Day23 回溯算法Part02
39. 组合总和
与216. 组合总和 III不同,不要求每个数字仅能使用一次。但这样很容易出现重复的结果,剪枝还是要注意。不过这道题让我更认识到把回溯问题看成是一个多叉树的遍历的问题,当遇到一个题目,先画出它的树结构,也就是代码随想录中的这张图,for循环(横向遍历)怎么做,递归(纵向遍历)又怎么去做。这就是回溯问题最重要的两个部分。
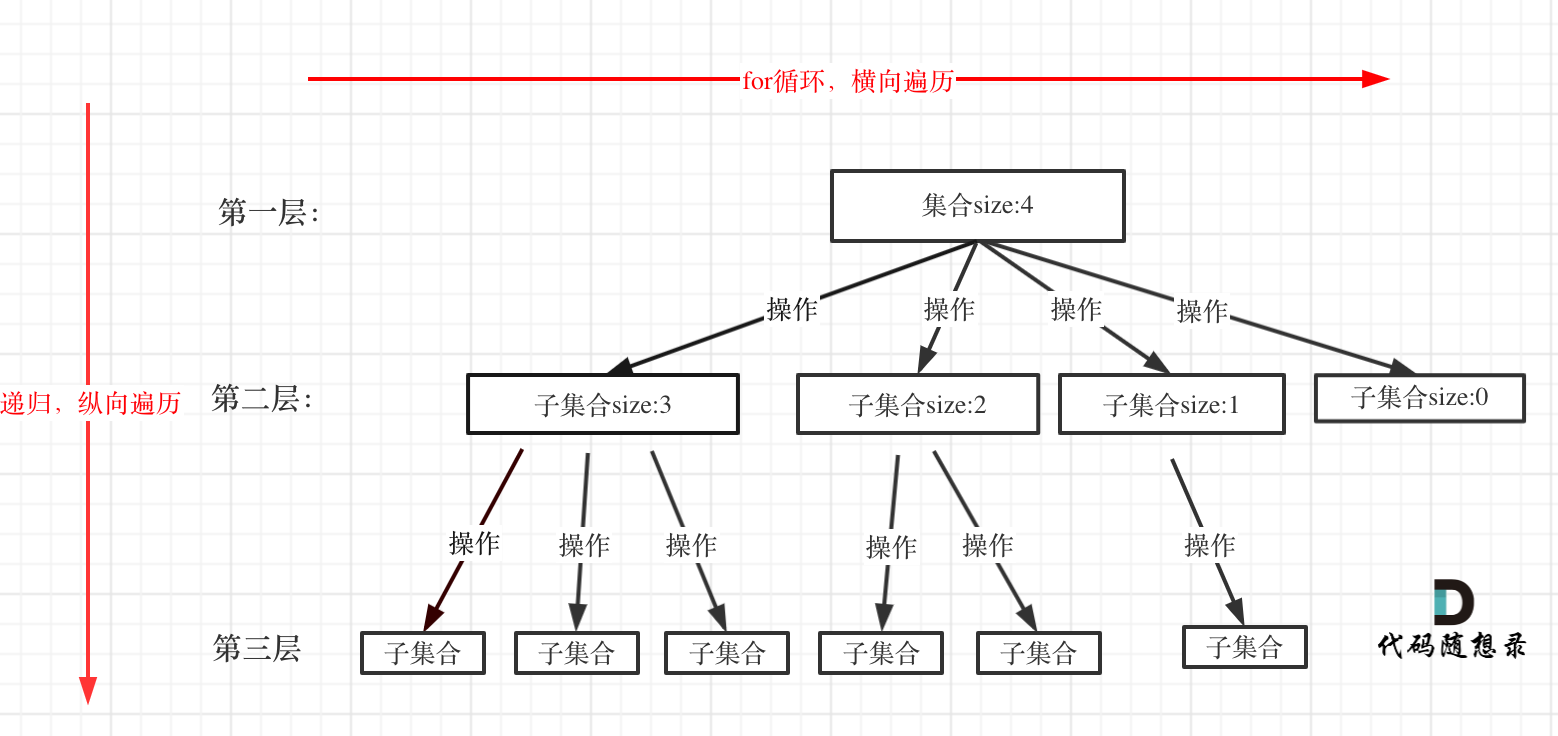
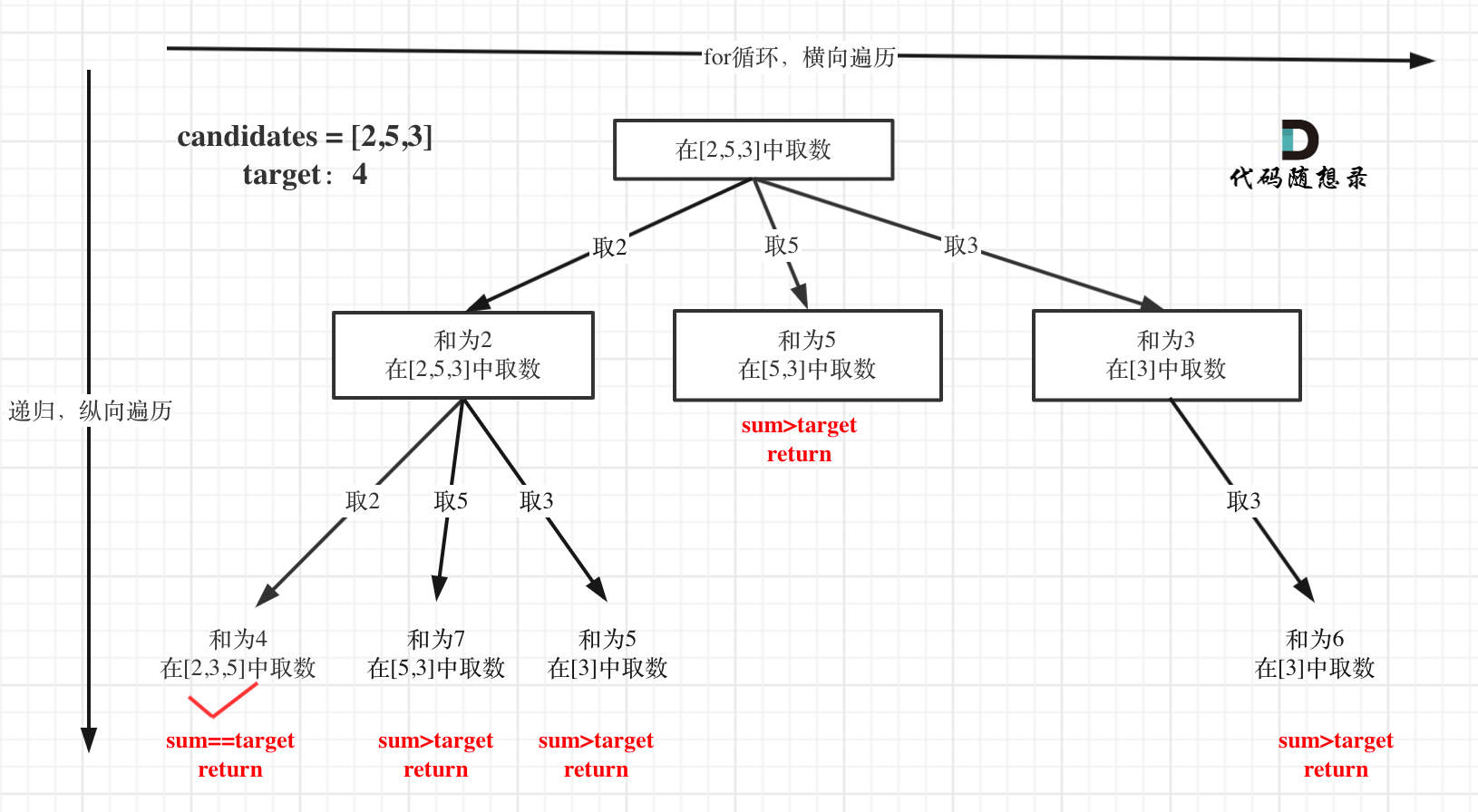
具体到这道题,可以绘制出这样的树形结构。从这张图就可以看出代码的逻辑,for循环和递归。具体看注释
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
public List<Integer> path = new ArrayList();
public int[] candidates;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
this.candidates = candidates;
backTracking(0, target);
return ans;
}
public void backTracking(int start, int target){ // start记录当前调用可以横向遍历的第一个元素的下标
if(target < 0) return; //剪枝
if(target == 0) { //本题对于path的长度并没有限制
ans.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++){
path.add(candidates[i]);
backTracking(i, target-candidates[i]); //注意看这个递归的参数,第一位为i,代表了元素可以重复
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
40. 组合总和 II
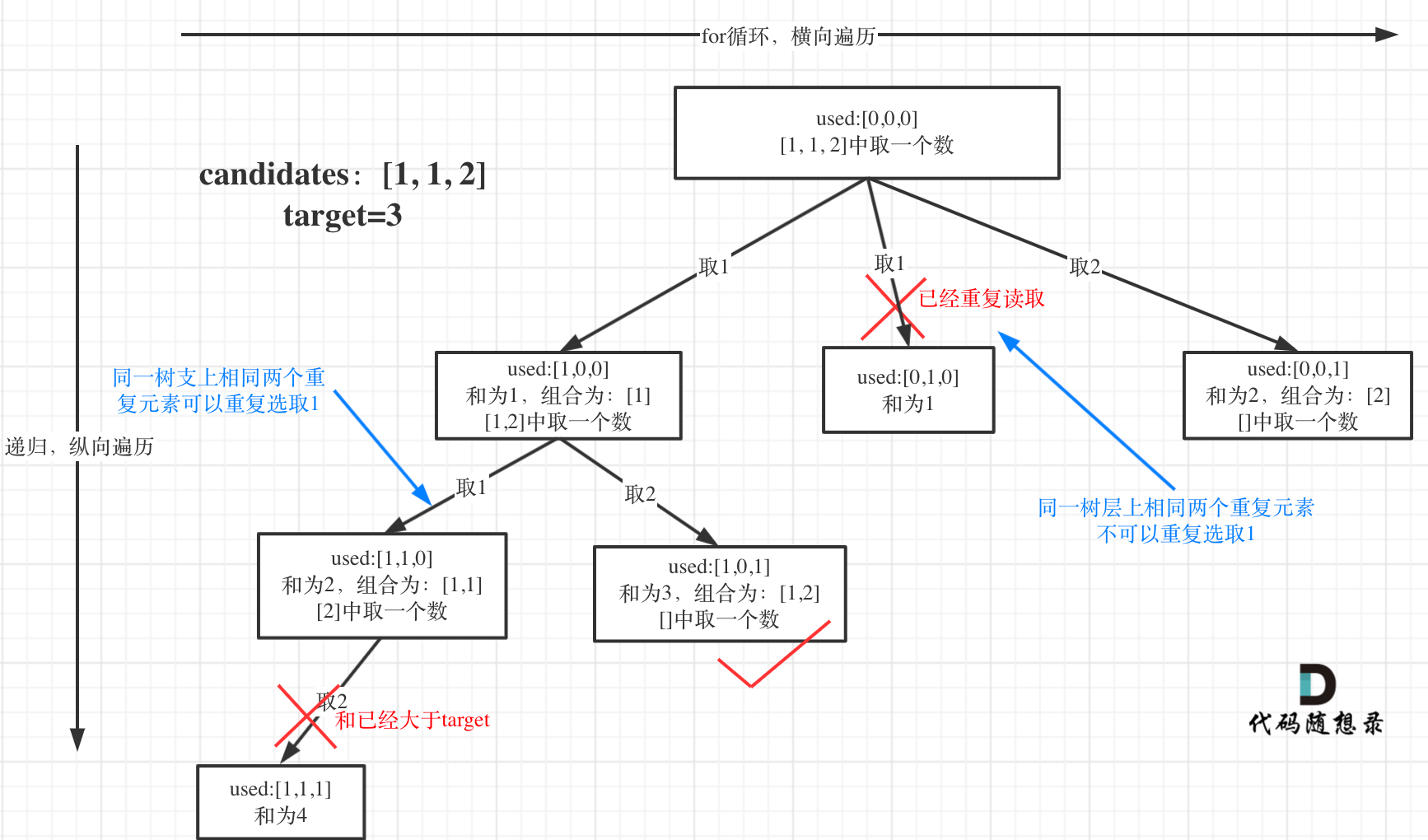
这道题更是体现了绘制树结构的重要性。需要注意的是,本题的candidates数组中会出现重复元素,每个数字在每个组合中仅能出现一次。为了更容易的去重复,像这样的题目第一步都需要先对数组进行排序。回溯在处理后的数组上进行。
树结构如下,不需要去管used数组,这里是代码随想录中给出的使用数组记录访问过元素的方法,不用也是可以的。注意看两个蓝色箭头的地方,这两个取1若反映在调用代码上,他们肯定是完全相同的,都是backTracking(1, target),但很显然,左边箭头的部分是必要的,而右边箭头(即和上一个1在同一层)是不必要的,否则会出现重复。
然而反映在递归的代码中,这两个的调用是完全相同的。我们只能在for循环中删除第二个1的调用。具体看注释
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList();
int[] candidates;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
this.candidates = candidates;
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backTracking(0, target);
return ans;
}
public void backTracking(int start, int target){
if(target == 0){
ans.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
//由于数组已经排序,因此当target-candidates[i] < 0,i之后的数字一定也满足这个条件,直接跳出可以避免这些调用
for(int i = start; i < candidates.length && target-candidates[i] >= 0; i++){
if(i != start && candidates[i-1] == candidates[i]) continue; //同一层的调用中需要去重
path.add(candidates[i]);
backTracking(i+1, target-candidates[i]); //不同层是可以重复的,就如上图中的1,1
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
131. 分割回文串
目前还不会动态规划,所以只是用回溯来做。下面简单说我的思路
分割其实也可以看作是组合问题,不过组合的是分割点的位置。分割点间就形成了子串,需要判断他们是否是回文的,从而确定分割点的正确性。所以回溯其实也就是遍历了所有分割点的组合,将生成了不是回文子串的分割方式舍弃。
class Solution {
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList();
List<String> substrings = new ArrayList();
String s;
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
this.s = s;
findSeperate(0);
return ans;
}
public void findSeperate(int start){ //start记录未被分割的部分的起始index
if(start == s.length()) { //说明前面的所有分割点都是满足要求的,所以可以保存结果
ans.add(new ArrayList(substrings));
return;
}
for(int i = start+1; i <= s.length(); i++){ //搜索分割点
String sub = s.substring(start, i);
if(!isPalindrome(sub)) continue;
substrings.add(sub);
findSeperate(i); //若当前分割点满足要求,继续分割后序部分
substrings.removeLast();
}
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String s){
int left = 0, right = s.length()-1;
while(left < right){
if(s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) return false;
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 为什么 退出登录 或 修改密码 无法使 token 失效