代理模式(Proxy Pattern)
代理模式:为另一个对象提供一个替身或占位符以控制对这个对象的访问。
一般代理模式类图:

远程代理:Java RMI
RMI:远程方法调用,提供客户辅助对象和服务辅助对象,为客户辅助对象创建和服务对象相同的方法。RMI的好处在于不必亲自写任何网络或I/O代码。客户程序调用远程方法(真正的服务)就和在运行在客户自己本地JVM上对对象进行正常方法调用一样。
RMI的查找服务可以用来寻找和访问远程对象。
RMI调用模型:

外部观察RMI过程:
1.运行服务器,服务器实现类会去实例化一个服务的实例,并将这个服务注册到RMI registry。注册之后,这个服务就可以供客户调用了。
2.运行客户端,客户端通过查找服务(lookup service),根据服务的名字,找到对应的服务。
3.现在在客户端就可以调用远程服务器的方法了。
在外部观察RMI的过程,并不能知道其实是代理在背后起作用。
内部观察RMI过程:
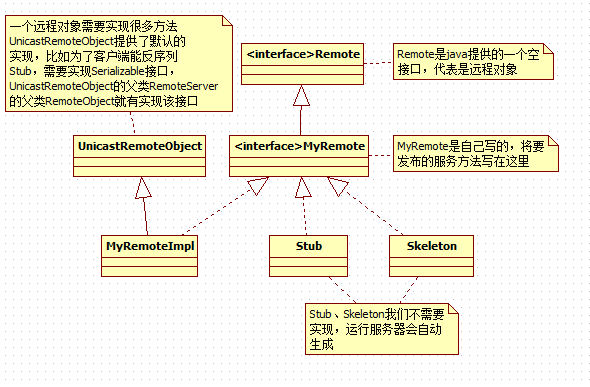
1.服务器实例化服务实例的同时,实例化一个RMI Skeleton代理和RMI Stub代理
2.当客户端通过查找服务,找到该服务,服务器将Stub通过网络传给客户,此时是二进制流,客户端需反序列成Stub
3.客户调用客户对象的方法会调用Stub的同名方法,Stub代理打包调用信息,通过网络转给Skeleton,Skeleton把信息解包,找出被调用的方法(以及方法在哪个对象内),然后调用真正的服务对象上的真正方法
4.服务对象上的方法被调用,将结果返回给Skeleton
5.Skeleton把方法返回信息打包,然后通过网络转给Stub
6.Stub将信息解包,返回给客户对象
一个简单的RMI例子:
服务器端:
public interface MyRemote extends Remote {//Remote接口是jdk提供的一个接口 public String sayHello() throws RemoteException; } public class MyRemoteImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements MyRemote {//实现UnicastRemoteObject是创建远程对象的最容易方法,由jdk提供 protected MyRemoteImpl() throws RemoteException { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } @Override public String sayHello() throws RemoteException { return "Server says, 'Hey'"; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { MyRemote service = new MyRemoteImpl(); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);//端口号1099 registry.bind("RemoteHello", service);//注册服务对象,服务名字为RemoteHello } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
客户端:
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { MyRemote service = (MyRemote) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/RemoteHello");//127.0.0.1代表本机,RemoteHello是服务的名字 String s = service.sayHello();//在客户端调用远程对象的方法,返回一个String System.out.println(s);将方法返回值打印出来 } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
测试结果:
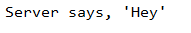
一个小问题:为了在网络传输,远程方法的返回值都必须是可序列化的,所以需要实现Serializable接口,例子中的返回值是String,所以没有问题,如果是自定义的对象,那么需要实现Serializable接口才能正常运行。
RMI类图模型:
虚拟代理:
虚拟代理作为创建开销大的对象的代表。虚拟代理经常直到我们真正需要一个对象的时候才创建它。当对象在创建前和创建中,由虚拟代理来扮演对象的替身。对象创建后,代理就会将请求直接委托给对象。
现在有一个应用是从网站取得图像,然后显示出来,限制在于带宽和网络负载,下载需要一些时间,但是在等待图像加载的时候,应该显示一些东西。我们不希望等待图像的时候整个应用被挂起,一旦加载完成,刚才显示的东西应该消失,图像显示出来。
设计类图:

public class ImageComponent extends JComponent { private Icon icon; public ImageComponent(Icon icon) { this.icon = icon; } public void setIcon(Icon icon) { this.icon = icon; } public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { super.paintComponent(g); int w = icon.getIconWidth(); int h = icon.getIconHeight(); int x = (800 - w)/2; int y = (600 - h)/2; icon.paintIcon(this, g, x, y); } } public class ImageProxy implements Icon { ImageIcon imageIcon; URL imageURL; Thread retrievalThread; boolean retrieving = false; public ImageProxy(URL url) { imageURL = url; } @Override public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) { if(imageIcon != null) {//如果已经加载出来,即imageIcon实例化了 imageIcon.paintIcon(c, g, x, y);//将请求转给真正的对象 } else { g.drawString("Loading, please wait...", x+300, y+190);//否则显示一个提示字符串 if(!retrieving) {//这个变量的目的是只开一个线程去实例化真正的对象 retrieving = true; retrievalThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {//如果未加载出来,开一个新线程加载,避免程序被挂起 @Override public void run() { try { imageIcon = new ImageIcon(imageURL, "CD Cover"); c.repaint(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); retrievalThread.start(); } } } @Override public int getIconWidth() { if(imageIcon != null) { return imageIcon.getIconWidth(); } else { return 800; } } @Override public int getIconHeight() { if(imageIcon != null) { return imageIcon.getIconHeight(); } else { return 600; } } } public class Test { ImageComponent imageComponent; JFrame frame = new JFrame("CD Cover View"); JMenuBar menuBar; JMenu menu; Hashtable cds = new Hashtable(); public Test() throws Exception { cds.put("Ambient:Music for Airports", "http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000003S2L.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg"); cds.put("Ima", "http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B000005IRM.01.LZZZZZZZ.jpg"); URL initialURL = new URL((String)cds.get("Ima")); menuBar = new JMenuBar(); menu = new JMenu("Favorite CDs"); menuBar.add(menu); frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar); for(Enumeration e = cds.keys(); e.hasMoreElements();) { String name = (String)e.nextElement(); JMenuItem menuItem = new JMenuItem(name); menu.add(menuItem); menuItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { imageComponent.setIcon(new ImageProxy(getCDUrl(e.getActionCommand()))); frame.repaint(); } }); } Icon icon = new ImageProxy(initialURL); imageComponent = new ImageComponent(icon); frame.getContentPane().add(imageComponent); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setSize(800, 600); frame.setVisible(true); } URL getCDUrl(String name) { try { return new URL((String)cds.get(name)); } catch(MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Test t = new Test(); } }
测试结果:
图像还未加载成功:
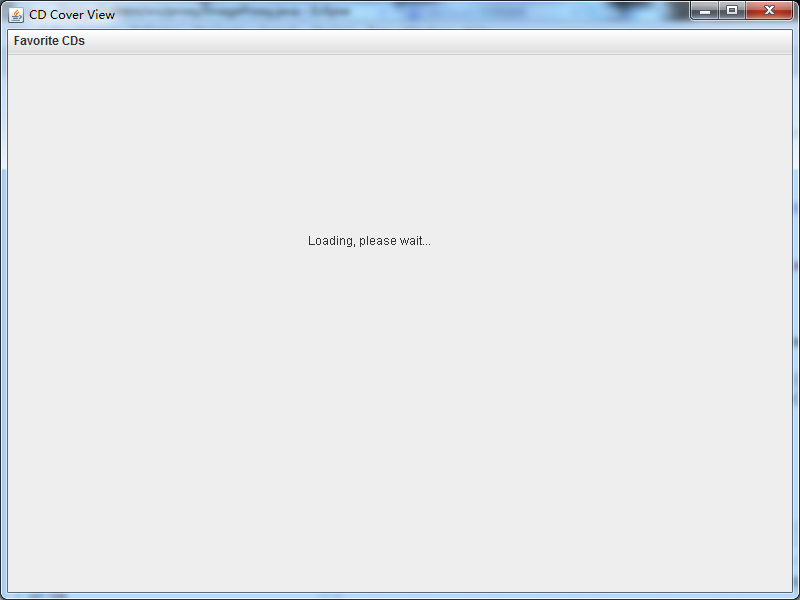
图像加载成功:

保护代理:

例子代码:
public interface PersonBean { String getName(); String getGender(); String getInterest(); int getHotOrNotRating(); void setName(String name); void setGender(String gender); void setInterest(String interests); void setHotOrNotRating(int rating); } public class PersonBeanImpl implements PersonBean { String name; String gender; String interest; int rating; int ratingCount = 0; public PersonBeanImpl(String name, String gender, String interest) { this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.interest = interest; } @Override public String getName() { return name; } @Override public String getGender() { return gender; } @Override public String getInterest() { return interest; } @Override public int getHotOrNotRating() { if(ratingCount == 0) return 0; return (rating/ratingCount); } @Override public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } @Override public void setInterest(String interest) { this.interest = interest; } @Override public void setHotOrNotRating(int rating) { this.rating += rating; ratingCount++; } } public class OwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { PersonBean person; public OwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean person) { this.person = person; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException { try { if(method.getName().startsWith("get")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } else if(method.getName().equals("setHotOrNotRating")) { throw new IllegalAccessException(); } else if(method.getName().startsWith("set")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } } catch(InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } } public class NonOwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { PersonBean person; public NonOwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean person) { this.person = person; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException { try { if(method.getName().startsWith("get") || method.getName().equals("setHotOrNotRating")) { return method.invoke(person, args); } else { throw new IllegalAccessException(); } } catch(InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } } public class TestDrive { static PersonBean getOwnerProxy(PersonBean person) { return (PersonBean)Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(), person.getClass().getInterfaces(), new OwnerInvocationHandler(person)); } static PersonBean getNonOwnerProxy(PersonBean person) { return (PersonBean)Proxy.newProxyInstance(person.getClass().getClassLoader(), person.getClass().getInterfaces(), new NonOwnerInvocationHandler(person)); } public static void main(String[] args) { PersonBean joe = new PersonBeanImpl("joe", "male", "football"); PersonBean ownerProxy = getOwnerProxy(joe); ownerProxy.setInterest("ping pong"); System.out.println("owner setInterest"); try { ownerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(10); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("setHotOrRating faild"); } System.out.println("rating:" + ownerProxy.getHotOrNotRating()); PersonBean nonOwnerProxy = getNonOwnerProxy(joe); nonOwnerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(10); try { nonOwnerProxy.setInterest("basketball"); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("setInterest faild"); } } }
测试结果:

本文提到三个代理:远程代理、虚拟代理、保护代理。
在实际应用中,代理模式的变体有很多,如还有防火墙代理,写入时复制代理,缓存代理...
不变的是:它们都是为了控制对象的访问。



