hdu4255筛素数+广搜
Mr. B has recently discovered the grid named "spiral grid".
Construct the grid like the following figure. (The grid is actually infinite. The figure is only a small part of it.)
![]()
Considering traveling in it, you are free to any cell containing a composite number or 1, but traveling to any cell containing a prime number is disallowed. You can travel up, down, left or right, but not diagonally. Write a program to find the length of the shortest path between pairs of nonprime numbers, or report it's impossible.
![]()
Construct the grid like the following figure. (The grid is actually infinite. The figure is only a small part of it.)
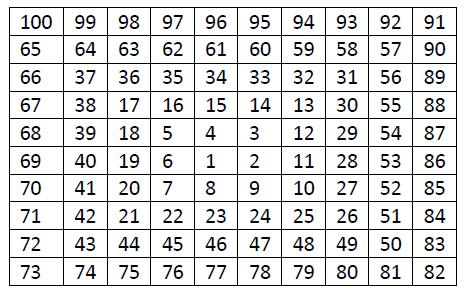
Considering traveling in it, you are free to any cell containing a composite number or 1, but traveling to any cell containing a prime number is disallowed. You can travel up, down, left or right, but not diagonally. Write a program to find the length of the shortest path between pairs of nonprime numbers, or report it's impossible.
Input
Each test case is described by a line of input containing two nonprime integer 1 <=x, y<=10,000.
Output
For
each test case, display its case number followed by the length of the
shortest path or "impossible" (without quotes) in one line.
Sample Input
1 4
9 32
10 12
Sample Output
Case 1: 1
Case 2: 7
Case 3: impossible
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int book[401][401];
int a[401][401];
int b[401][401];
int vis[160005];
int prime[160005];
struct node
{
int x;
int y;
int s;
} que[160005];
void make1()
{
for(int i=1;i<=160001;i++)
prime[i]=1;
prime[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= 160001; i++)
{
if(prime[i])
{
for(int j = 2*i; j <= 160001; j+=i)
prime[j] = 0;
}
}
int x,y;
int n=400;
int tot=160000;
a[0][0]=160000;
x=0,y=0;
while(tot>1)
{
while(y+1<n&&!a[x][y+1])
{
a[x][++y]=--tot;
}
while(x+1<n&&!a[x+1][y])
{
a[++x][y]=--tot;
}
while(y-1>=0&&!a[x][y-1])
{
a[x][--y]=--tot;
}
while(x-1>=0&&!a[x-1][y])
{
a[--x][y]=--tot;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<400; i++)
for(int j=0; j<400; j++)
{
if(prime[a[i][j]]==1)
b[i][j]=1;
else
b[i][j]=0;
}
}
int main()
{
int t1,t2;
int ans=0;
make1();
while(scanf("%d%d",&t1,&t2)!=EOF)
{
int next[4][2]= {0,1,1,0,0,-1,-1,0};
memset(book,0,sizeof(book));
if(t1==t2)
printf("Case %d: 0\n",++ans);
else
{
int startx,starty,endx,endy;
for(int i=0; i<=399; i++)
for(int j=0; j<=399; j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==t1)
{
startx=i;
starty=j;
}
if(a[i][j]==t2)
{
endx=i;
endy=j;
}
}
int head=1,tail=1;
que[head].x=startx;
que[head].y=starty;
tail++;
book[startx][starty]=1;
int flag=0;
while(head<tail)
{
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int tx=que[head].x+next[k][0];
int ty=que[head].y+next[k][1];
if(tx<0||tx>399||ty<0||ty>399)
continue;
if(b[tx][ty]==0&&book[tx][ty]==0)
{
book[tx][ty]=1;
que[tail].x=tx;
que[tail].y=ty;
que[tail].s=que[head].s+1;
tail++;
}
if(tx==endx&&ty==endy)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1)
break;
head++;
}
if(flag==1)
printf("Case %d: %d\n",++ans,que[tail-1].s);
else
printf("Case %d: impossible\n",++ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int book[401][401];
int a[401][401];
int b[401][401];
int vis[160005];
int prime[160005];
struct node
{
int x;
int y;
int s;
} que[160005];
void make1()
{
for(int i=1;i<=160001;i++)
prime[i]=1;
prime[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= 160001; i++)
{
if(prime[i])
{
for(int j = 2*i; j <= 160001; j+=i)
prime[j] = 0;
}
}
int x,y;
int n=400;
int tot=160000;
a[0][0]=160000;
x=0,y=0;
while(tot>1)
{
while(y+1<n&&!a[x][y+1])
{
a[x][++y]=--tot;
}
while(x+1<n&&!a[x+1][y])
{
a[++x][y]=--tot;
}
while(y-1>=0&&!a[x][y-1])
{
a[x][--y]=--tot;
}
while(x-1>=0&&!a[x-1][y])
{
a[--x][y]=--tot;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<400; i++)
for(int j=0; j<400; j++)
{
if(prime[a[i][j]]==1)
b[i][j]=1;
else
b[i][j]=0;
}
}
int main()
{
int t1,t2;
int ans=0;
make1();
while(scanf("%d%d",&t1,&t2)!=EOF)
{
int next[4][2]= {0,1,1,0,0,-1,-1,0};
memset(book,0,sizeof(book));
if(t1==t2)
printf("Case %d: 0\n",++ans);
else
{
int startx,starty,endx,endy;
for(int i=0; i<=399; i++)
for(int j=0; j<=399; j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==t1)
{
startx=i;
starty=j;
}
if(a[i][j]==t2)
{
endx=i;
endy=j;
}
}
int head=1,tail=1;
que[head].x=startx;
que[head].y=starty;
tail++;
book[startx][starty]=1;
int flag=0;
while(head<tail)
{
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int tx=que[head].x+next[k][0];
int ty=que[head].y+next[k][1];
if(tx<0||tx>399||ty<0||ty>399)
continue;
if(b[tx][ty]==0&&book[tx][ty]==0)
{
book[tx][ty]=1;
que[tail].x=tx;
que[tail].y=ty;
que[tail].s=que[head].s+1;
tail++;
}
if(tx==endx&&ty==endy)
{
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1)
break;
head++;
}
if(flag==1)
printf("Case %d: %d\n",++ans,que[tail-1].s);
else
printf("Case %d: impossible\n",++ans);
}
}
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号