Java 快速排序法 冒泡排序法 选择排序法 插入排序法
1.快速排序的原理:
选择一个关键值作为基准值。比基准值小的都在左边序列(一般是无序的),比基准值大的都在右边(一般是无序的)。
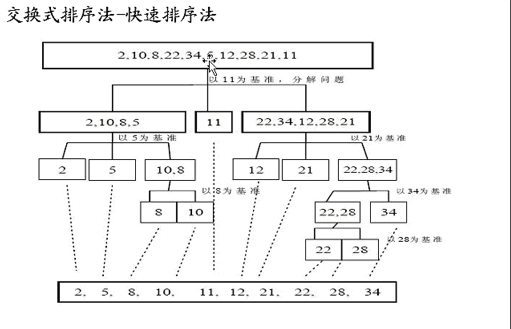
从后往前比较,用基准值和最后一个值比较,如果比基准值小的交换位置,如果没有继续比较下一个,直到找到第一个比基准值小的值才交换。找到这个值之后,又从前往后开始比较,如果有比基准值大的,交换位置,如果没有继续比较下一个,直到找到第一个比基准值大的值才交换。直到从前往后的比较索引>从后往前比较的索引,结束第一次循环,此时,对于基准值来说,左右两边就是有序的了。
接着分别比较左右两边的序列,重复上述的循环。
代码实例:
public class FastSort { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("快速排序法测试"); int[] a = { 121, 16,12,222,3333,212, 15, 1, 30,23, 9,33,56,66,543,65,665 }; int start = 0; int end = a.length - 1; sort(a, start, end); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } } public static void sort(int[] a, int low, int high) { int start = low; int end = high; int key = a[low]; while (end > start) { // 从后往前比较 while (end > start && a[end] >= key) // 如果没有比关键值小的,比较下一个,直到有比关键值小的交换位置
//然后又从前往后比较 end--; if (a[end] <= key) { int temp = a[end]; a[end] = a[start]; a[start] = temp; } // 从前往后比较 while (end > start && a[start] <= key) // 如果没有比关键值大的,比较下一个,直到有比关键值大的交换位置 start++; if (a[start] >= key) { int temp = a[start]; a[start] = a[end]; a[end] = temp; } // 此时第一次循环比较结束,关键值的位置已经确定了。
// 左边的值都比关键值小,右边的值都比关键值大
// 但是两边的顺序还有可能是不一样的,进行下面的递归调用 } // 递归 if (start > low) sort(a, low, start - 1);// 左边序列。第一个索引位置到关键值索引-1 if (end < high) sort(a, end + 1, high);// 右边序列。从关键值索引+1到最后一个 } }
2.冒泡排序法
//冒泡排序 class MaoPao { public void sort(int[] arr) { int temp = 0; // 外层循环,它决定一共走几趟 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { // 内层循环开始逐个比较,如果发现前一个比后一个大则交换 for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; } } } } }
3.选择排序法
//选择排序 class Select { public void sort(int arr[]) { // 我认为第一个数就是最小 int temp = 0; for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1; j++) { int min = arr[j]; // 记录最小数的下标 int minIndex = j; for (int k = j + 1; k < arr.length; k++) { if (min > arr[k]) { // 修改最小 min = arr[k]; minIndex = k; } } // 当退出for就找到这次最小 temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[minIndex]; arr[minIndex] = temp; ; } } }
4.插入排序法
//插入排序 class InsertSort { public void sort(int arr[]) { for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { int insertVal = arr[i]; // insertVal准备和前一个数进行比较 int index = i - 1; while (index >= 0 && insertVal < arr[index]) { // 把arr[index]向后移动 arr[index + 1] = arr[index]; // 让index向前移动 index--; } // 将inserVal插入到适当位置 arr[index + 1] = insertVal; } } }
测试类:
public class PaiXu { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] t = { 33, 32, 12, 122, 1132, -22, 1237, 89, 222, 44, 55, 22, 24, 9776, -54, 0, 4432, 753, 56, 3, 37, 67 }; //验证冒泡 // MaoPao mao = new MaoPao(); // mao.sort(t); //验证选择 // Select s=new Select(); // s.sort(t); //验证插入 InsertSort ins = new InsertSort(); ins.sort(t); // 输出结果 for (int i = 0; i < t.length; i++) { System.out.print(t[i] + " "); } } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号