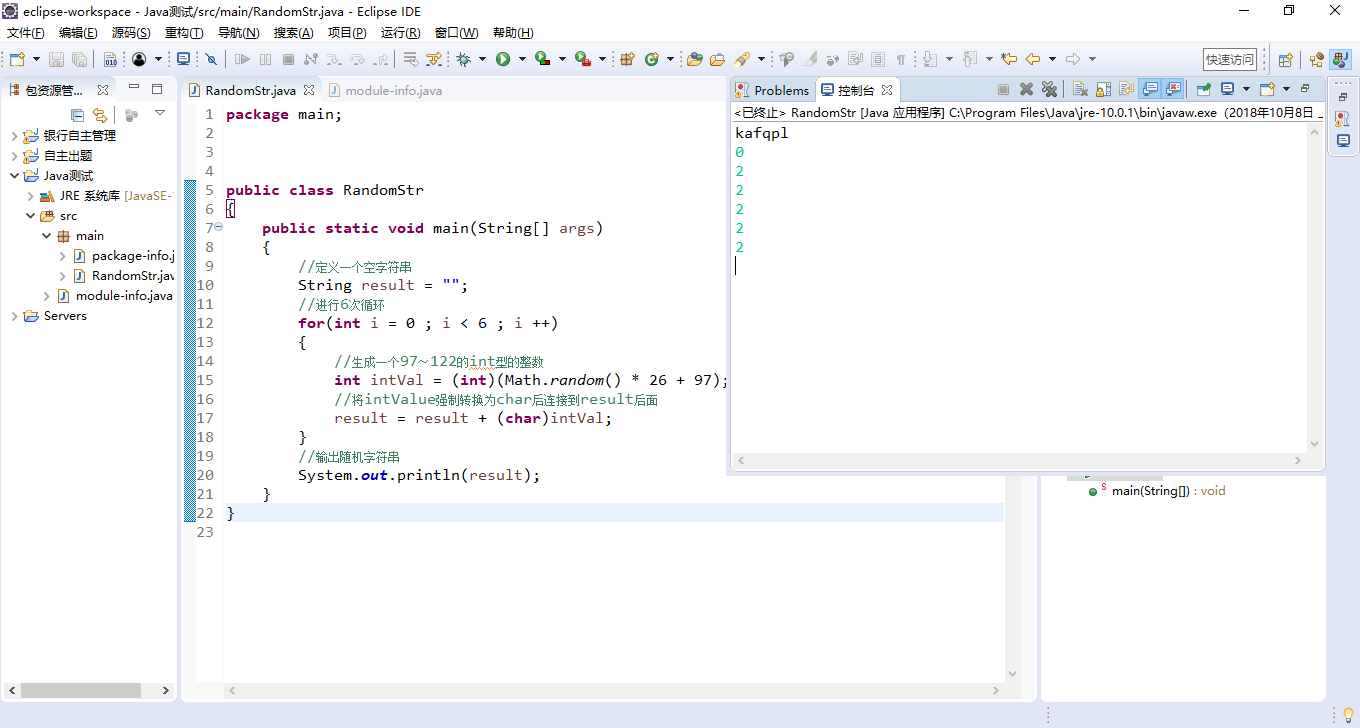
动手动脑课后练习
动手动脑
public class EnumTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Size s=Size.SMALL;
Size t=Size.LARGE;
//s和t引用同一个对象?
System.out.println(s==t); //
//是原始数据类型吗?
System.out.println(s.getClass().isPrimitive());
//从字符串中转换
Size u=Size.valueOf("SMALL");
System.out.println(s==u); //true
//列出它的所有值
for(Size value:Size.values()){
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
enum Size{SMALL,MEDIUM,LARGE};
枚举类型用于声明一组命名的常数,当一个变量有几种可能的取值时,可以将它定义为枚举类型。
枚举可以根据Integer、Long、Short或Byte中的任意一种数据类型来创建一种新型变量。这种变量能设置为已经定义的一组之中的一个,有效地防止用户提供无效值。该变量可使代码更加清晰,因为它可以描述特定的值。
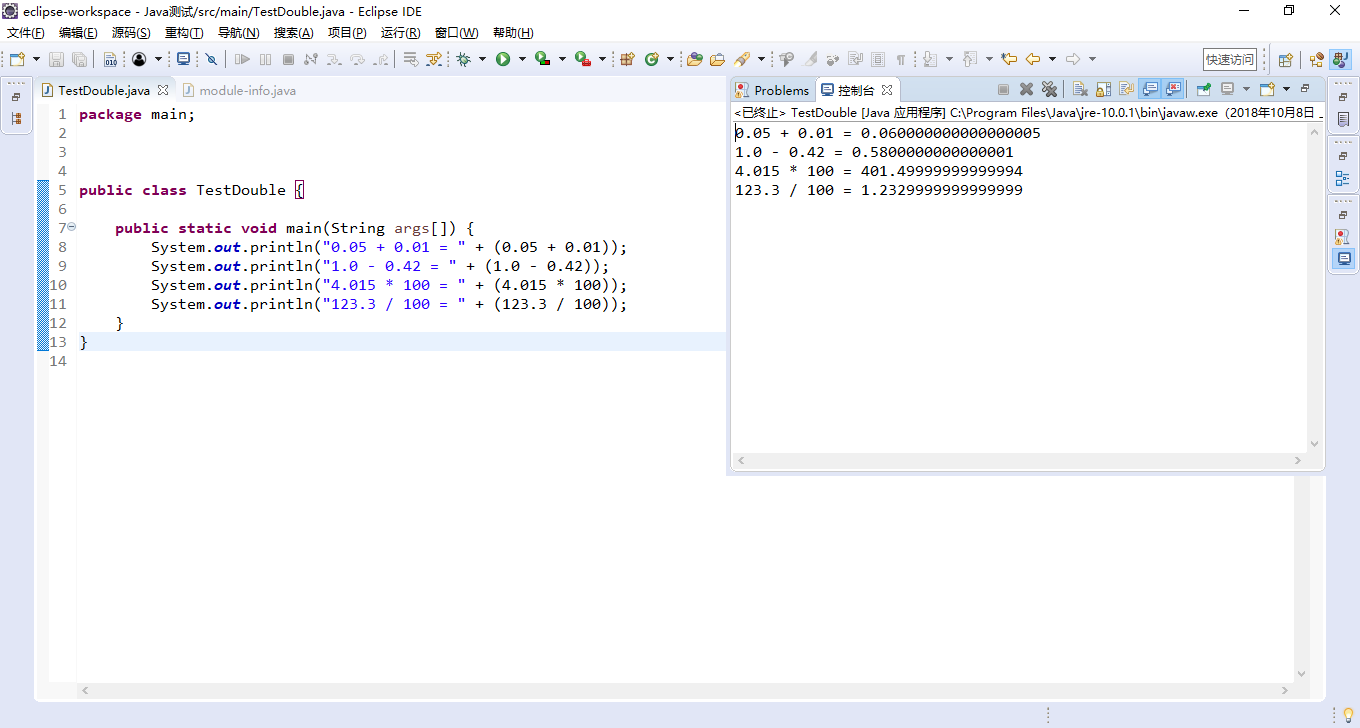
public class TestDouble {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("0.05 + 0.01 = " + (0.05 + 0.01));
System.out.println("1.0 - 0.42 = " + (1.0 - 0.42));
System.out.println("4.015 * 100 = " + (4.015 * 100));
System.out.println("123.3 / 100 = " + (123.3 / 100));
}
}
输出的结果 不正常
不精确
因为是计算机计算时用的是 计算机语言1 0 二进制
当出现小数时 不能被 2整 开方
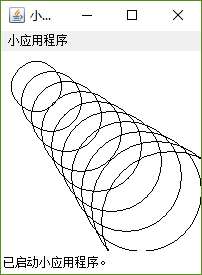
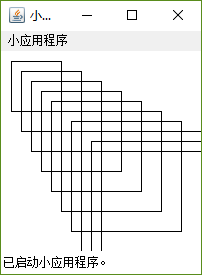
// Drawing shapes
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.*;
public class SwitchTest extends JApplet {
int choice;
public void init()
{
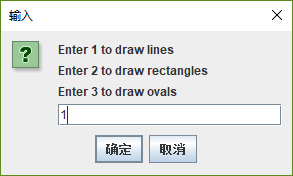
String input;
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(
"Enter 1 to draw lines\n" +
"Enter 2 to draw rectangles\n" +
"Enter 3 to draw ovals\n" );
choice = Integer.parseInt( input );
}
public void paint( Graphics g )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) {
switch( choice ) {
case 1:
g.drawLine( 10, 10, 250, 10 + i * 10 );
break;
case 2:
g.drawRect( 10 + i * 10, 10 + i * 10,
50 + i * 10, 50 + i * 10 );
break;
case 3:
g.drawOval( 10 + i * 10, 10 + i * 10,
50 + i * 10, 50 + i * 10 );
break;
default:
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(
null, "Invalid value entered" );
} // end switch
} // end for
} // end paint()
} // end class SwitchTest
/**************************************************************************
* (C) Copyright 1999 by Deitel & Associates, Inc. and Prentice Hall. *
* All Rights Reserved. *
* *
* DISCLAIMER: The authors and publisher of this book have used their *
* best efforts in preparing the book. These efforts include the *
* development, research, and testing of the theories and programs *
* to determine their effectiveness. The authors and publisher make *
* no warranty of any kind, expressed or implied, with regard to these *
* programs or to the documentation contained in these books. The authors *
* and publisher shall not be liable in any event for incidental or *
* consequential damages in connection with, or arising out of, the *
* furnishing, performance, or use of these programs. *
*************************************************************************/
// An addition program
import javax.swing.JOptionPane; // import class JOptionPane
public class Addition {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String firstNumber, // first string entered by user
secondNumber; // second string entered by user
int number1, // first number to add
number2, // second number to add
sum; // sum of number1 and number2
// read in first number from user as a string
firstNumber =
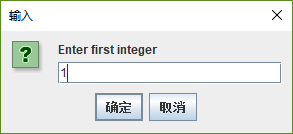
JOptionPane.showInputDialog( "Enter first integer" );
// read in second number from user as a string
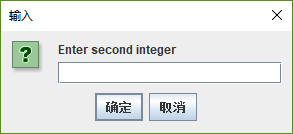
secondNumber =
JOptionPane.showInputDialog( "Enter second integer" );
// convert numbers from type String to type int
number1 = Integer.parseInt( firstNumber );
number2 = Integer.parseInt( secondNumber );
// add the numbers
sum = number1 + number2;
// display the results
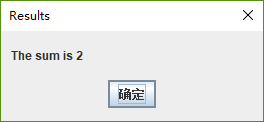
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(
null, "The sum is " + sum, "Results",
JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE );
System.exit( 0 ); // terminate the program
}
}
/**
@version 1.10 2004-02-10
@author Cay Horstmann
*/
import java.util.*;
public class InputTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// get first input
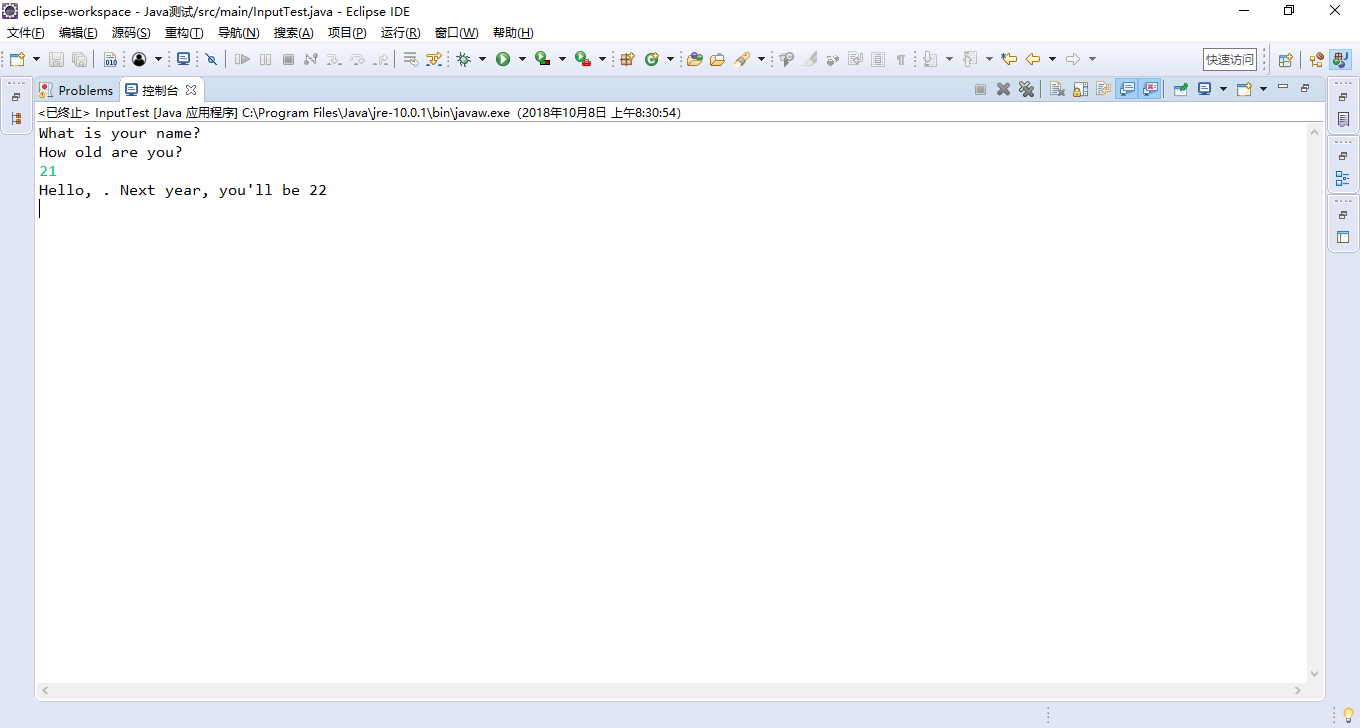
System.out.print("What is your name? ");
String name = in.nextLine();
// get second input
System.out.print("How old are you? ");
int age = in.nextInt();
/* int i;
String value="100";
i=Integer.parseInt(value);
i=200;
String s=String.valueOf(i);*/
// display output on console
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + ". Next year, you'll be " + (age + 1));
}
}
。