Java基础——collection接口
一、Collection接口的定义
public interfaceCollection<E>extends iterable<E>
从接口的定义中可以发现,此接口使用了泛型的定义,在操作时必须指定具体的操作类型。这样可以保证类集操作的安全性,避免发生ClassCastException异常。
Collection是最基本的集合接口,一个Colletion代表一组Object,即Collection的元素(Elements)。Java JDK提供的类都是继承自Collection的“子接口”如List和Set。
所有实现Collection接口的类都必须提供两个标准的构造函数:
1.无参数的构造函数用于创建一个空的Collection;
2.有一个Collection参数的构造函数用于创建一个新的Collection,这个行的Collection与传统的Collection有相同的元素。这个构造函数允许用户复制一个Collection。
回顾:数组
1 int [] x=new int[5]; //声明一个数组,长度为5,每个元素都是 int型 2 Student [] list=new Student[5]; //声明一个数组,长度为5,每个元素都是 Student 型

二、Collection常用的方法
直接撸代码:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 Collection<String> d = new ArrayList<String>(); 10 Collection<String> e = new ArrayList<String>(); 11 Collection<String> f = new ArrayList<String>(); 12 13 // Integer中的i要大写 14 ArrayList<Integer> h = new ArrayList<Integer>();// h和g做比较 15 16 h.add(4); 17 h.add(33); 18 h.add(66); 19 h.add(77); 20 h.add(345); 21 h.add(44); 22 // h.add("aaa");—报错 23 // h.add(ff);—报错 24 25 // Object[] g={"aaa",4,33,66,ff,77,88,345,44,"dd","cfc"}; 26 27 a.add("白"); 28 a.add("日"); 29 a.add("依"); 30 a.add("山"); 31 a.add("尽"); 32 33 c.add("黃"); 34 c.add("河"); 35 36 d.add("白"); 37 d.add("日"); 38 d.add("依"); 39 d.add("山"); 40 d.add("尽"); 41 42 e.add("山"); 43 e.add("尽"); 44 45 f.add("5"); 46 // f.add(6); 47 48 Object[] g = { "aaa", 4, 33, 66, 77, 88, 345, 44, "dd", "cfc" }; 49 50 System.out.println(a.isEmpty()); 51 System.out.println(a.add("白")); 52 System.out.println(a.addAll(c)); 53 System.out.println(a); 54 55 System.out.println(a.contains("地")); 56 System.out.println(a.containsAll(c));// true 57 System.out.println(a.equals(c)); 58 System.out.println(c); 59 60 a.clear(); 61 System.out.println(a); 62 System.out.println(a.containsAll(d)); 63 64 d.remove("白"); 65 System.out.println(d); 66 d.remove("wang");// 没有反应 67 System.out.println(d); 68 69 System.out.println(a.hashCode());// a此时已经被晴空了 70 // 第一次时,我竟然是这么写的:a.hashCode(); 71 System.out.println(c.hashCode()); 72 System.out.println(d.hashCode()); 73 74 a.add("浪花滚滚"); 75 System.out.println(a); 76 77 System.out.println(e.removeAll(d)); 78 System.out.println(d.removeAll(e)); 79 System.out.println(d); 80 System.out.println(e); 81 System.out.println(e.size()); 82 // 我之前写成e.size(); 83 System.out.println(d.size()); 84 85 System.out.println(a.toArray());// 哈哈哈注意 86 System.out.println(f.toArray());// 哈哈哈注意 87 88 System.out.println("=========分割线========="); 89 90 // System.out.println(g); 91 for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++) 92 System.out.println(g); 93 94 System.out.println("**********分割线*********"); 95 96 // 获取数组 97 Integer[] array = h.toArray(new Integer[h.size()]); 98 // 遍历数组 99 /** 100 * for(int i=0;i<h.length;i++){ System.out.println(h[i]+""); length 101 * 报错:cannot be resolved or is not a field 102 */ 103 for (int element : array) { 104 System.out.println(element);// 和下面的一起打印,结果竟然!!! 105 106 System.out.print(element + "\t");// 复习一下而已 107 108 } 109 110 } 111 112 }
Output:
1 //上面示例的打印结果!! 2 false 3 true 4 true 5 [白, 日, 依, 山, 尽, 白, 黃, 河] 6 false 7 true 8 false 9 [黃, 河] 10 [] 11 false 12 [日, 依, 山, 尽] 13 [日, 依, 山, 尽] 14 1 15 1288721 16 798365125 17 [浪花滚滚] 18 true 19 false 20 [日, 依, 山, 尽] 21 [] 22 0 23 4 24 [Ljava.lang.Object;@16925b0 25 [Ljava.lang.Object;@297ffb 26 =========分割线========= 27 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 28 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 29 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 30 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 31 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 32 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 33 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 34 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 35 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 36 [Ljava.lang.Object;@914f6a 37 **********分割线********* 38 4 39 4 33 40 33 66 41 66 77 42 77 345 43 345 44 44 44
Collection常用方法小总结:
boolean add(E e) //注意它的参数类型 boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中 boolean remove(Object o) boolean contains(Object o) //判断集合中指定的元素是否存在 boolean containsAll()// 如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true。 boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) 仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可选操作)(取交集) clear() size() toArray() boolean isEmpty() Iterator<E> iterator() 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
代码实例(关注比较结果)
例一:(主要对比1.有无注释掉的内容;2.true和false和打印位置;3思考执行顺序和字符串类型的比较)
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> b = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 10 a.add("白"); 11 a.add("日"); 12 a.add("依"); 13 a.add("山"); 14 a.add("尽"); 15 16 a.remove("4"); 17 18 b.add("白"); 19 b.add("日"); 20 b.add("依"); 21 b.add("山"); 22 b.add("尽"); 23 24 System.out.println(b.equals(a)); 25 26 System.out.println(a); 27 System.out.println(b); 28 29 System.out.println(a.hashCode()); 30 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); 31 32 System.out.println(a.removeAll(b)); 33 34 System.out.println(a); 35 System.out.println("==================="); 36 37 Object[] c = a.toArray(); 38 String s = null; 39 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 40 s = (String) c[i]; 41 System.out.println(s); 42 } 43 44 } 45 }
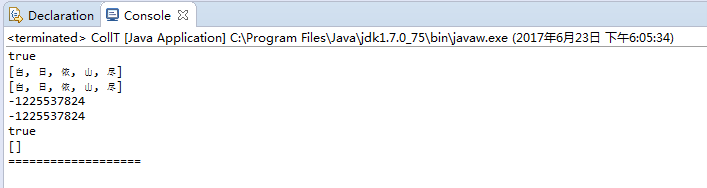
例二:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> b = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 10 a.add("白"); 11 a.add("日"); 12 a.add("依"); 13 a.add("山"); 14 a.add("尽"); 15 16 //a.remove("4"); 17 18 b.add("白"); 19 b.add("日"); 20 b.add("依"); 21 b.add("山"); 22 b.add("尽"); 23 24 System.out.println(b.equals(a)); 25 26 System.out.println(a); 27 System.out.println(b); 28 29 System.out.println(a.hashCode()); 30 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); 31 32 //System.out.println(a.removeAll(b)); 33 34 System.out.println(a); 35 System.out.println("==================="); 36 37 Object[] c = a.toArray(); 38 String s = null; 39 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 40 s = (String) c[i]; 41 System.out.println(s); 42 } 43 44 } 45 }

例三:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> b = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 10 a.add("白"); 11 a.add("日"); 12 a.add("依"); 13 a.add("山"); 14 a.add("尽"); 15 16 a.remove("4"); 17 18 b.add("黃"); 19 b.add("河"); 20 b.add("入"); 21 b.add("海"); 22 b.add("流"); 23 24 System.out.println(b.equals(a)); 25 26 System.out.println(a); 27 System.out.println(b); 28 29 System.out.println(a.hashCode()); 30 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); 31 32 System.out.println(a.removeAll(b)); 33 34 System.out.println(a); 35 System.out.println("==================="); 36 37 Object[] c = a.toArray(); 38 String s = null; 39 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 40 s = (String) c[i]; 41 System.out.println(s); 42 } 43 44 } 45 }

例四:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> b = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 10 a.add("白"); 11 a.add("日"); 12 a.add("依"); 13 a.add("山"); 14 a.add("尽"); 15 16 //a.remove("4"); 17 18 b.add("黃"); 19 b.add("河"); 20 b.add("入"); 21 b.add("海"); 22 b.add("流"); 23 24 System.out.println(b.equals(a)); 25 26 System.out.println(a); 27 System.out.println(b); 28 29 System.out.println(a.hashCode()); 30 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); 31 32 //System.out.println(a.removeAll(b)); 33 34 System.out.println(a); 35 System.out.println("==================="); 36 37 Object[] c = a.toArray(); 38 String s = null; 39 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 40 s = (String) c[i]; 41 System.out.println(s); 42 } 43 44 } 45 }

例五:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> b = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 10 a.add("白"); 11 a.add("日"); 12 a.add("依"); 13 a.add("山"); 14 a.add("尽"); 15 16 //a.remove("4"); 17 18 b.add("黃"); 19 b.add("河"); 20 b.add("入"); 21 22 23 System.out.println(b.equals(a)); 24 25 System.out.println(a); 26 System.out.println(b); 27 28 System.out.println(a.hashCode()); 29 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); 30 31 //System.out.println(a.removeAll(b)); 32 33 System.out.println(a); 34 System.out.println("==================="); 35 36 Object[] c = a.toArray(); 37 String s = null; 38 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 39 s = (String) c[i]; 40 System.out.println(s); 41 } 42 43 } 44 }

例六:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class CollT { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 Collection<String> b = new ArrayList<String>(); 9 10 a.add("白"); 11 a.add("日"); 12 a.add("依"); 13 a.add("山"); 14 a.add("尽"); 15 16 a.remove("4"); 17 18 b.add("黃"); 19 b.add("河"); 20 b.add("入"); 21 22 23 System.out.println(b.equals(a)); 24 25 System.out.println(a); 26 System.out.println(b); 27 28 System.out.println(a.hashCode()); 29 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); 30 31 System.out.println(a.removeAll(b)); 32 33 System.out.println(a); 34 System.out.println("==================="); 35 36 Object[] c = a.toArray(); 37 String s = null; 38 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 39 s = (String) c[i]; 40 System.out.println(s); 41 } 42 43 } 44 }
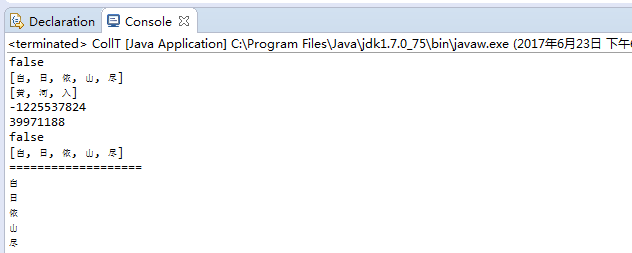
二、List与set常用方法
List实现类包括:LinkedList,Vector,ArrayList
注意:
List列表借口,继承于Collection,可以按索引的顺序访问,有索引的Collection。
具有列表的功能,元素顺序均是按添加的先后进行列表的。
这里的 Collection、List、Set和Map都是接口(Interface),不是具体的类实现。
List list = new ArrayList(); 这是我们平常经常使用的创建一个新的List的语句,在这里 List是接口,ArrayList才是具体的类。
List
List 接口扩展了 Collection 并声明存储一系列元素的类集的特性。使用一个基于零的下 标,元素可以通过它们在列表中的位置被插入和访问。一个列表可以包含重复元素。除了由 Collection 定义的方法之外,List 还定义了一些它自己的方法。再次注意当类集不能被修改时,
当一个对象与另一个不兼容,例 如当企图将一个不兼容的对象加入一个类集中时,将产生 ClassCastException 异常。
对于由 Collection 定义的 add()和 addAll()方法,List 增加了方法 add(int, Object)和 addAll(int, Collection)。 这些方法在指定的下标处插入元素。
由 Collection 定义的 add(Object)和 addAll(Collection)的 语义也被 List 改变了,以便它们在列表的尾部增加元素。
为获得在指定位置存储的对象, 可以用对象的下标调用 get()方法。
为给类表中的一个元素赋值,可以调用 set()方法,指定被改变的对象的下标。
调用 indexOf()或 lastIndexOf()可以得到一个对象的下标。
通过调用 subList()方法,可以获得列表的一个指定了开始下标和结束下标的子列表。此方法使得 列表处理十分方便。
Set
set集合接口定义了一个集合。它扩展了 Collection并说明了不允许复制元素的类集的特性。 因此,如果试图将复制元素加到集合中时,add()方法将返回 false。它本身并没有定义任何 附加的方法。
总结:
List 集合的特点
1) 元素有序 (可以按索引访问)
2) 元素可以重复,可以存放多个null值
Set 集合的特点:
1) 元素无序(不可以按索引访问)
2)元素不能重复,只能有一个null值
代码实例:
1 /*List集合的特有特性 2 * 3 *public interface List<E>extends Collection<E> 4 *-- add(int index, E element) 在列表的指定位置插入指定元素 5 *-- addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 6 *-- E get(int index) //返回列表中指定位置的元素。 7 *-- int indexOf(Object o) // 返回此列表中第一次出现的指定元素的索引 8 *-- listIterator() 9 *-- e set(int index, E element) // 用指定元素替换列表中指定位置的元素 10 *-- void remove(int position) 移除指定位置的元素 11 *-- List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex ) 类似substring() 12 */ 13 import java.util.ArrayList; 14 15 class CollT { 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 18 list.add("Java"); // 下標是0 19 list.add("Class"); // 下標是1 20 list.add("Array"); // 下標是2 21 list.add("Collection"); // 下標是3 22 list.add("List"); // 下標是4 23 list.add("Set"); // 下標是5 24 System.out.println(list.subList(0, 3));// 注意不包含下標是3的 25 } 26 }

个人学习笔记,针对本人在自学中遇到的问题。
标签:
Java基础




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· Vue3状态管理终极指南:Pinia保姆级教程