nginx使用ssl证书配置https
验证 nginx 是否支持 ssl
通过查看nginx版本,确认是否包含http_ssl_module 模块
nginx -V
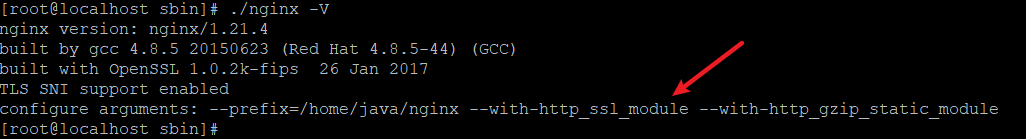
如果出现 --with-http_ssl_module 就是已经安装了
配置 nginx ssl
server {
# 服务器端口使用443,开启ssl, 这里ssl就是上面安装的ssl模块
listen 443 ssl;
# 域名
server_name cqxxxx.top;
# ssl on; // 这种已经不使用了,这么写会报警告,可以直接去掉采用第一行的写法
# ssl证书地址
ssl_certificate /home/cqxxxx.top_bundle.pem; # pem文件的路径
ssl_certificate_key /home/cqxxxx.top.key; # key文件的路径
# ssl验证相关配置
ssl_session_timeout 5m; #缓存有效期
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4; #加密算法
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #安全链接可选的加密协议
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #使用服务器端的首选算法
# 当http请求出错时,使用https请求
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000";
error_page 497 https://$host$request_uri;
# 测试请求
location /test2 {
return "test success!";
}
location /test1 {
proxy_pass http://43.156.23.43:8002/test1/;
}
location /test {
alias /usr/local/files/web/test/dist;
}
}
# 443 ssl 可以配置多个
server {
# 服务器端口使用443,开启ssl, 这里ssl就是上面安装的ssl模块
listen 443 ssl;
# 域名
server_name tc.cqxxxx.top;
# ssl on; // 这种已经不使用了,这么写会报警告,可以直接去掉采用第一行的写法
# ssl证书地址
ssl_certificate /home/tc.cqxxxx.top_bundle.pem; # pem文件的路径
ssl_certificate_key /home/tc.cqxxxx.top.key; # key文件的路径
# ssl验证相关配置
ssl_session_timeout 5m; #缓存有效期
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4; #加密算法
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #安全链接可选的加密协议
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #使用服务器端的首选算法
# 当http请求出错时,使用https请求
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000";
error_page 497 https://$host$request_uri;
location /test2 {
proxy_pass http://43.156.23.43:8002/test1/;
}
location /test3 {
alias /usr/local/files/web/test/dist;
}
}
# 配置 https 转发,选择配置
server {
listen 8001;
server_name cqxxxx.top; # 域名
rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host:443$1 permanent; # 把http的域名请求转成https且转发到443端口
}
配置完成后,就可以使用 https://cqxxxx.top/test 请求了
- 问题:配置好了使用 google浏览器 打开,https向http,原本发送 http 请求,但是发送请求是 https 并且报 net::ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
解决:使用google浏览器,会强制自动升级协议,虽然可以在浏览器里面设置,但是这样不好,所以还是直接把 http 请求在 nginx 里配置成 https 的请求
如果 https向https 配置都正常还是报错,可能就是证书的问题了
配置非 443 端口使用https请求
首先和平常配置是一样的,只是配置的端口不一样
server {
# 服务器端口使用8080,开启ssl, 这里ssl就是上面安装的ssl模块
listen 8080 ssl;
# 域名
server_name localhost;
# ssl on; // 这种已经不使用了,这么写会报警告,可以直接去掉采用第一行的写法
# ssl证书地址
ssl_certificate /home/cqxxxx.top_bundle.pem; # pem文件的路径
ssl_certificate_key /home/cqxxxx.top.key; # key文件的路径
# ssl验证相关配置
ssl_session_timeout 5m; #缓存有效期
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384::HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4:!DH:!EDH:!3DES; #加密算法
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #安全链接可选的加密协议
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #使用服务器端的首选算法
# 当http请求出错时,使用https请求
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000";
error_page 497 https://$host$request_uri;
location /test1 {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods '*';
add_header Access-Control-Max-Age 3600;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin '*';
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers '*';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://43.156.23.43:8002/test1/;
}
location /test {
alias /usr/local/files/web/test/dist;
}
}
openssl生成IP自签名证书
CA证书,大部分情况都是对域名签名的,而且很多CA都是要收费的(费用还不低),
如果只是个人或者小范围的使用,并且没有域名的情况下,大的CA可能并不适合;尤其是局域网内部的使用,一边CA不会给你签的
所以在这个情况下,就需要对IP地址进行自签名
安装 openssl
yum install openssl
- 创建CA,也就是证书认证机构
创建私钥
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048
pi@raspberrypi:~/ssl $ openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
..........................................+++++
......+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
通过私钥创建公钥 -days 208 过期时间,建议设置长点
openssl req -new -x509 -days 208 -key ca.key -out ca.crt
pi@raspberrypi:~/ssl $ openssl req -new -x509 -days 208 -key ca.key -out ca.crt
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:XXX Gmbh
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:www.xxx.com
Email Address []:
Country Name到Email Address 那里是需要填写的,不过不重要,可以随便填。建议在Organization Name 填一下有意义的名字,这样导入以后容易找
- 创建服务器的密钥对,需要准备两个文件
第一个文件,openssl.cnf, 内容是
[req]
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = v3_req
[req_distinguished_name]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = US
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
stateOrProvinceName_default = NY
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
localityName_default = NYC
organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section)
organizationalUnitName_default = xxx
commonName = xxx
commonName_max = 64
[ v3_req ]
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:TRUE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = 192.168.0.10
IP.2 = x.x.x.x
[req_distinguished_name] 那部分也是随便填的
重点是[alt_names],这里写的ip地址是最后认证的,比较重要。端口不需要,一旦认证了ip以后所有端口都可以是https的
alt_names里的IP列填设备要访问的服务端的IP地址。
alt_names里的DNS列填设备要访问的服务端的域名地址。
commonName 填设备要访问的服务端的IP或域名地址。
当客户端访问服务端的地址为IP地址,那么只会在x509的扩展项subjectAltName中寻找IP进行 匹配,也就是到alt_names里面的IP列去寻找IP进行匹配。
当客户端访问服务端的地址为域名地址,则除了在 subjectAltName 中寻找域名进行匹配(也就是到alt_names里面的DNS列去匹配)外,还会检查req_distinguished_name中的 commonName 是否和域名匹配。
第二个文件,v3.ext, 内容是
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
keyUsage=digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
subjectAltName=@alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = 192.168.0.10
IP.2 = x.x.x.x
[alt_names]与openssl.cnf一致
- 生成签服务器证书
私钥
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
pi@raspberrypi:~/ssl $ openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
............+++++
.............................................................................................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
公钥
openssl req -new -days 208 -key server.key -out server.csr -config openssl.cnf
pi@raspberrypi:~/ssl $ openssl req -new -days 208 -key server.key -out server.csr -config openssl.cnf
Ignoring -days; not generating a certificate
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [US]:
State or Province Name (full name) [NY]:
Locality Name (eg, city) [NYC]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [xxx]:
- 用自己的CA给自己的服务器签名
openssl x509 -days 208 -req -sha256 -extfile v3.ext -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -in server.csr -out server.crt
pi@raspberrypi:~/ssl $ openssl x509 -days 208 -req -sha256 -extfile v3.ext -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -in server.csr -out server.crt
Signature ok
subject=C = US, ST = NY, L = Centereach, OU = TD-Hydro
Getting CA Private Key
这样就得到了两组密钥对
把server的这组名钥对放进HTTP服务器里
如果是Nginx的话,参考
server {
listen 443 ssl default_server;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key;
error_page 497 https://$host/$request_uri;
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库