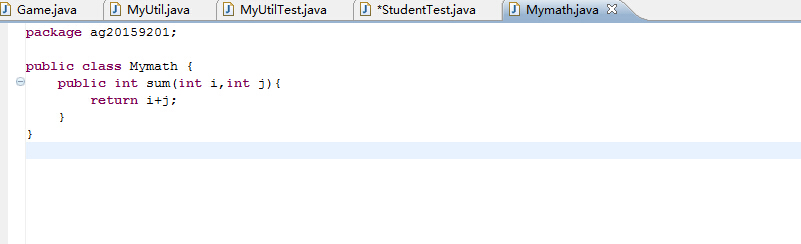
重构后的代码:
3、重构的第二项功能---封装
原始程序为:

选择需要封装的变量s.name,点击Refactor->Encapsulate Field:
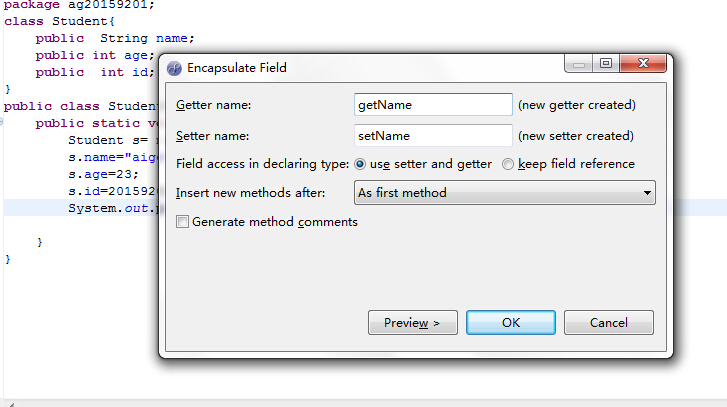
用同样的方法封装age和id,得到如下代码:

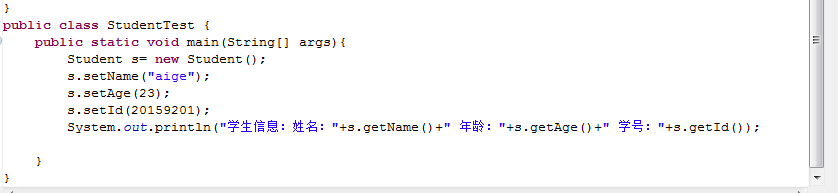
使用Eclipse中Source->Generate toString(),给Student类产生一个toString方法,得到代码:

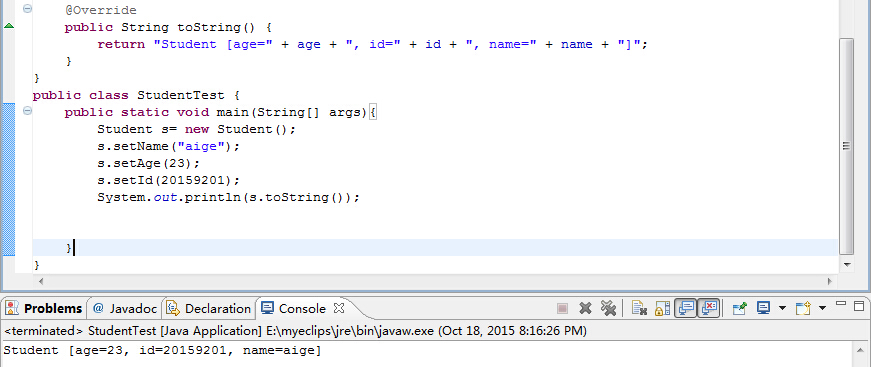
4、修改代码的目的:
增加新功能,原有功能有BUG,改善原有程序的结构,优化原有系统的性能。
5、有Bad Smell的代码需要重构:
重复代码(Duplicated Code),过长方法,过长参数列,条件逻辑过度复杂,分支语句,基本类型迷恋,数据泥团。
6、重构的完整流程:
(1)从版本控制系统代码库中Check out code;
(2)读懂代码(包括测试代码);
(3)发现bad smell;
(4)Refactoring;
(5)运行所有的Unit Tests;
(6)往代码库中Check in code;
(六)实践项目
编写小游戏:连连看。
结对同学:20159205 石宇婷
Blog网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/20159205syt/
1、实验步骤:
我们两个首先选取一个游戏进行需求分析,尝试用TDD思想编写测试代码与产品代码,参考网上现有资料,完成游戏的实现。
2、连连看代码:
package ag20159201; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Container; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; public class Game implements ActionListener { JFrame mainFrame; // 主面板 Container thisContainer; JPanel centerPanel, southPanel, northPanel; // 子面板 JButton diamondsButton[][] = new JButton[6][5];// 游戏按钮数组 JButton exitButton, resetButton, newlyButton; // 退出,重列,重新开始按钮 JLabel fractionLable = new JLabel("0"); // 分数标签 JButton firstButton, secondButton; // 分别记录两次被选中的按钮 int grid[][] = new int[8][7];// 储存游戏按钮位置 static boolean pressInformation = false; // 判断是否有按钮被选中 int x0 = 0, y0 = 0, x = 0, y = 0, firstMsg = 0, secondMsg = 0, validateLV; // 游戏按钮的位置坐标 int i, j, k, n;// 消除方法控制 public void init() { mainFrame = new JFrame("连连看"); thisContainer = mainFrame.getContentPane(); thisContainer.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); centerPanel = new JPanel(); southPanel = new JPanel(); northPanel = new JPanel(); thisContainer.add(centerPanel, "Center"); thisContainer.add(southPanel, "South"); thisContainer.add(northPanel, "North"); centerPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(6, 5)); for (int cols = 0; cols < 6; cols++) { for (int rows = 0; rows < 5; rows++) { diamondsButton[cols][rows] = new JButton(String.valueOf(grid[cols + 1][rows + 1])); diamondsButton[cols][rows].addActionListener(this); centerPanel.add(diamondsButton[cols][rows]); } } exitButton = new JButton("退出"); exitButton.addActionListener(this); resetButton = new JButton("重列"); resetButton.addActionListener(this); newlyButton = new JButton("再来一局"); newlyButton.addActionListener(this); southPanel.add(exitButton); southPanel.add(resetButton); southPanel.add(newlyButton); fractionLable.setText(String.valueOf(Integer.parseInt(fractionLable.getText()))); northPanel.add(fractionLable); mainFrame.setBounds(280, 100, 500, 450); mainFrame.setVisible(true); } public void randomBuild() { int randoms, cols, rows; for (int twins = 1; twins <= 15; twins++) { randoms = (int) (Math.random() * 25 + 1); for (int alike = 1; alike <= 2; alike++) { cols = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1); rows = (int) (Math.random() * 5 + 1); while (grid[cols][rows] != 0) { cols = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1); rows = (int) (Math.random() * 5 + 1); } this.grid[cols][rows] = randoms; } } } public void fraction() { fractionLable.setText(String.valueOf(Integer.parseInt(fractionLable.getText()) + 100)); } public void reload() { int save[] = new int[30]; int n = 0, cols, rows; int grid[][] = new int[8][7]; for (int i = 0; i <= 6; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= 5; j++) { if (this.grid[i][j] != 0) { save[n] = this.grid[i][j]; n++; } } } n = n - 1; this.grid = grid; while (n >= 0) { cols = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1); rows = (int) (Math.random() * 5 + 1); while (grid[cols][rows] != 0) { cols = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1); rows = (int) (Math.random() * 5 + 1); } this.grid[cols][rows] = save[n]; n--; } mainFrame.setVisible(false); pressInformation = false; // 这里一定要将按钮点击信息归为初始 init(); for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { if (grid[i + 1][j + 1] == 0) diamondsButton[i][j].setVisible(false); } } } public void estimateEven(int placeX, int placeY, JButton bz) { if (pressInformation == false) { x = placeX; y = placeY; secondMsg = grid[x][y]; secondButton = bz; pressInformation = true; } else { x0 = x; y0 = y; firstMsg = secondMsg; firstButton = secondButton; x = placeX; y = placeY; secondMsg = grid[x][y]; secondButton = bz; if (firstMsg == secondMsg && secondButton != firstButton) { xiao(); } } } public void xiao() { // 相同的情况下能不能消去。仔细分析,不一条条注释 if ((x0 == x && (y0 == y + 1 || y0 == y - 1))|| ((x0 == x + 1 || x0 == x - 1) && (y0 == y))) { // 判断是否相邻 remove(); } else { for (j = 0; j < 7; j++) { if (grid[x0][j] == 0) { // 判断第一个按钮同行哪个按钮为空 if (y > j) { // 如果第二个按钮的Y坐标大于空按钮的Y坐标说明第一按钮在第二按钮左边 for (i = y - 1; i >= j; i--) { // 判断第二按钮左侧直到第一按钮中间有没有按钮 if (grid[x][i] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 1; } // K=1说明通过了第一次验证 } if (k == 1) { linePassOne(); } } if (y < j) { // 如果第二个按钮的Y坐标小于空按钮的Y坐标说明第一按钮在第二按钮右边 for (i = y + 1; i <= j; i++) { // 判断第二按钮左侧直到第一按钮中间有没有按钮 if (grid[x][i] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 1; } } if (k == 1) { linePassOne(); } } if (y == j) { linePassOne(); } } if (k == 2) { if (x0 == x) { remove(); } if (x0 < x) { for (n = x0; n <= x - 1; n++) { if (grid[n][j] != 0) { k = 0; break; } if (grid[n][j] == 0 && n == x - 1) { remove(); } } } if (x0 > x) { for (n = x0; n >= x + 1; n--) { if (grid[n][j] != 0) { k = 0; break; } if (grid[n][j] == 0 && n == x + 1) { remove(); } } } } } for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) { // 列 if (grid[i][y0] == 0) { if (x > i) { for (j = x - 1; j >= i; j--) { if (grid[j][y] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 1; } } if (k == 1) { rowPassOne(); } } if (x < i) { for (j = x + 1; j <= i; j++) { if (grid[j][y] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 1; } } if (k == 1) { rowPassOne(); } } if (x == i) { rowPassOne(); } } if (k == 2) { if (y0 == y) { remove(); } if (y0 < y) { for (n = y0; n <= y - 1; n++) { if (grid[i][n] != 0) { k = 0; break; } if (grid[i][n] == 0 && n == y - 1) { remove(); } } } if (y0 > y) { for (n = y0; n >= y + 1; n--) { if (grid[i][n] != 0) { k = 0; break; } if (grid[i][n] == 0 && n == y + 1) { remove(); } } } } } } } public void linePassOne() { if (y0 > j) { // 第一按钮同行空按钮在左边 for (i = y0 - 1; i >= j; i--) { // 判断第一按钮同左侧空按钮之间有没按钮 if (grid[x0][i] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 2; } // K=2说明通过了第二次验证 } } if (y0 < j) { // 第一按钮同行空按钮在与第二按钮之间 for (i = y0 + 1; i <= j; i++) { if (grid[x0][i] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 2; } } } } public void rowPassOne() { if (x0 > i) { for (j = x0 - 1; j >= i; j--) { if (grid[j][y0] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 2; } } } if (x0 < i) { for (j = x0 + 1; j <= i; j++) { if (grid[j][y0] != 0) { k = 0; break; } else { k = 2; } } } } public void remove() { firstButton.setVisible(false); secondButton.setVisible(false); fraction(); pressInformation = false; k = 0; grid[x0][y0] = 0; grid[x][y] = 0; } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { if (e.getSource() == newlyButton) { int grid[][] = new int[8][7]; this.grid = grid; randomBuild(); mainFrame.setVisible(false); pressInformation = false; init(); } if (e.getSource() == exitButton) System.exit(0); if (e.getSource() == resetButton) reload(); for (int cols = 0; cols < 6; cols++) { for (int rows = 0; rows < 5; rows++) { if (e.getSource() == diamondsButton[cols][rows]) estimateEven(cols + 1, rows + 1, diamondsButton[cols][rows]); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Game llk = new Game(); llk.randomBuild(); llk.init(); } }
1、对vi命令并不熟悉,尤其是不清楚如何退回命令行
解决方法:由于实验一也遇到同样问题,所以可以查看实验一报告中遇到的问题和解决方案
(1)首先按下字母i切换至插入模式(Insert mode)开始编辑文件;
(2)退出vi及保存文件:文件编辑完之后,按esc键或Ctrl+o切换至命令行模式,在按ZZ保存原文件并退出。
解决方法:在多次尝试失败后只好借用同学电脑完成这项工作,在自己电脑上手动编写了这段代码。
(八)实验收获体会
前半部分是自己实验,学习敏捷开发与XP、编码标准、版本控制和重构。由于学校网速太慢,实验楼经常断线,所以实验花了挺长时间。这部分知识比较难的是使用版本控制中的git功能,在vim中返回命令行界面时遇到困难,这个问题在实验一中出现过,返回自己博客园查看当时的记录,找到按下Ctrl+o,再输入ZZ退出输入模式返回命令行的方法,调试过后可以顺利进行后面的实验。通过这次实验我发现了及时总结问题的好处,同时发现要经常重温以前实验问题体会,以免知识的遗忘。其次,我印象最深的是重构,通过运用好重构可以大大提升我们编写代码的质量,让这个代码具有可读性、可改性、可用性。这是值得我们以后编程中要学以致用的地方。
后半部分是编写一个java小游戏,和石宇婷两人借鉴了网上连连看代码,一起分析这个代码中语句的功能,发现这个程序用到我们没学过的窗体程序设计等方面知识,所以阅读起来有一定的困难。也让我意识到自己的编程能力还需要很大的提升。





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】博客园携手 AI 驱动开发工具商 Chat2DB 推出联合终身会员
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 对象分配(Alloc)底层原理浅谈
· 聊一聊 C#异步 任务延续的三种底层玩法
· 敏捷开发:如何高效开每日站会
· 为什么 .NET8线程池 容易引发线程饥饿
· golang自带的死锁检测并非银弹
· 一个适用于 .NET 的开源整洁架构项目模板
· API 风格选对了,文档写好了,项目就成功了一半!
· 【开源】C#上位机必备高效数据转换助手
· .NET 9.0 使用 Vulkan API 编写跨平台图形应用
· .NET 依赖注入中的 Captive Dependency