第01周 预习、实验与作业:绪论与Java基本语法(JAVA预习作业)
- 第一个JAVA程序
-
HelloWorld.java
HelloWorld是主文件名
.java是源程序的扩展名 -
HelloWorld
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
1)class后面的HelloWorld是类名
2)主文件名与类名需一样
- 虚拟机(JVM)
- 怎么实现跨平台?
使用虚拟机!
Java Virtual Machine - .class文件可以运行,但
不是直接运行在操作系统
上,而是运行在虚拟机上! - JVM又是什么?
jvm是一个程序,可直接运
行在各操作系统上,并且可
载入.class字节码文件。
每个操作系统都有对应的虚
拟机程序。
- 课前问题列表(选做)
- 怎么比较两个字符串内容是否相同?可以直接用= =吗?为什么对基本数据类型可以直接使用= =?对引用数据类型不行?
答:
“==”操作符用于比较两个对象的地址是否相等。
.equals() 方法用于比较两个对象的内容是否相等。
要比较两个字符串的内容是否相同,应该使用 equals() 方法。
这是 String 类提供的一个实例方法,它比较两个字符串的内容。
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "hello";
boolean areEqual = str1.equals(str2);
// areEqual 将会是 true
对于基本数据类型(如 int、char、double 等),它们不是对象,它们直接存储值。因此,当使用 == 比较基本数据类型时,比较的是它们的值。
- 阅读如下代码
Integer x = Integer.valueOf("10");
Integer y = x + 1;
int z = x + y;
x是Integer类型,1是int类型,为什么他们可以相加,使用了什么技术?z是int,x与y是Integer类型,却可以直接将x + y 赋给z,使用了什么技术?
答:
- PTA编程
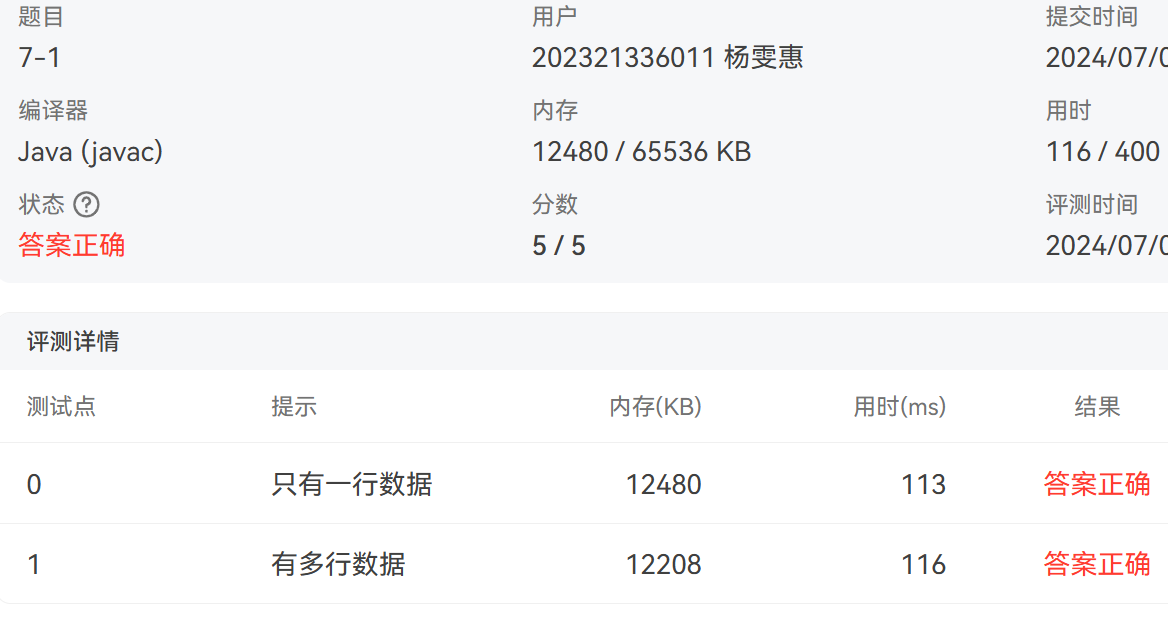
1. 7-1 jmu-java-01入门-基本输入
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextInt()) {
int a =sc.nextInt();
int b =sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+b);
}
sc.close();
}
}
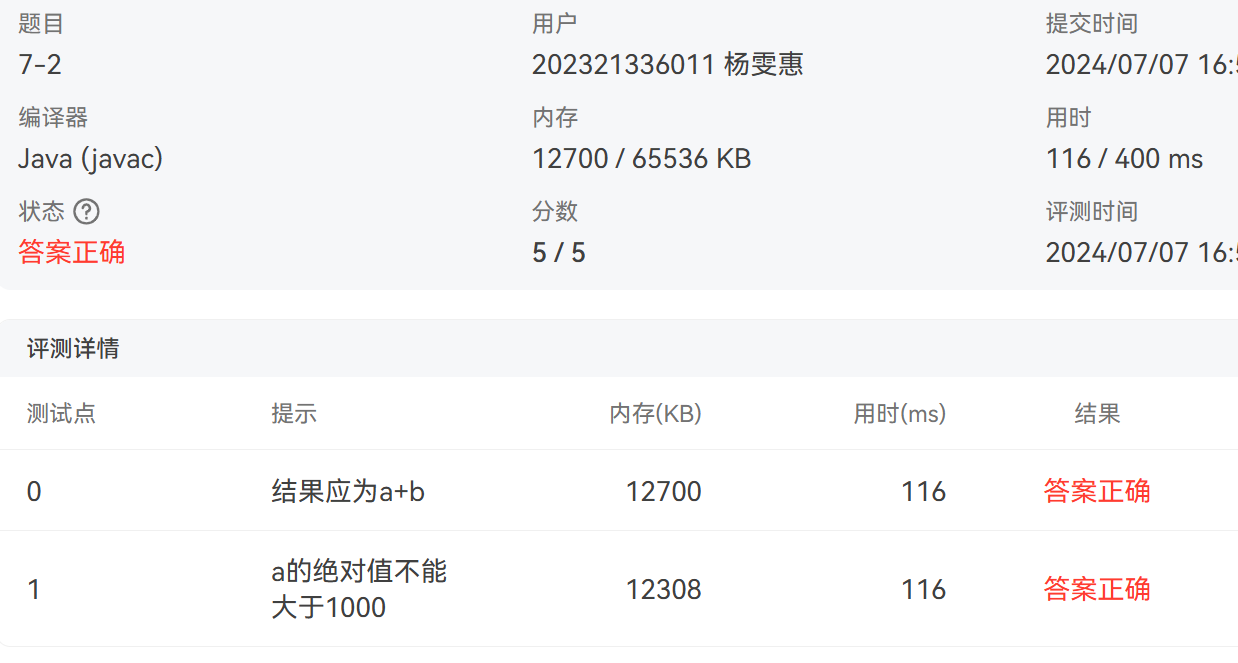
2. 7-2 jmu-Java-01入门-第一个PTA上Java程序
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextInt()){
int a=sc.nextInt();
int b=sc.nextInt();
if(Math.abs(a)>1000){
System.out.println("|a|>1000");
}
if(Math.abs(a)<=1000){
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
}
}
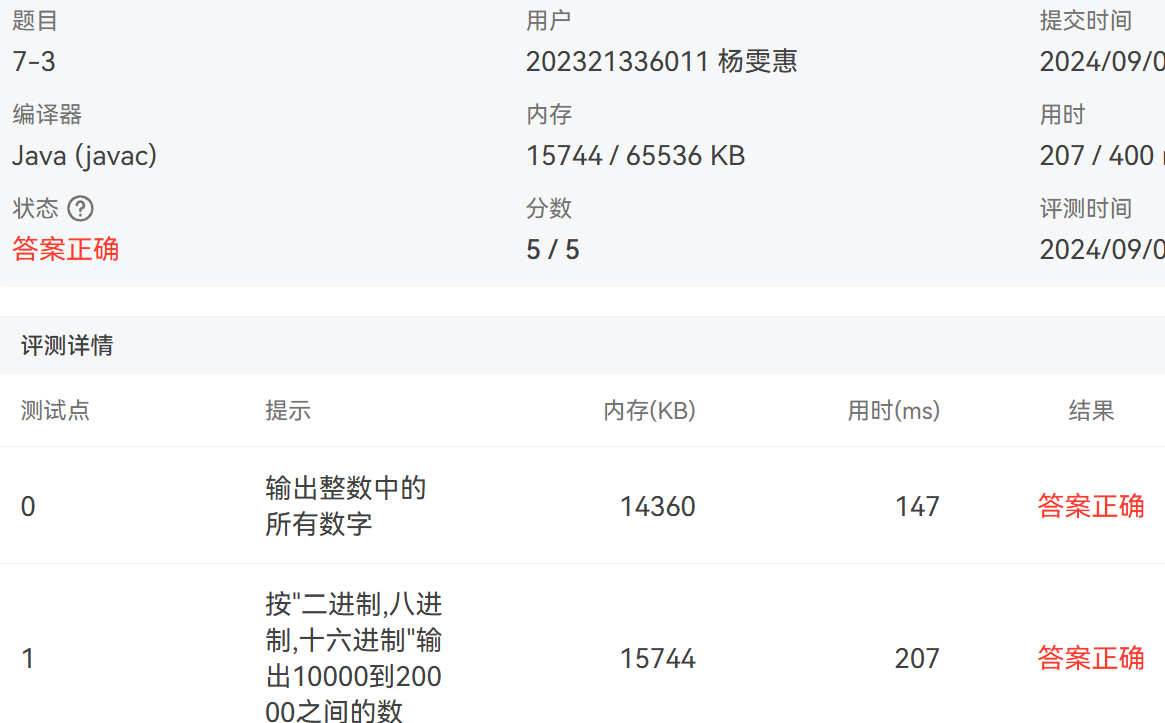
3. 7-3 jmu-Java-01入门-取数字
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (sc.hasNext()) {
String a = sc.next();
int x = Integer.parseInt(a);
if (x >= 1_0000 && x <= 2_0000) {
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(x)+","+Integer.toOctalString(x)+","+Integer.toHexString(x));
} else {
char[] charArray = a.toCharArray();
int b = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
if (charArray[i] >= '0' && charArray[i] <= '9') {
System.out.print(charArray[i] + " ");
b += charArray[i] - '0';
}
}
System.out.println(b);
}
}
sc.close();
}
}
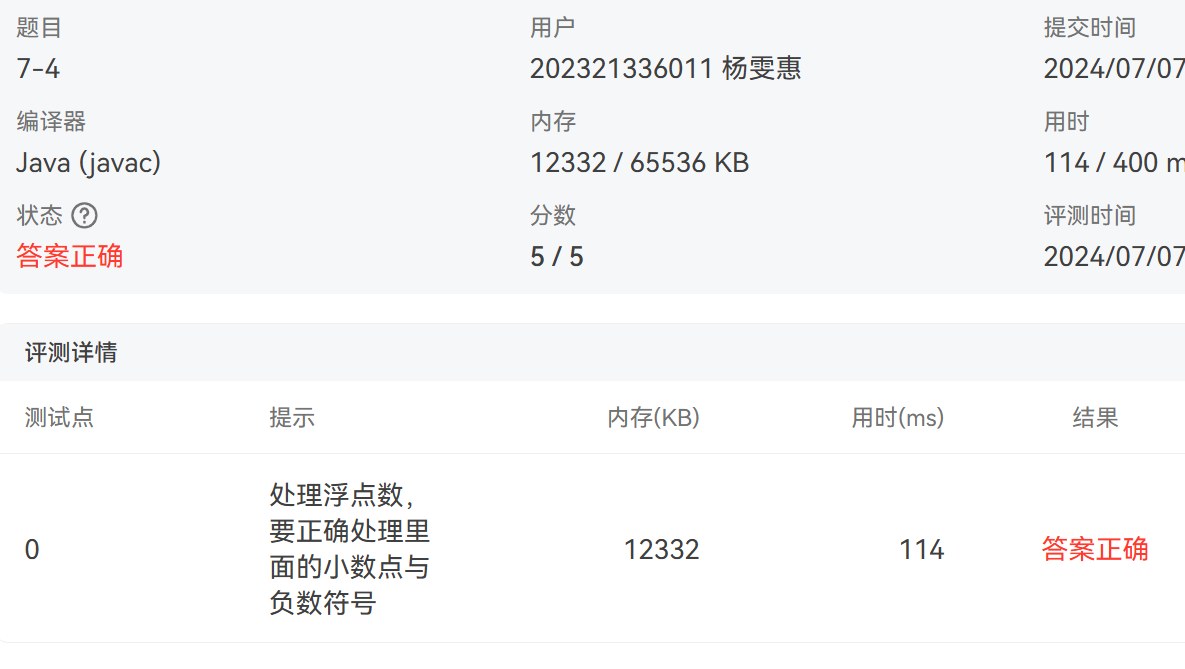
4. 7-4 jmu-Java-01入门-取数字浮点数
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String x;
while (sc.hasNext()) {
x = sc.nextLine();
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < x.length(); i++) {
if(x.charAt(i)>='0'&&x.charAt(i)<='9')
{
sum+=x.charAt(i)-'0';//转化成数字了
}
}
System.out.println(sum);//要for循环结束再累加
}
sc.close();
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号