Android视图控件架构分析之View、ViewGroup
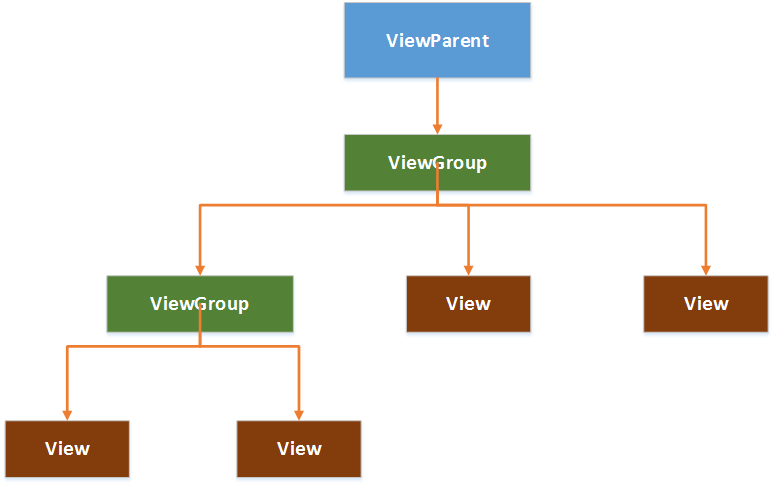
在Android中,视图控件大致被分为两类,即ViewGroup和View,ViewGroup控件作为父控件,包含并管理着子View,通过ViewGroup和View便形成了控件树,各个ViewGoup对象和View对象就是控件树中的节点。在控件树中,以树的深度来遍历查找对应的控件元素,同时,上层控件负责子控件的测量与绘制,并传递交互事件。
Android控件树:
AndroidUI界面架构图:

一.测量View的工具类:MeasureSpec
1.MeasureSpec包含了测量的模式和测量的大小,通过MeasureSpec.getMode()获取测量模式,通过MeasureSpec.getSize()获取测量大小;
2.MeasureSpec是一个32位的int值,高2位为测量的模式,低30位为测量的大小,使用位运算的目的在于提高优化效率。
二.测量的模式
1.EXACTLY,精确值模式:将layout_width或layout_height属性指定为具体数值或者match_parent。
2.AT_MOST,最大值模式:将layout_width或layout_height指定为wrap_content。
3.UNSPECIFIED: View想多大就多大
三.View类默认的onMeasure()方法只支持EXACTLY模式,如果要支持其它模式,就必须重写onMeasure(),重写onMeasure()的模板代码:
1 package com.example.demoapp.views; 2 3 import android.content.Context; 4 import android.view.View; 5 6 public class MeasuredView extends View { 7 public MeasuredView(Context context) { 8 super(context); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 13 // 调用父类的onMeasure() 14 super.onMeasure(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec), measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec)); 15 // 或者直接调用父类的setMeasuredDimension(),因为父类的onMeasure()最终调用了setMeasuredDimension() 16 // setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec), measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec)); 17 } 18 19 /** 20 * 测量View的width 21 * @param measureSpec MeasureSpec对象 22 * @return View的width 23 */ 24 private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) { 25 int result = 0; 26 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); 27 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); 28 29 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) { 30 result = specSize; 31 } else { 32 result = 200; 33 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { 34 result = Math.min(result, specSize); 35 } 36 } 37 return result; 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * 测量View的height 42 * @param measureSpec MeasureSpec对象 43 * @return View的height 44 */ 45 private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) { 46 int result = 0; 47 int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); 48 int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); 49 50 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) { 51 result = specSize; 52 } else { 53 result = 200; 54 if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { 55 result = Math.min(result, specSize); 56 } 57 } 58 return result; 59 } 60 }
四.View的绘制
1.2D绘图必备利器——Canvas
1)获取Canvas对象的方式:
a.由方法中的参数传入,例如,View的onDraw()中有一个参数就是Canvas对象
b.通过构造方法构造,即:Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmap),在Canvas的构造方法传入一个Bitmap对象,即可获取一个Canvas对象。通过传入Bitmap对象构造Canvas对象的过程称为“画布的装载”,传入的Bitmap对象承载了多有绘制在Canvas上的像素信息,调用Canvas.drawXXX方法(如:Canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, null))都将发生在该Bitmap对象上。
2)利用Canvas绘图
a.通过Canvas.drwaXXX进行绘制操作将直接作用于Bitmap对象,当再次刷新View的时候,我们将会被绘制的Bitmap对象发生了改变;
b.利用Canvas和Paint进行绘图;
c.不管多么复杂、精美的空间,都可以被拆分为一个个小的图形单元,我们只要找到这些图形单元,就可以将控件绘制出来。
五.ViewGroup的测量
1.ViewGroup的作用:管理子View,如子View的大小、位置;
2.ViewGroup通过遍历子View,调用子View的Measure()来获得每一个子View的测量结果;
3.ViewGroup测量完子View,调用子View的Layout()将子View放到合适的位置;
4.在自定义ViewGroup的时候,通常会重写onLayout()控制子View的显示;
5.如果需要支持wrap_content属性,必须重写onMeasure()。
六、ViewGroup的绘制
通常情况下,ViewGoup不需要绘制,但是ViewGroup会使用dispatchDraw()来绘制其子View。
七.自定义View
1.自定义View的时候,通常需要重写onDraw()来绘制View要显示的内容,如果还需要支持wrap_content属性,必须重写onMeasure();
2.通过自定义attrs属性,可以设置新的View属性;
3.View中一些重要的回调方法:
1)onFinishInflate():从XML中加载组建后回调;
2)onSizeChanged():组件大小改变时回调;
3)onMeasure():进行测量;
4)onLayout():设置显示的位置;
5)onTouchEvent():触摸事件。
4.实现自定义View的三种常用方法:
1)通过重写onDraw()对原生控件进行扩展;
2)通过组合实现新的控件,通常集成一个合适的额ViewGoup,再通过addView()给它添加指定功能的控件,从而组合成新的复合控件。
3)重写View实现全新的控件,通过重写onDraw(),onMeasure()实现绘制逻辑,重写onTouchEvent()实现交互逻辑。
5.自定义属性
1)自定义属性的方法:在res资源目录的values目录下创建一个attrs.xml的属性定义文件,文件模板:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <resources> 3 <declare-styleable name="customAttr"> 4 <attr name="title" format="string" /> 5 <attr name="fontSize" format="dimension" /> 6 <attr name="fontColor" format="color" /> 7 <attr name="background" format="reference|color" /> 8 <attr name="fontStyle" format="enum" /> 9 <attr name="shadeSupport" format="boolean" /> 10 </declare-styleable> 11 </resources>
2)通过TypedArray获取自定义属性集,通过TypedArray.getString()、TypedArray.getColor()等方法获取属性值,模板代码:
1 package com.jy.myrecyclerview.test; 2 3 import android.content.Context; 4 import android.content.res.TypedArray; 5 import android.util.AttributeSet; 6 import android.view.View; 7 8 import com.jy.myrecyclerview.R; 9 10 /** 11 * Created by 123 on 2016/5/6. 12 */ 13 public class TestCustomAttrs extends View { 14 private Context mContext; 15 private AttributeSet mAttrs; 16 private String mTitle; 17 private float mFontSize; 18 private int mFontColor; 19 private int mBackground; 20 private int mFontStyle; 21 private boolean mShadeSupport; 22 23 public TestCustomAttrs(Context context) { 24 super(context); 25 this.mContext = context; 26 } 27 28 public TestCustomAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { 29 super(context, attrs); 30 this.mContext = context; 31 this.mAttrs = attrs; 32 } 33 34 public TestCustomAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { 35 super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); 36 this.mContext = context; 37 this.mAttrs = attrs; 38 } 39 40 private void getCustomAttrs() { 41 TypedArray ta = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(mAttrs, R.styleable.customAttr); 42 mTitle = ta.getString(R.styleable.customAttr_title); 43 mFontSize = ta.getDimension(R.styleable.customAttr_fontSize, 10); 44 mFontColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.customAttr_fontColor, 0); 45 mBackground = ta.getColor(R.styleable.customAttr_background, 0); 46 mFontStyle = ta.getInt(R.styleable.customAttr_fontStyle, 0); 47 mShadeSupport = ta.getBoolean(R.styleable.customAttr_shadeSupport, false); 48 ta.recycle(); 49 } 50 }
6.定义回调接口,实现自定义控件的灵活控制;
7.引用UI模板
1)自定义控件需要使用命名空间进行引入:xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto",即将自定义控件的命名空间取名为custom
2)在XML文件中使用自定义属性的时候,就可以通过这个命名空间来引用,代码模板如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.jy.myrecyclerview.test.TestCustomAttrs android:id="@+id/id_recyclerview" android:divider="#ffff0000" android:dividerHeight="10dp" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" custom:title="title" custom:fontSize="12sp" custom:fontColor="@color/colorPrimary" custom:background="@color/colorPrimary" custom:shadeSupport="false" /> </RelativeLayout>
九.自定义ViewGroup
1.需要重写的方法:
1)onMeasure():对子View进行测量;
2)onLayout():设置子View的位置;
3)onTouchEvent():设置触摸交互事件。
注:本文参阅了徐宜生的《Android群英传》一书。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号