Thread同步测试
任务详情
1 编译运行附件中的代码,提交运行结果截图,并说明程序功能
2 修改代码,把同步资源个数减少为3个,把使用资源的线程增加到 (你的学号%3 + 4)个,编译代码,提交修改后的代码和运行结果截图。
任务一
原代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM 5
int queue[NUM];
sem_t blank_number, product_number;
void *producer ( void * arg )
{
static int p = 0;
for ( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &blank_number );
queue[p] = rand() % 1000;
printf("Product %d \n", queue[p]);
p = (p+1) % NUM;
sleep ( rand() % 5);
sem_post( &product_number );
}
}
void *consumer ( void * arg )
{
static int c = 0;
for( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &product_number );
printf("Consume %d\n", queue[c]);
c = (c+1) % NUM;
sleep( rand() % 5 );
sem_post( &blank_number );
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
pthread_t pid, cid;
sem_init( &blank_number, 0, NUM );
sem_init( &product_number, 0, 0);
pthread_create( &pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join( pid, NULL );
pthread_join( cid, NULL );
sem_destroy( &blank_number );
sem_destroy( &product_number );
return 0;
}
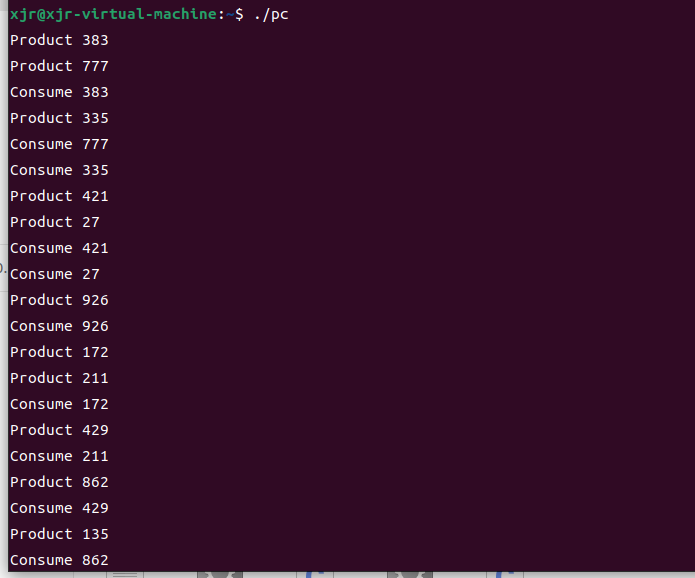
执行结果:
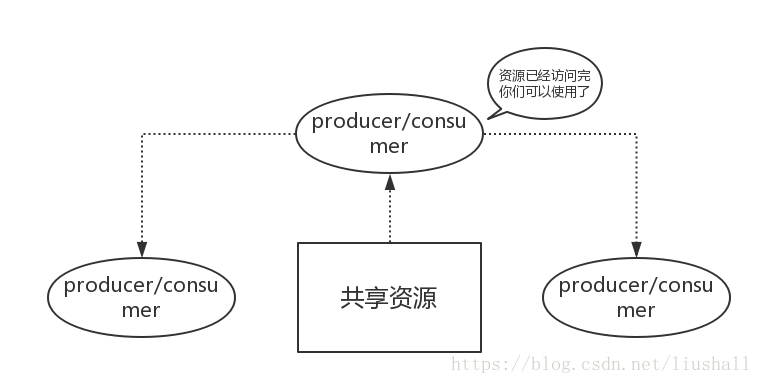
我根据代码以及运行结果分析认为附件中的代码功能为实现生产者和消费者问题,即生产者每次生产一次消息,消费者才能消费,这就是同步,就是生产之后才能消费,消费永远不能在生产之前。如下图

该问题需要注意的几点:
-
在缓冲区为空时,消费者不能再进行消费
-
在缓冲区为满时,生产者不能再进行生产
-
在一个线程进行生产或消费时,其余线程不能再进行生产或消费等操作,即保持线程间的同步
-
注意条件变量与互斥锁的顺序
任务二
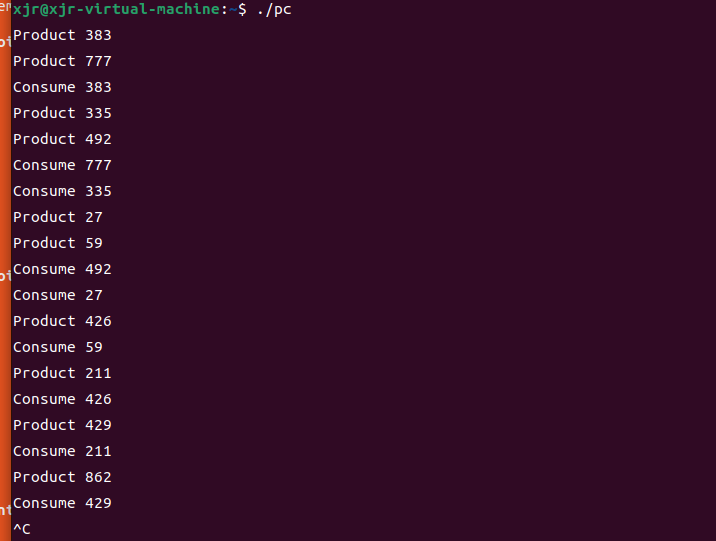
1.自己学好为20201325,故(20201325%3+4)= 4,所以需要创建四个消费者线程,即在原来的基础上新创建三个即可,另外对于资源总数修改NUM即可,将NUM宏定义修改为3.
代码修改如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM 3
int queue[NUM];
sem_t blank_number, product_number;
void *producer ( void * arg )
{
static int p = 0;
for ( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &blank_number );
queue[p] = rand() % 1000;
printf("Product %d \n", queue[p]);
p = (p+1) % NUM;
sleep ( rand() % 5);
sem_post( &product_number );
}
}
void *consumer ( void * arg )
{
static int c = 0;
for( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &product_number );
printf("Consume %d\n", queue[c]);
c = (c+1) % NUM;
sleep( rand() % 5 );
sem_post( &blank_number );
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
pthread_t pid, cid,cid1,cid2,cid3;
sem_init( &blank_number, 0, NUM );
sem_init( &product_number, 0, 0);
pthread_create( &pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid1, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid2, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid3, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join( pid, NULL );
pthread_join( cid, NULL );
pthread_join( cid1, NULL );
pthread_join( cid2, NULL );
pthread_join( cid3, NULL );
sem_destroy( &blank_number );
sem_destroy( &product_number );
return 0;
}
执行结果