面向对象
p43 Point案例
p 43 定义一个“点”(Point)类用来表示三 维空间中的点(有三个坐标)。要求如 下: 1.可以生成具有特定坐标的点对象。 2.提供可以设置三个坐标的方法。 3. 提供可以计算该“点"距原点距离平 方的方法。 4.编写程序验证上述三条。
public class test1 { public static void main(String[]args){ Point P = new Point(3.2,4.2,5.2); Point b = new Point(0,0,0); System.out.println(P.disPlay(b)); System.out.println(P.disPlay(new Point(2.1,4.2,1.1))); } static class Point{ protected double x; protected double y; protected double z; Point(double x,double y,double z){ this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; } public void seTX(double x){ this.x = x; } public double getX(){ return x; } public void setY(double y){ this.y = y; } public double getY(){ return y; } public void setZ(double z){ this.z = z; } public double getZ(){ return z; } public double disPlay(Point b){ return (x-b.x)*(x-b.x)+(y-b.y)*(y-b.y)+(z-b.z)*(z-b.y); } } }
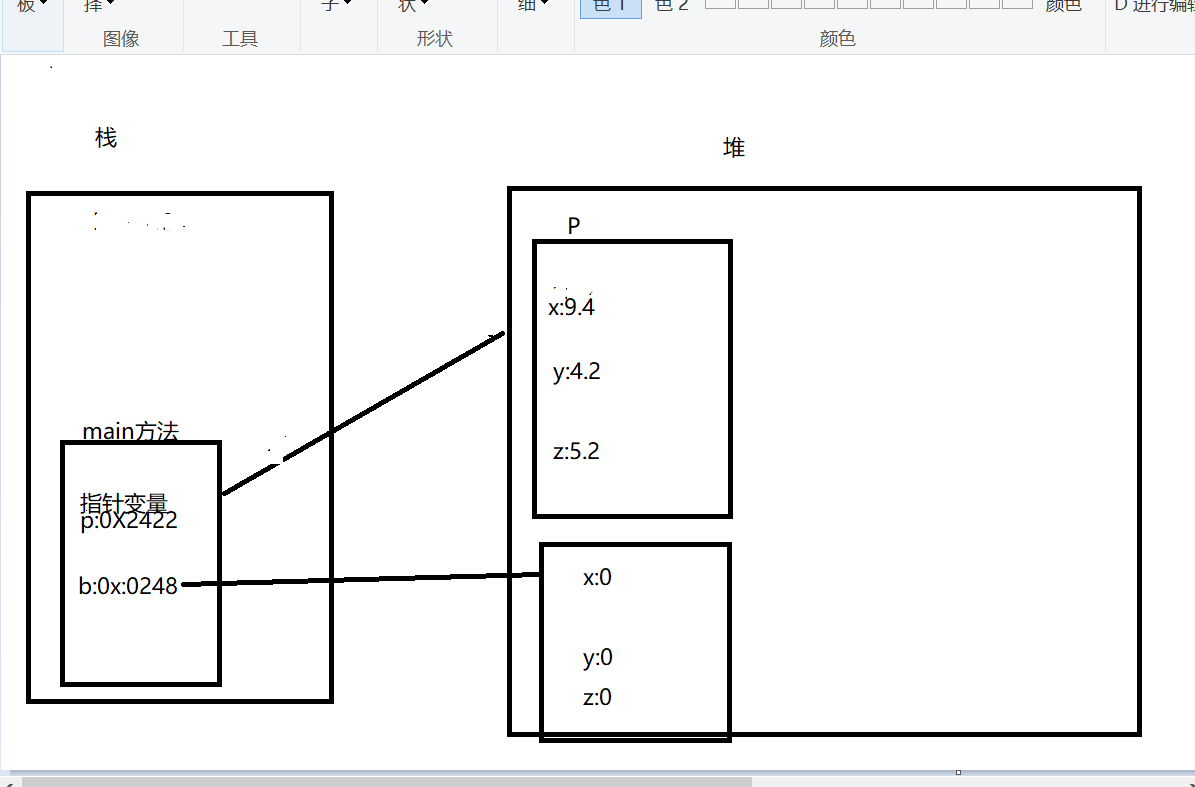
内存分析:
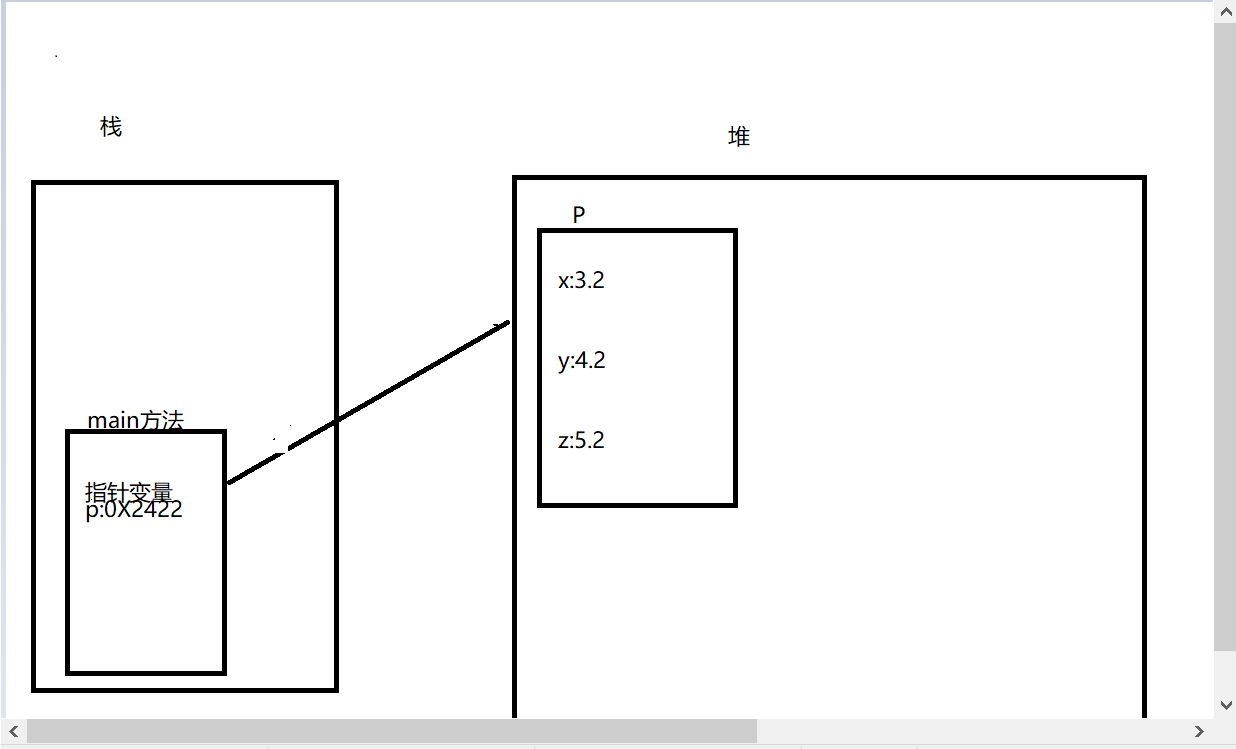
2:
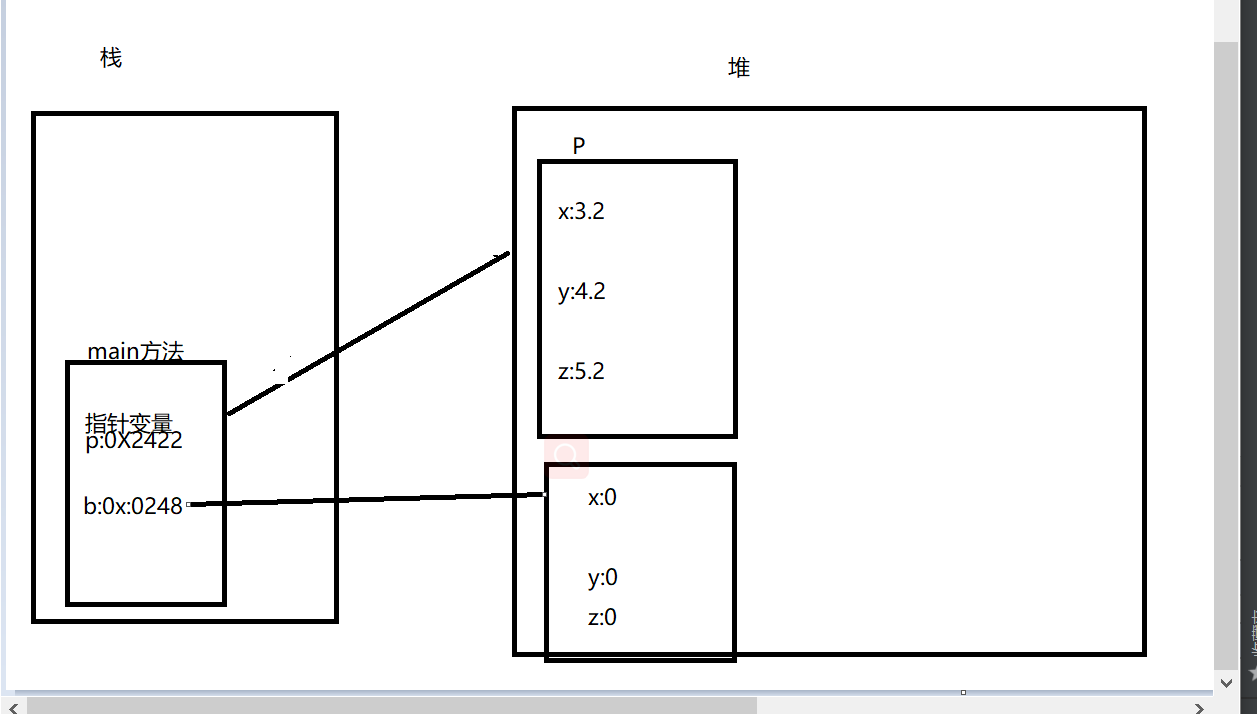
3:当方法调用完后会从栈中弹出来,局部变量也会弹出,知道被垃圾回收
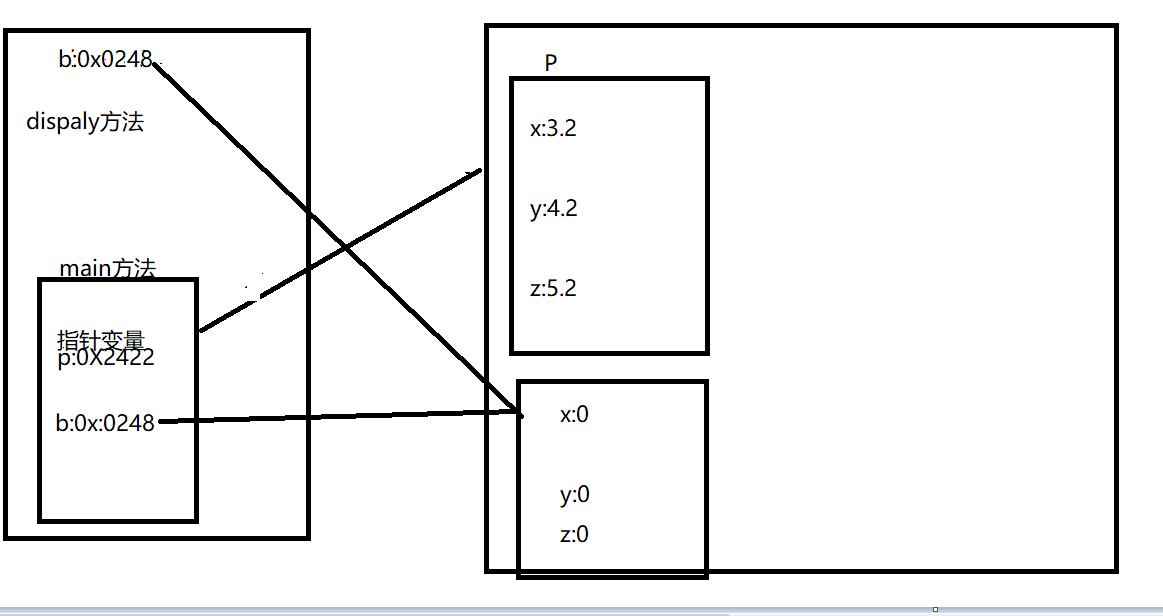
4:
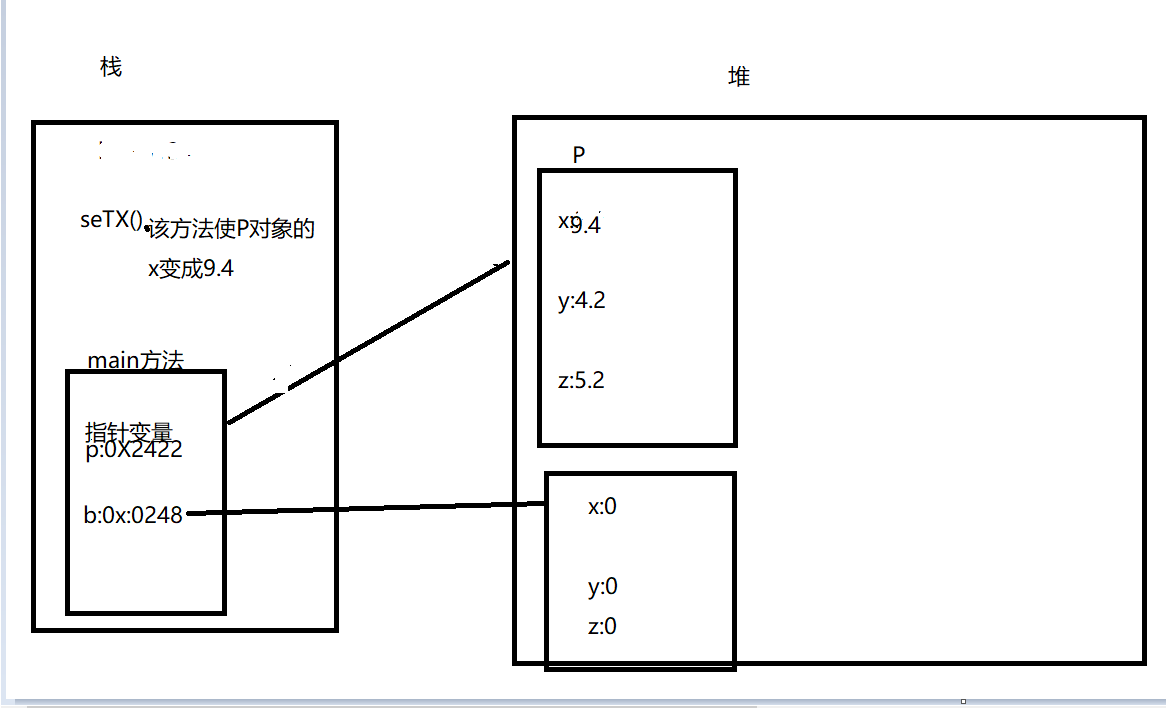
5:
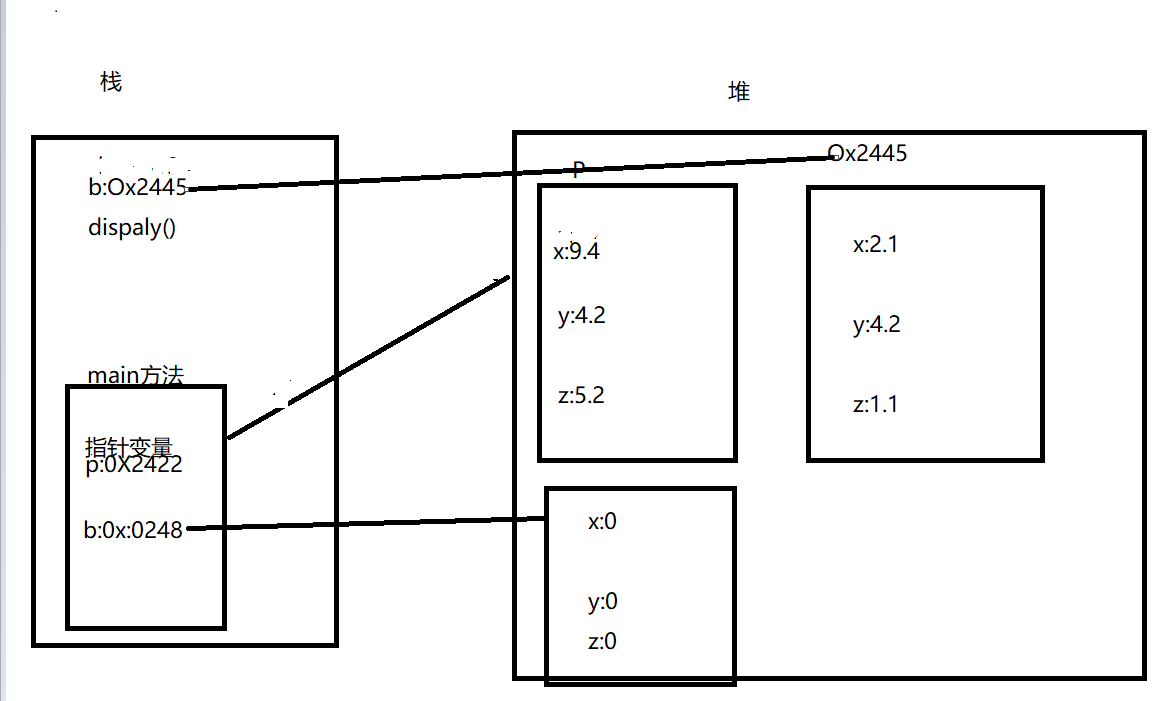
6:
7:
main方法结束后所有的变量都会弹出栈
栈是先进后出
当new出来的对象在堆里面,没有变量引用,或者说没有指针指变量存储地址时,会被回收
p49
class Point { private double x; private double y; Point(double x1, double y1) { x = x1; y = y1; } public double getX() { return x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setX(double i) { x = i; } public void setY(double i) { y = i; } } class Circle { private Poi nt o; private double radius; Circle(Point p, double r) { o = p; radius = r; } Circle(double r) { o = new Point(0.0, 0.0); radius = r; } boolean contains(Point p) { double x = p.getX() - o.getX(); double y = p.getY() - o.getY(); if(x*x + y*y > radius * radius) return false; else return true; } public void setO(double x, double y) { o.setX(x); o.setY(y); } public Point getO() { return o; } public double getRadius() { return radius;} public void setRadius(double r) { radius = r;} public double area() { return 3.14 * radius * radius; } } public class TestCircle { public static void main(String args[]) { Circle c1 = new Circle(new Point(1.0,2.0), 2.0); Circle c2 = new Circle(5.0); System.out.println("c1:("+c1.getO().getX()+"," +c1.getO().getY()+"),"+c1.getRadius()); System.out.println("c2:("+c2.getO().getX() +","+c2.getO().getY()+"),"+c2.getRadius()); System.out.println("c1 area = "+c1.area()); System.out.println("c1 area = "+c2.area()); c1.setO(5,6); c2.setRadius(9.0); System.out.println("c1:("+c1.getO().getX()+"," +c1.getO().getY()+"),"+c1.getRadius()); System.out.println("c2:("+c2.getO().getX()+"," +c2.getO().getY()+"),"+c2.getRadius()); System.out.println("c1 area = "+c1.area()); System.out.println("c1 area = "+c2.area()); Point p1 = new Point(5.2, 6.3); System.out.println(c1.contains(p1)); System.out.println(c1.contains(new Point(10.0,9.0))); } }
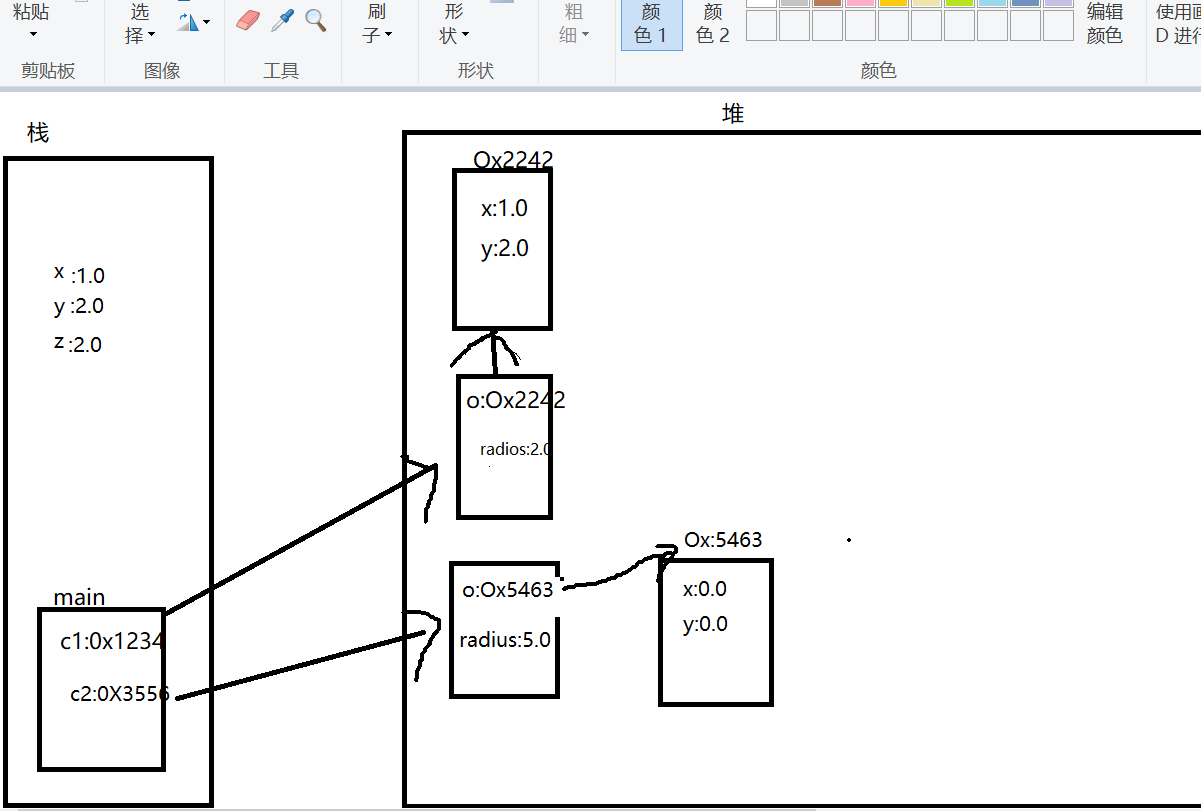
内存分析
1 Circle c1 = new Circle(new Point(1.0,2.0), 2.0); 2 Circle c2 = new Circle(5.0);

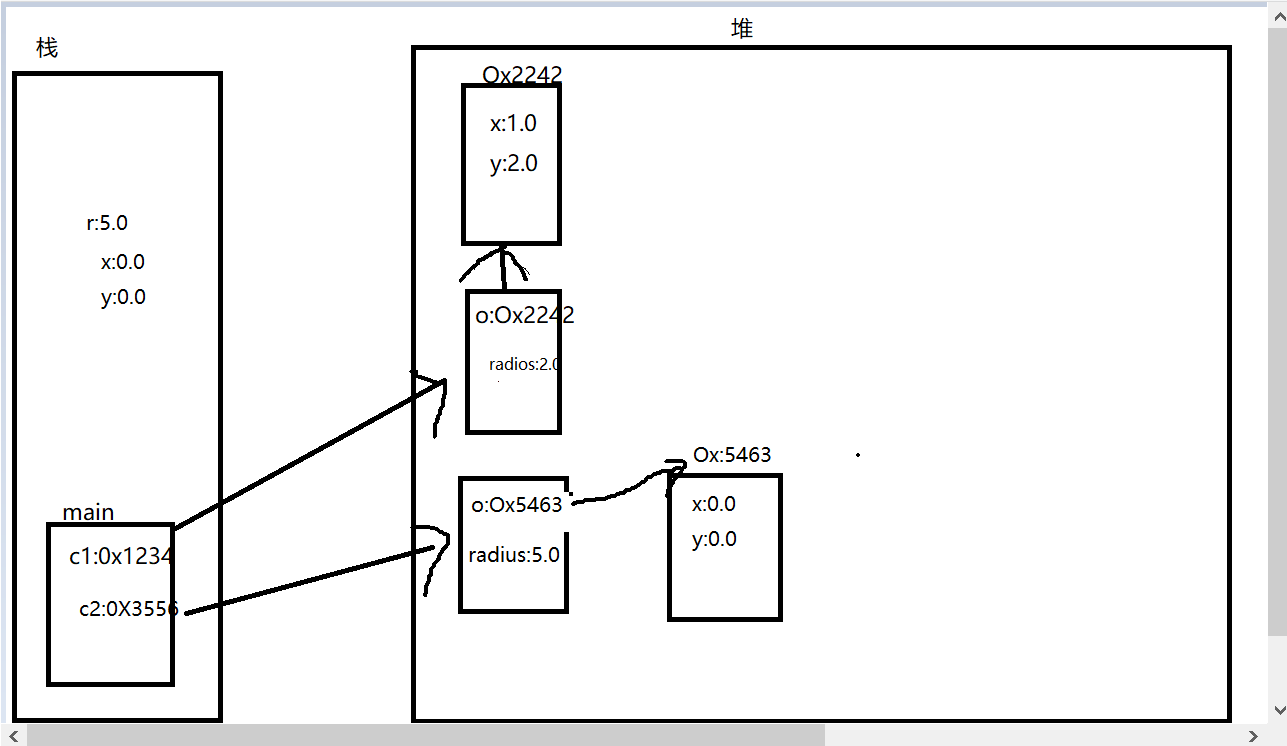
3 System.out.println("c1:("+c1.getO().getX()+","
+c1.getO().getY()+"),"+c1.getRadius()); 4 Point p1 = new Point(5.2, 6.3);
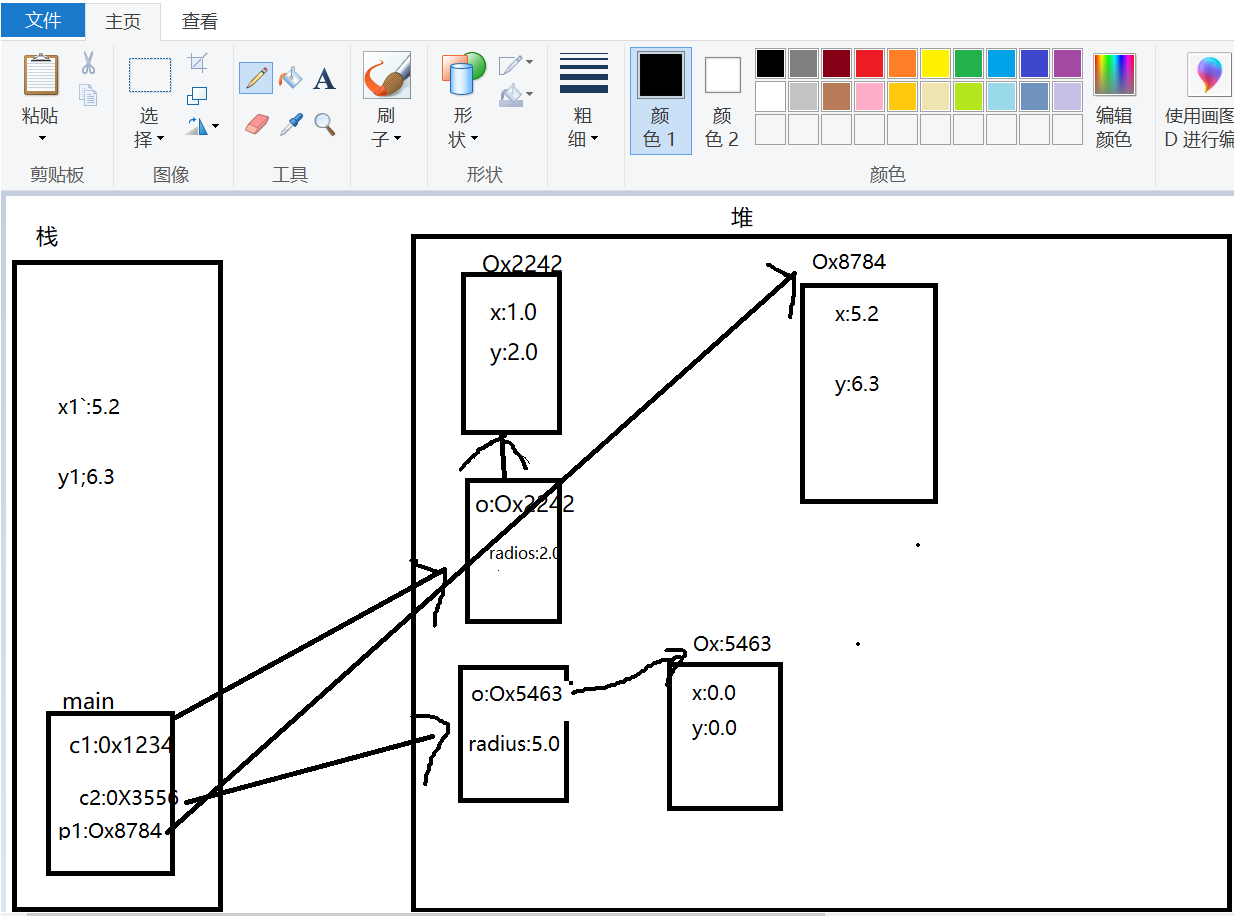
5 System.out.println(c1.contains(p1));
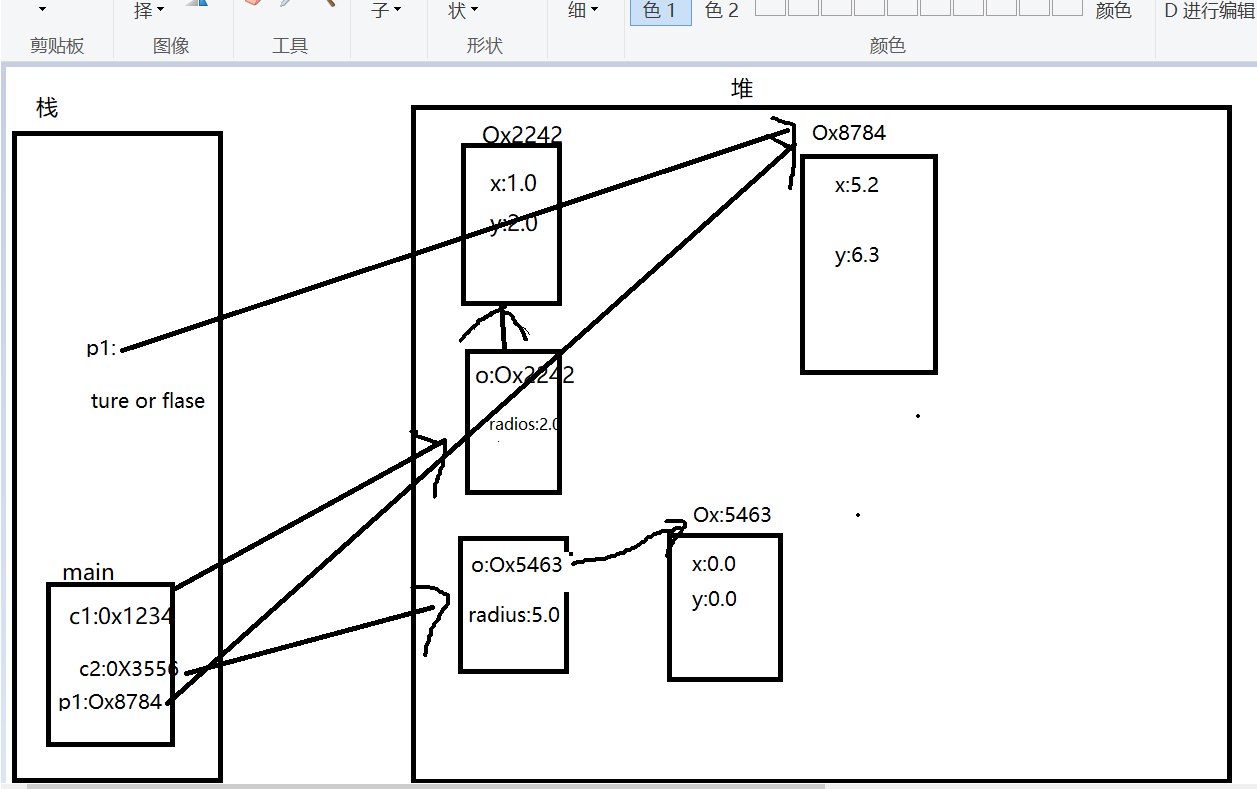
6 System.out.println(c1.contains(new Point(10.0,9.0)));
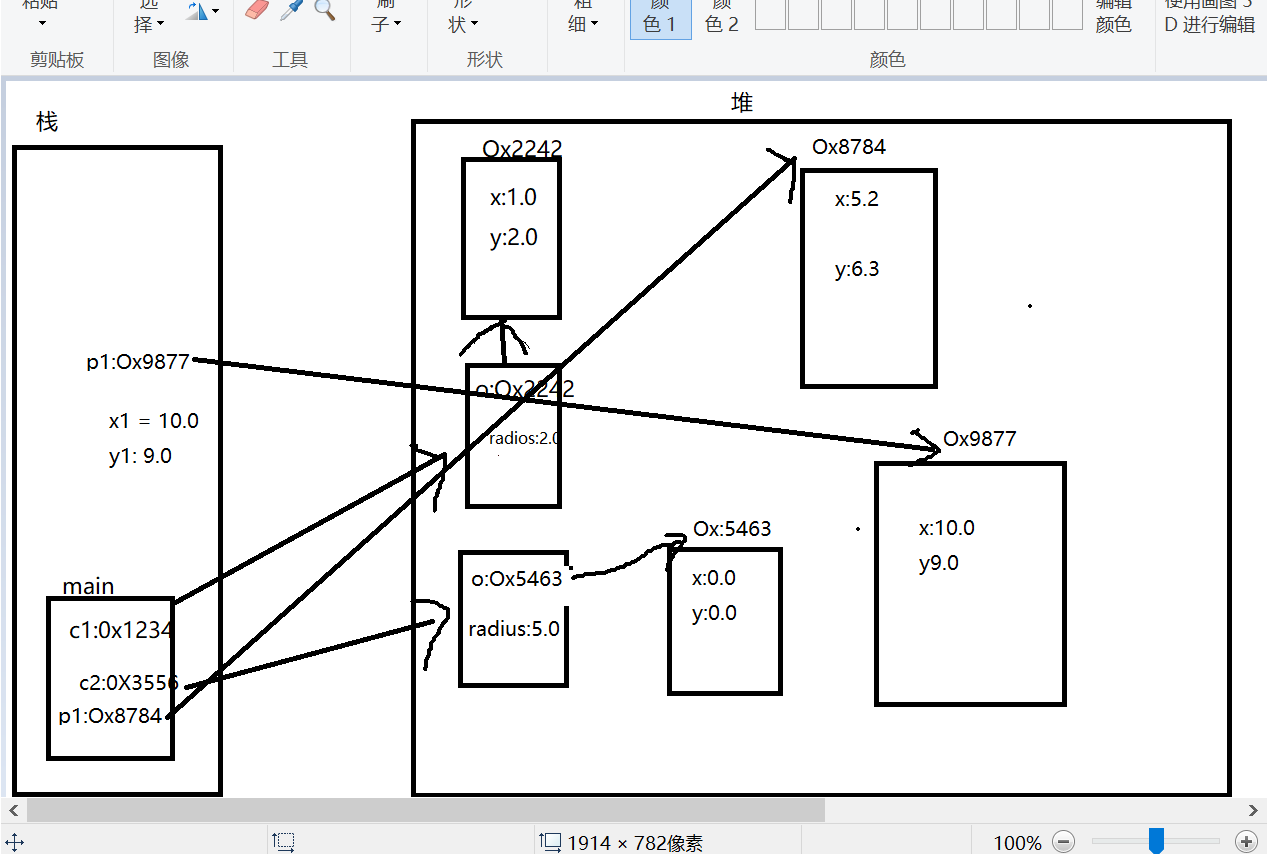
p51 static 关键字
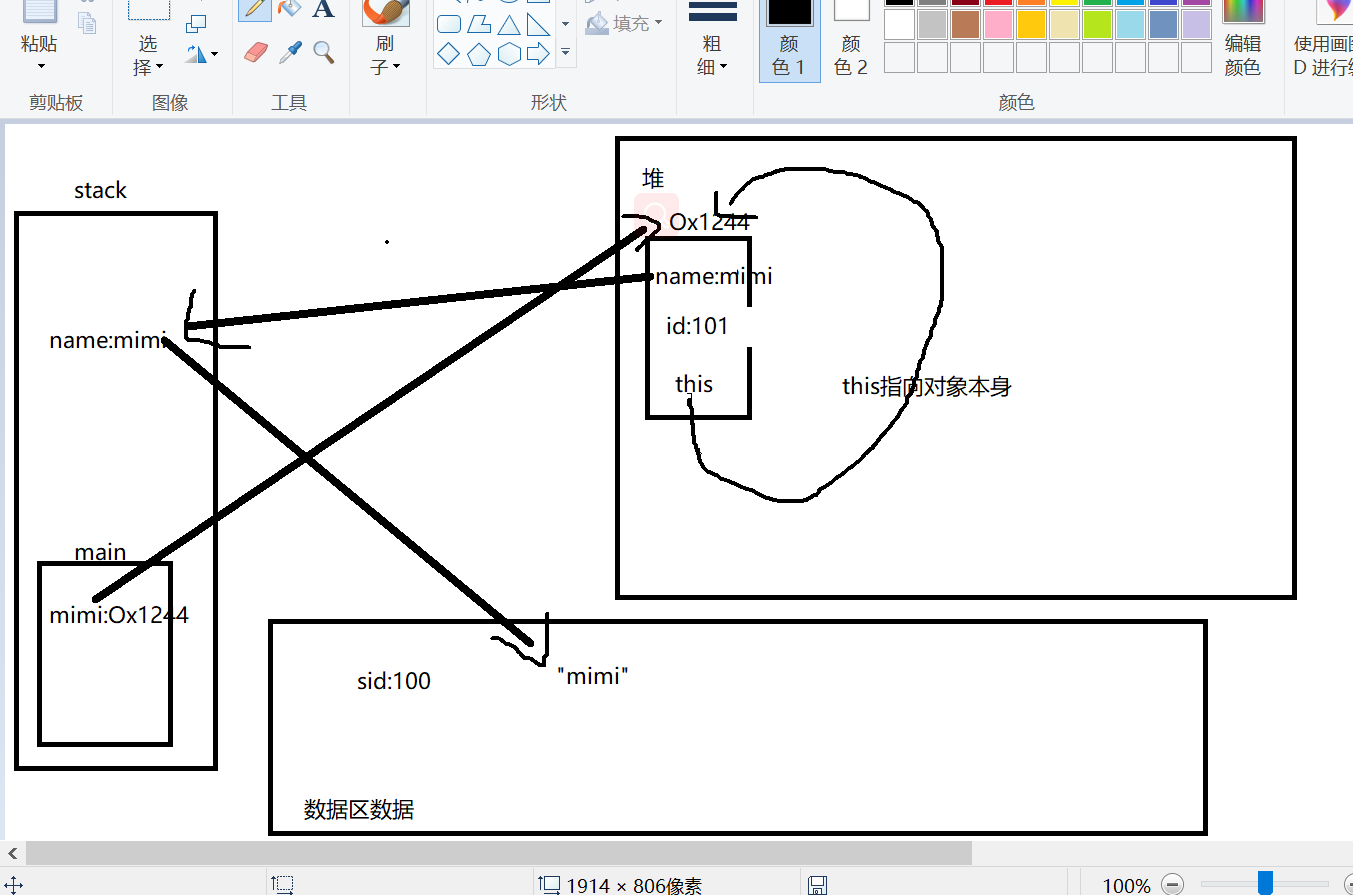
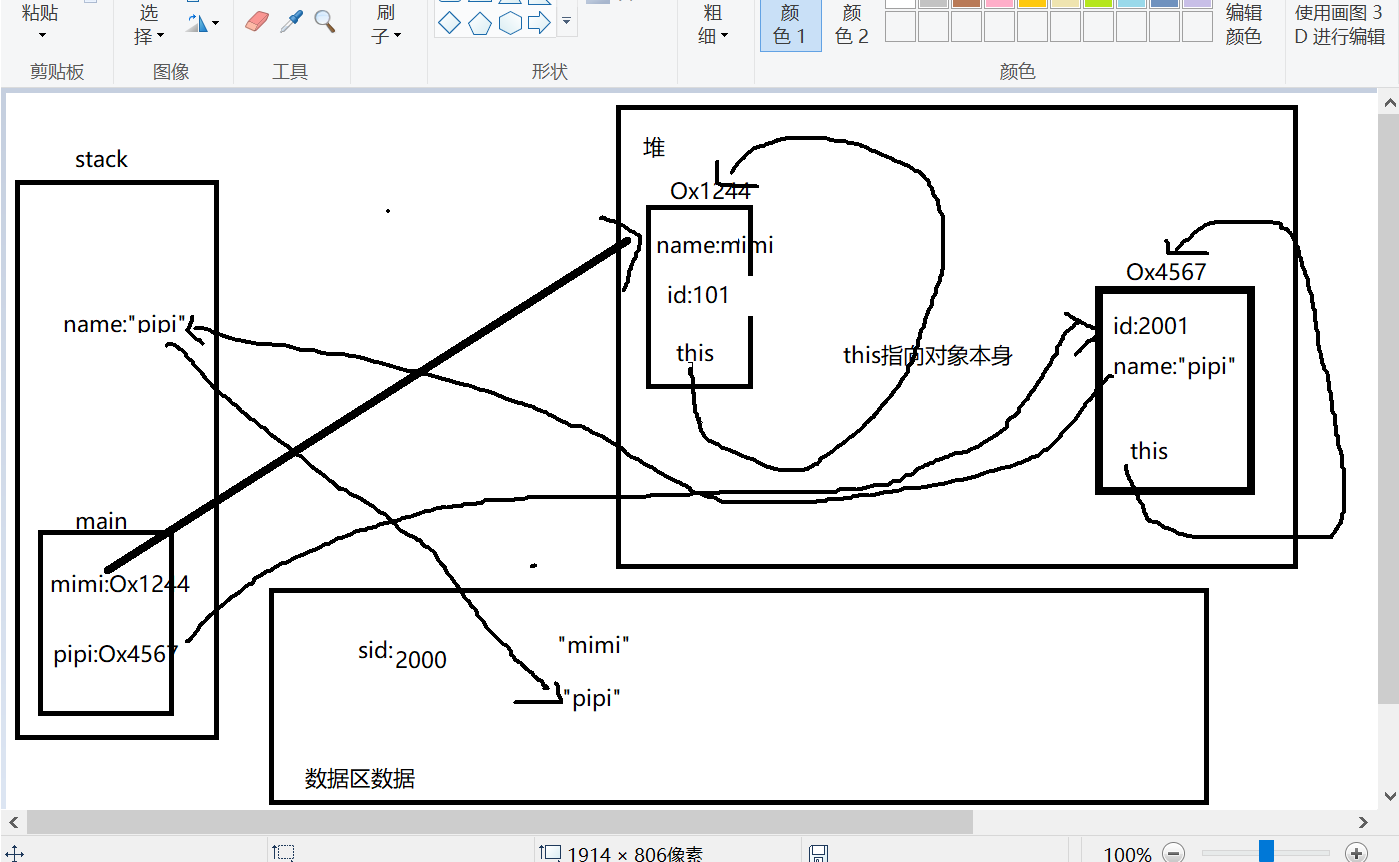
public class Cat { private static int sid = 0; private String name; int id; Cat(String name) { this.name = name; id = sid++; } public void info(){ System.out.println ("My name is "+name+" No."+id); } public static void main(String arg[]){ Cat.sid = 100; Cat mimi = new Cat("mimi"); mimi.sid = 2000; Cat pipi = new Cat("pipi"); mimi.info(); pipi.info(); } }
static xx 静态成员变量 放在数据区服务于整个类,没有new出对象也能调用,通过类调用,而且只有一个,无论new出多少对象也只有一个而且在数据区,字符串常量也放在数据区 字符串也是一种对象 在静态方法里面不能直接访问非静态的成员和方法,必须先new一个对象,然后用对象访问,如果是静态的成员和方法,可以直接用类访问
this 指向对象本身
内存分析
Cat.sid = 100;
Cat mimi = new Cat("mimi");
id = sid++; 错误应该先赋值,sid再自增 所以 id = 100 sid = 101
mimi.sid = 2000;
Cat pipi = new Cat("pipi");
id = sid++; 错误应该先赋值,sid再自增 所以 id = 2000 sid = 2001
p59 重写
class test4 { public static void main(String[] args){ Student1 s = new Student1(); Person1 p = new Person1(); p.setAge(32); p.setName("wet"); p.display(); s.setAge(31); s.setName("we"); s.setSchool("ert"); s.display(); } } class Person1{ int age; String name; public void setAge(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge(){ return age; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void display(){ //重写 System.out.println("age:"+age+" "+"name:"+" "+name); } } class Student1 extends Person1 { String school; public void setSchool(String school){ this.school = school; } public String getSchool(){ return school; } public void display(){ //重写 System.out.println("age:"+age+" "+"name:"+name+" "+"school:"+school); } }
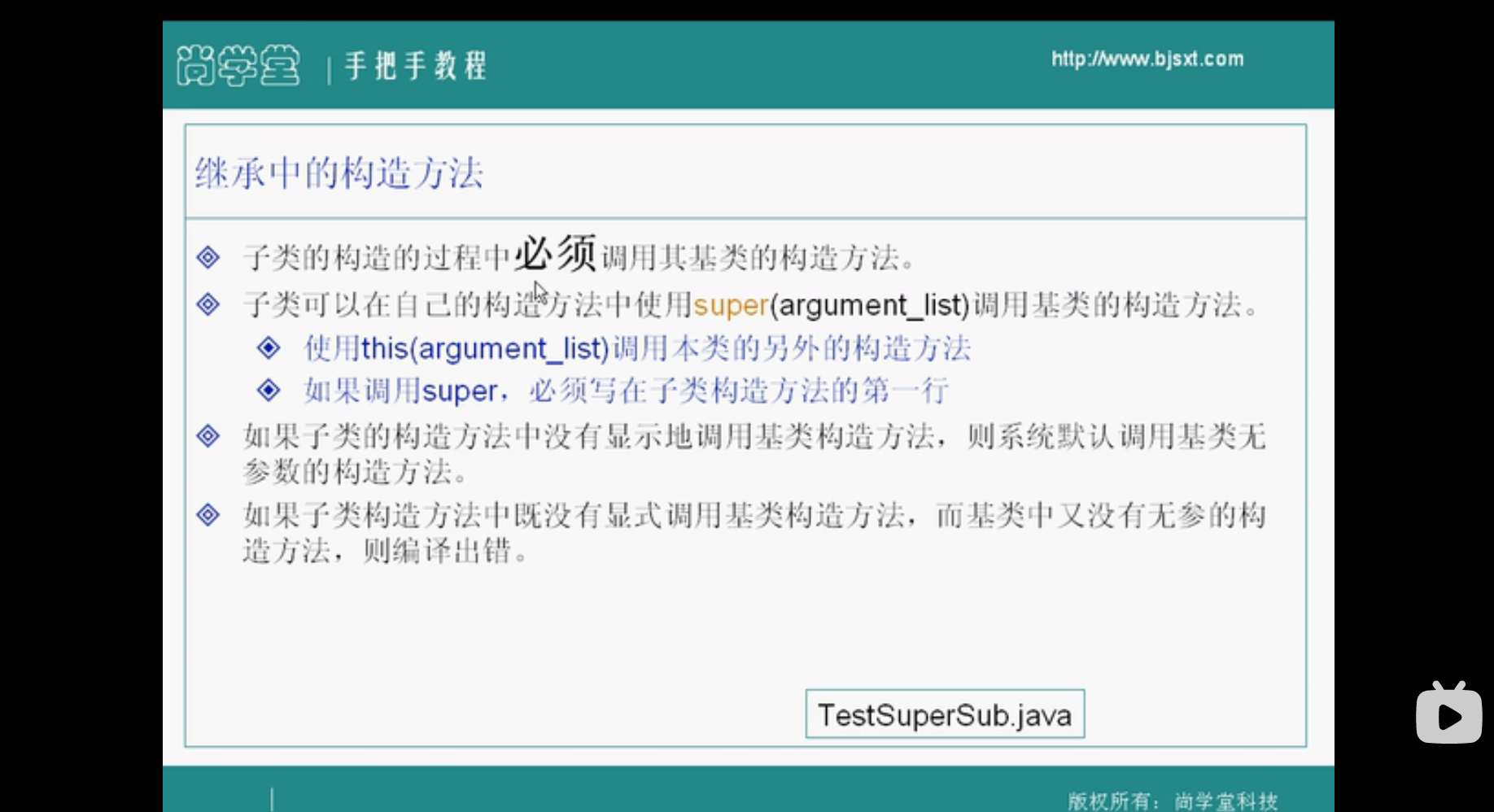
p61:继承中的构造方法
super指向父类的对象,this指向子类本身的对象,子类的构造过程中必须用super调用父类的构造方法
如果调用super必须写在子类构造方法的第一行,就是先调用父类的构造方法再调用子类的构造方法
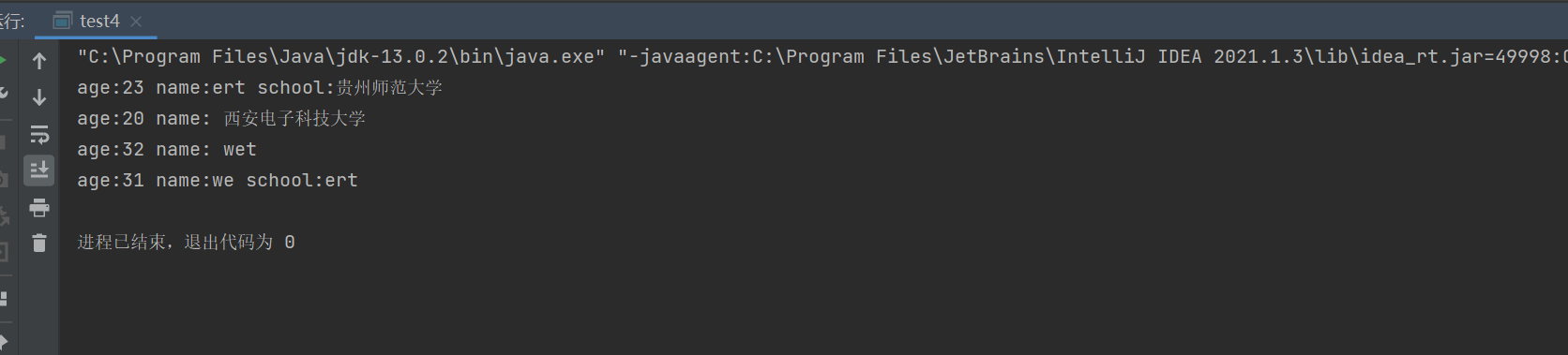
class test4 { public static void main(String[] args){ Student1 s = new Student1("贵州师范大学"); s.display(); Person1 p = new Person1(20,"西安电子科技大学"); p.display(); p.setAge(32); p.setName("wet"); p.display(); s.setAge(31); s.setName("we"); s.setSchool("ert"); s.display(); } } class Person1{ protected int age; String name; Person1(){ } Person1(int age,String name){ this.age = age; this.name = name; } void setAge(int age){ this.age = age; } protected int getAge(){ return age; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void display(){ System.out.println("age:"+age+" "+"name:"+" "+name); } } class Student1 extends Person1 { String school; Student1(){ } Student1(String school){ super(23,"ert"); //构造方法中的第一行 this.school = school; } public void setSchool(String school){ this.school = school; } public String getSchool(){ return school; } public void display(){ System.out.println("age:"+age+" "+"name:"+name+" "+"school:"+school); } }
p69 Object类---equals()
Object 是所有类的父类 所以在调用API里Object的方法时都是重写
equals()默认的是,引用指向对象的内存地址相同返回ture,反之返回false,所以自定义的类,重写equals()时应该重写
public class TestEquals { public static void main(String[] args){ Cat C = new Cat(2,3,4); Cat C1 = new Cat(2,3,4); System.out.println(C.equals(C1)); } } class Cat{ int weight; int height; int colour; Cat(int weight,int height,int colour){ this.weight = weight; this.height = height; this.colour = colour; } public boolean equals(Object obj){ //重写父类Object的方法 if(obj instanceof Cat){
if(((Cat) obj).colour==this.colour&&((Cat)obj).weight==this.weight&&((Cat)obj).height==this.height){
return true; } } return false; } }
p 71--对象转型
public class TeatAnimal { public static void main(String[] args){ TeatAnimal T = new TeatAnimal(); Animal A = new Animal(2,7); Cat1 C = new Cat1(3); Cat1 C1 = new Cat1(4); Dog D = new Dog("雄"); System.out.println(C instanceof Cat1); System.out.println(D instanceof Animal); System.out.println(A instanceof Dog); T.print(C); T.print(A); T.print(D); } public void print(Animal A){ //父类的指针变量可指向子类的对象,把子类的指针变量传参给父类的指针变量这个方法就不用写三个打印的方法了,当然子类的指针变量也可以指向父类的对象 if(A instanceof Cat1){ Cat1 c = (Cat1)A; System.out.println("weight:"+c.weight+" "+"height:"+c.height+" "+"colour:"+c.colour); }else if(A instanceof Dog){ //因为当父类的指针变量指向子类的对象时只能访问到,在子类对象中自身存在的成员变量,所以需强转父类的指针变量成为子类的指针变量才能访问该子类的所有成员变量 Dog d = (Dog)A; System.out.println("weight:"+d.weight+" "+"height:"+d.height+" "+"ext:"+d.ext); } } } class Animal { int weight; int height; Animal(){ } Animal(int weight,int height){ this.height = height; this.weight = weight; } } class Cat1 extends Animal{ int colour; Cat1(int colour){ super(3,5); this.colour = colour; } } class Dog extends Animal{ String ext; Dog(String ext){ super(3,4); this.ext = ext; } }
p72 --动态绑定或多态
动态绑定是new谁就调用谁的方法
多态产生的条件:
1,要有继承 2,要有重写 3,父类的引用指向子类
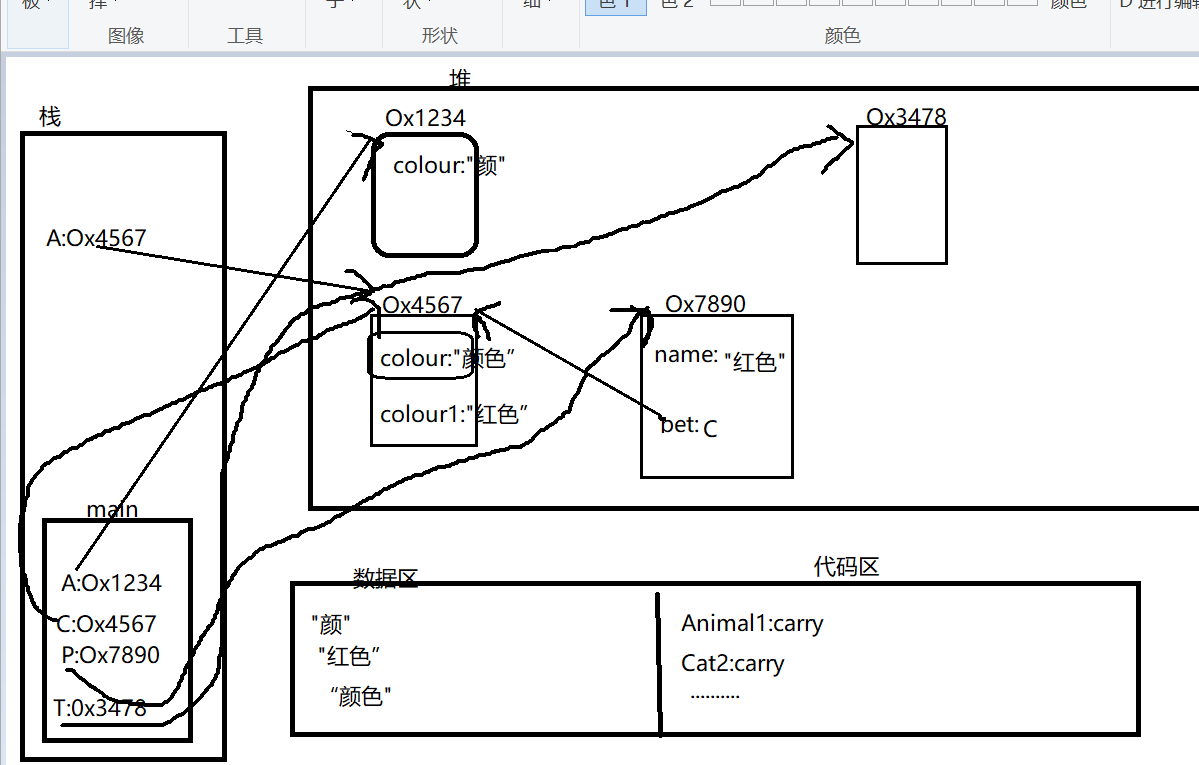
public class Test7 { public static void main(String[] args){ Animal1 A = new Animal1("颜"); Cat2 C = new Cat2("红色"); Person4 P = new Person4("白色",C); //多态,动态绑定,new的是Cat2的对象,就调用Cat2的重写方法,而不是父类的 P.println(); Test7 T = new Test7(); T.display(C); } void display(Animal1 A){ if(A instanceof Animal1){ Cat2 c = (Cat2)A; System.out.println("colour1:"+c.colour1); System.out.println(c.carry()); } } } class Animal1{ String colour; Animal1(String colour){ this.colour = colour; } boolean carry(){ System.out.println("叫了"); return false; } } class Cat2 extends Animal1{ String colour1; Cat2(String colour1){ super("颜色"); this.colour1 = colour1; } boolean carry(){ System.out.println("猫叫了"); return false; } } class Person4{ String name; Animal1 pet; Person4(String name,Animal1 pet){ this.name = name; this.pet = pet; } void println(){ pet.carry(); } }
内存分析:
Animal1 A = new Animal1("颜");
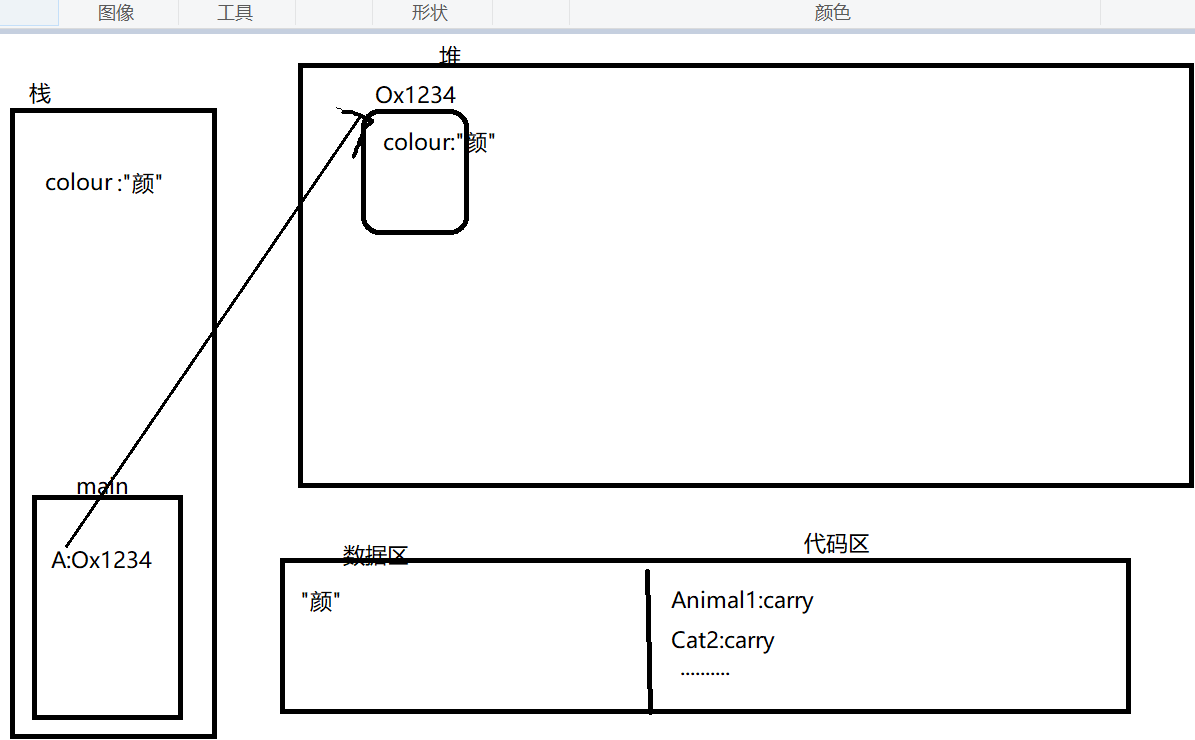
Cat2 C = new Cat2("红色");
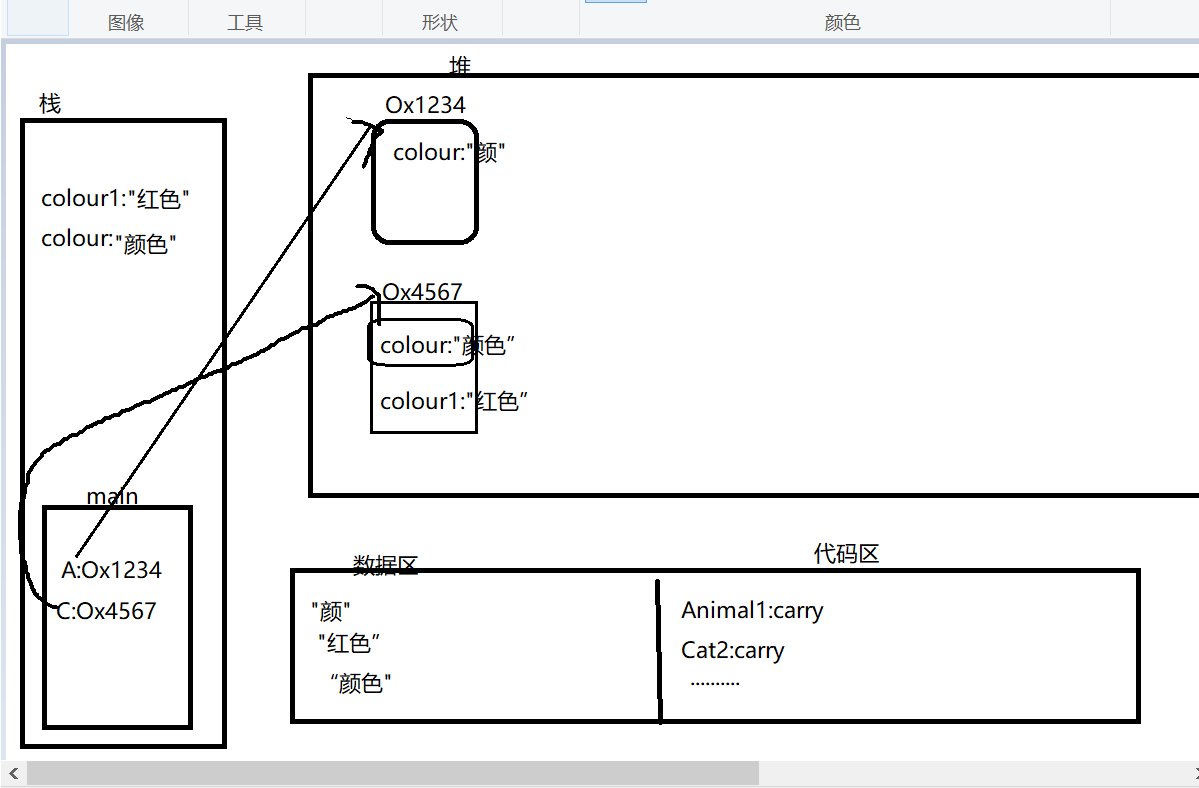
Person4 P = new Person4("白色",C);
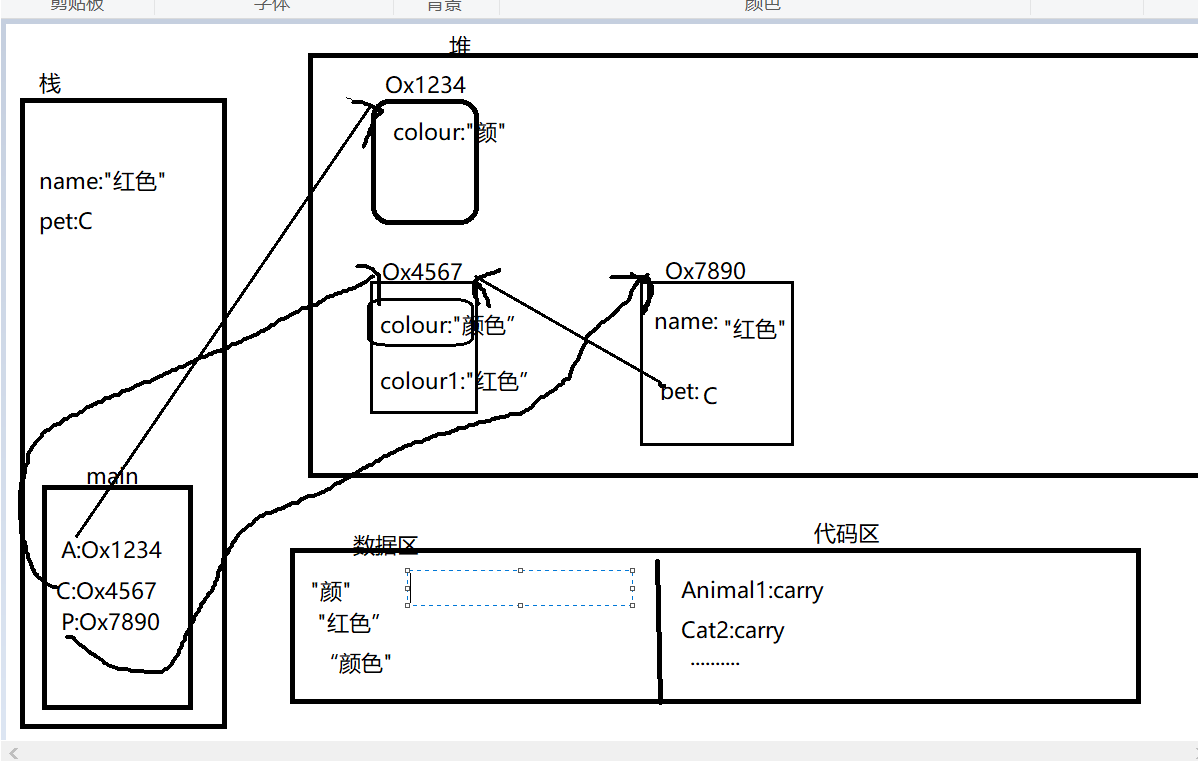
Test7 T = new Test7();
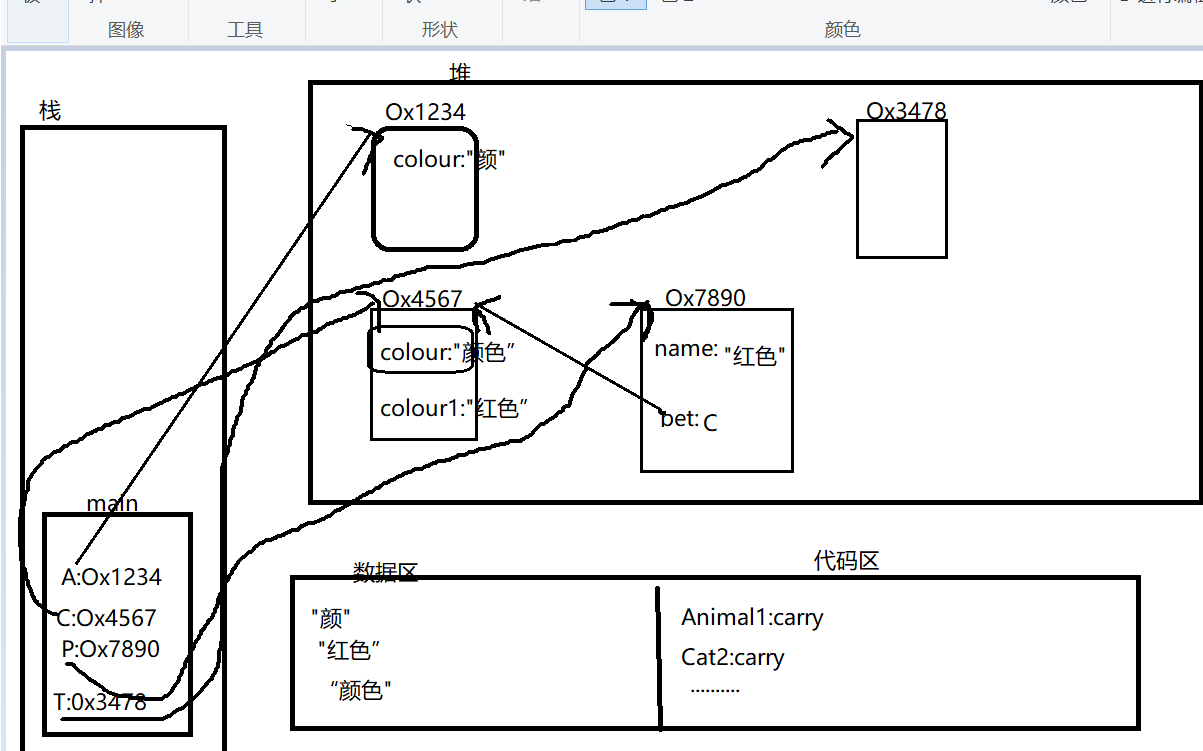
T.display(C);
P74 抽象类
抽象类是为了重写方便用的,因为子类重写父类的方法后,父类的方法就没有实现的必要了,所以父类的方法和类前面都要加上abstract关键字,类似c++的纯虚函数

abstract class Animal { private String name; Animal(String name) {this.name = name;} /* public void enjoy(){ System.out.println("叫声......"); } */ public abstract void enjoy(); } abstract class Cat extends Animal { private String eyesColor; Cat(String n,String c) {super(n); eyesColor = c;} /* public void enjoy() { System.out.println("猫叫声......"); } */ //public abstract void enjoy(); } class Dog extends Animal { private String furColor; Dog(String n,String c) {super(n); furColor = c;} public void enjoy() { System.out.println("狗叫声......"); } } class Bird extends Animal { Bird() { super("bird"); } public void enjoy() { System.out.println("鸟叫声......"); } } class Lady { private String name; private Animal pet; Lady(String name,Animal pet) { this.name = name; this.pet = pet; } public void myPetEnjoy(){pet.enjoy();} } public class Test { public static void main(String args[]){ Cat c = new Cat("catname","blue"); Dog d = new Dog("dogname","black"); Bird b = new Bird(); //Lady l1 = new Lady("l1",c); Lady l2 = new Lady("l2",d); Lady l3 = new Lady("l3",b); //l1.myPetEnjoy(); l2.myPetEnjoy(); l3.myPetEnjoy(); } }
P 76 接口
P 76 接口 接口也可以说是一种特殊的抽象类,不能实例化对象,其方法也不实现,要其他类来重写,和实现它的类,
而且变量也是默认是静态不可改变的,放在数据区,而且也像抽象父类一样,如果一个类实现了该接口,就必须重写该接口的方法
如果不想重写那么该类必须是抽象类 在c++多继承中,那么接口就是多继承的父类,只不过是纯虚函数的父类
接口可以继承接口 类可以继承类

public class TestInterface { public static void main(String[] args){ Sing s = new Student5("学生"); s.sing(); s.sleep(); Sing s3 = new Teacher5("老师" ); s3.sing(); s3.sleep(); Draw d2 = (Draw)s3; d2.draw(); TestInterface T2 = new TestInterface(); T2.Teat(new Student5("学生")); T2.Teat(new Teacher5("老师" )); } public void Teat(Sing sing){ if(sing instanceof Student5){ System.out.println(true); Student5 s2 = (Student5)sing; s2.study(); }else if(sing instanceof Teacher5){ System.out.println(true); Teacher5 T = (Teacher5)sing; T.draw(); } } } interface Sing{ public static final int id = 1;//如果不写默认也是public static final public void sing(); public void sleep(); } interface Draw{ public void draw(); } class Student5 implements Sing{ String name; Student5(String name){ this.name = name; } public void sing(){ System.out.println("学生会唱歌"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("学生会睡觉"); } public void study(){ System.out.println("学生会学习"); } } class Teacher5 implements Sing,Draw{ String name; Teacher5(String name){ this.name = name; } public void sing(){ System.out.println("老师会唱歌"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("老师会睡觉"); } public void draw(){ System.out.println("老师会画画"); } }
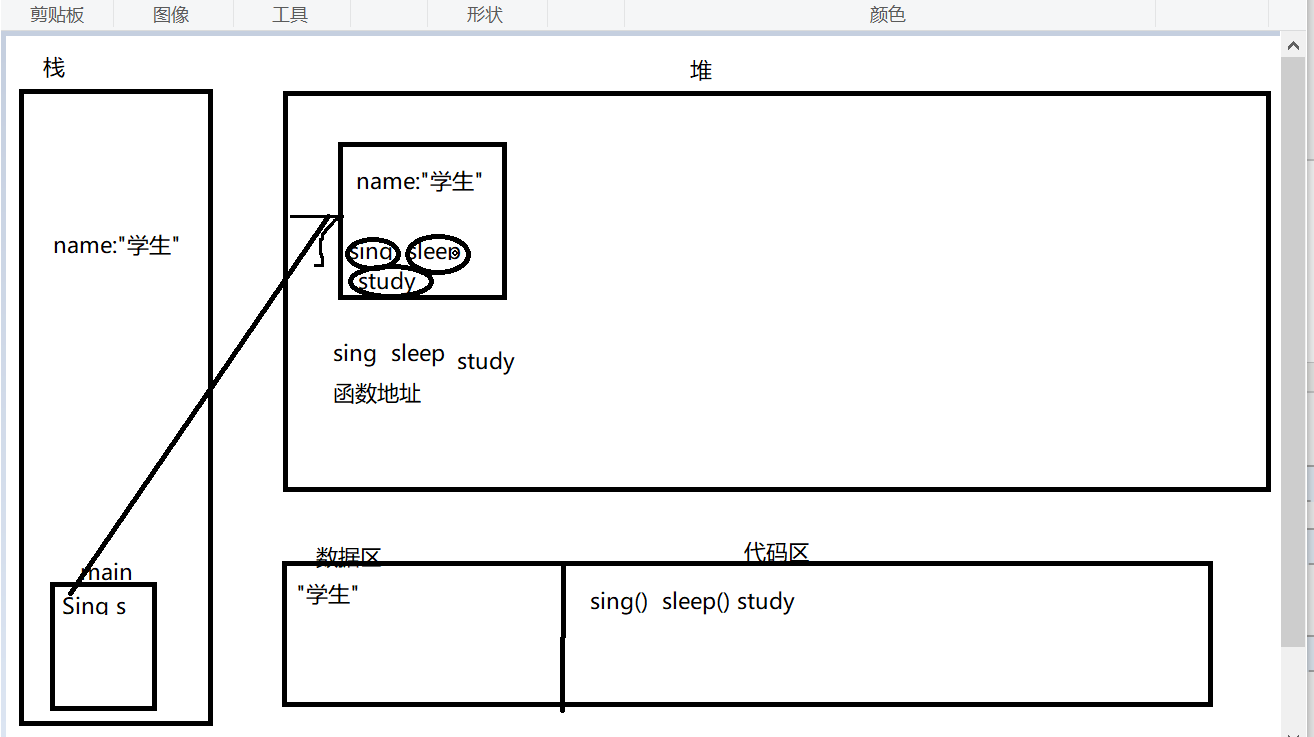
内存分析:
Sing s = new Student5("学生");
Sing s3 = new Teacher5("老师" );
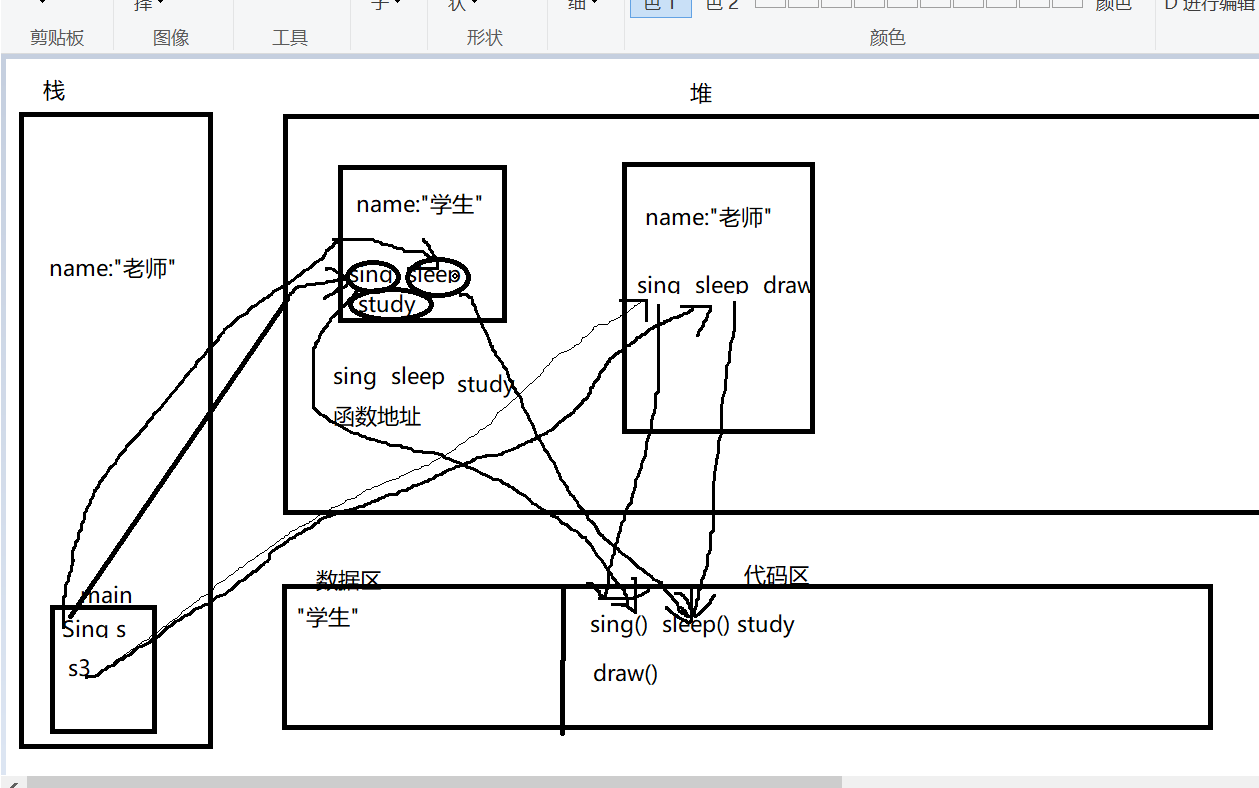
TestInterface T2 = new TestInterface();
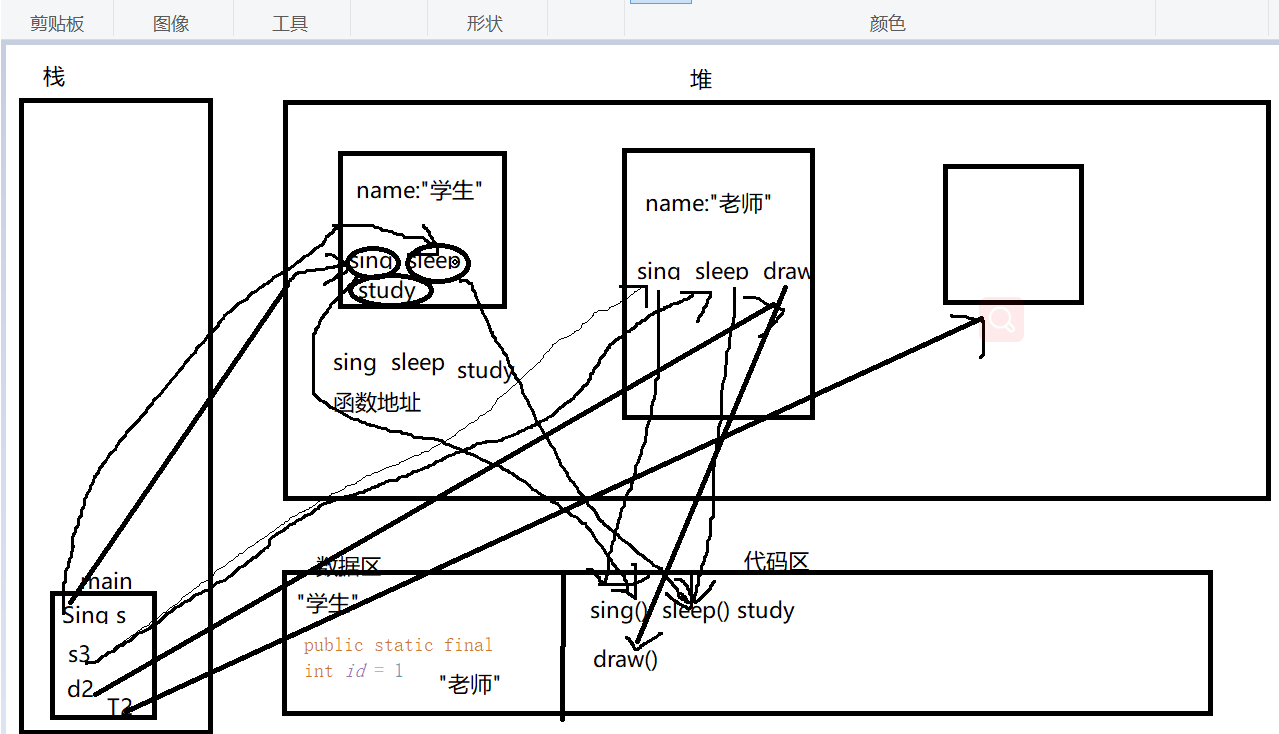
T2.Teat(new Student5("学生"));
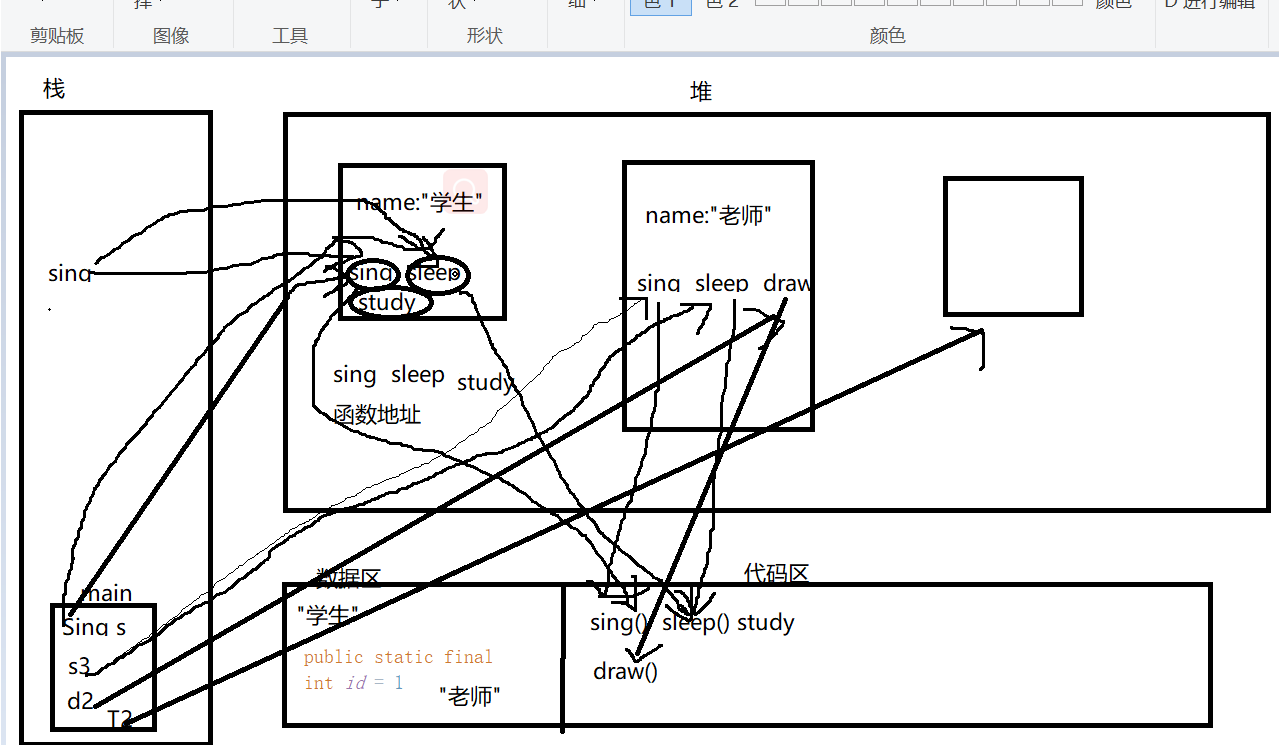
接口可以继承接口 类可以继承类
public class Test8 { public static void main(String[] args){ Animal8 A = new monkey("猴子"); monkey m = (monkey)A; System.out.println(m.value()); m.eat(); m.protect(); Value V = new monkey("猴子"); V.value(); } } abstract class Animal8{ Animal8(String name){ this.name = name; } String name; abstract void enjoy(); } interface Value{ public int value(); } interface Protect{ public void protect(); } interface Eat extends Value,Protect{ public void eat(); } class monkey extends Animal8 implements Eat{ String name; monkey(String name){ super("动物"); this.name = name; } public void enjoy(){ System.out.println("猴子的喜爱是爬树"); } public int value(){ return 10000; } public void protect(){ System.out.println("猴子受保护"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("猴子吃香蕉"); } }
p78面向对象总结