Linux 时间同步chrony
Linux 时间同步chrony
本文测试为服务器为
redhat8.6 做为服务器
centos8 做为客户端
1. 安装 chrony
一般系统已经装上了chrony包,可先检查一下
rpm -qa |grep chrony
安装命令:
yum install -y chrony
2. 关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld.service systemctl disable firewalld.service
3. Server端 ( redhat8.6 ) 配置chrony
vim /etc/chrony.conf
源文件为
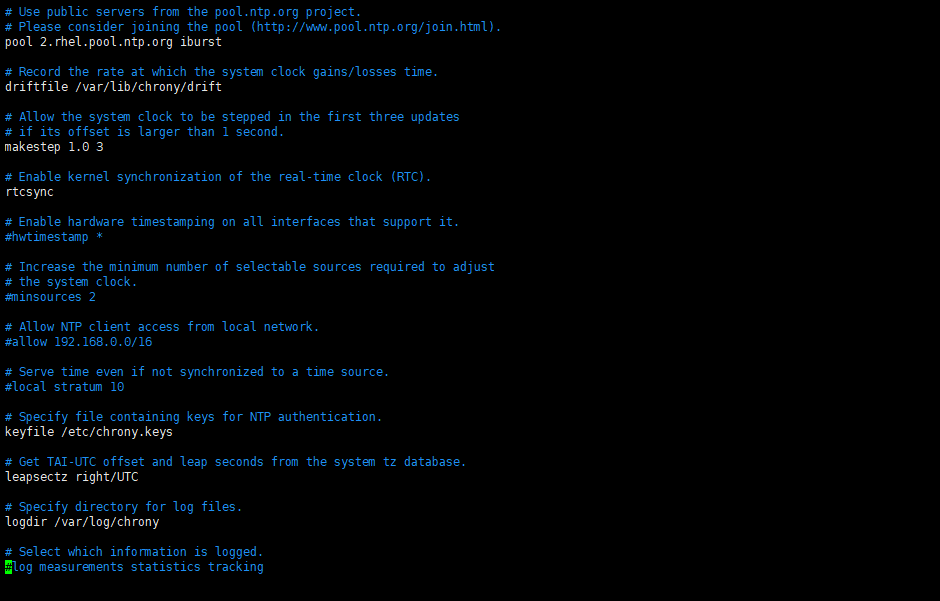
修改后:
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project. # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html). pool 2.rhel.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Record the rate at which the system clock gains/losses time. driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift # Allow the system clock to be stepped in the first three updates # if its offset is larger than 1 second. makestep 1.0 3 # Enable kernel synchronization of the real-time clock (RTC). rtcsync # Enable hardware timestamping on all interfaces that support it. #hwtimestamp * # Increase the minimum number of selectable sources required to adjust # the system clock. #minsources 2 # Allow NTP client access from local network. # allow 192.168.0.0/16 allow 192.168.91.0/24 # Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source. local stratum 10 # Specify file containing keys for NTP authentication. keyfile /etc/chrony.keys # Get TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system tz database. leapsectz right/UTC # Specify directory for log files. logdir /var/log/chrony # Select which information is logged. #log measurements statistics tracking ~ ~ ~
4. Client 端 ( centos8) 配置chrony
vim /etc/chrony.conf
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project. # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html). # pool 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst server 192.168.91.130 iburst # Record the rate at which the system clock gains/losses time. driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift # Allow the system clock to be stepped in the first three updates # if its offset is larger than 1 second. makestep 1.0 3 # Enable kernel synchronization of the real-time clock (RTC). rtcsync # Enable hardware timestamping on all interfaces that support it. #hwtimestamp * # Increase the minimum number of selectable sources required to adjust # the system clock. #minsources 2 # Allow NTP client access from local network. #allow 192.168.0.0/16 # Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source. #local stratum 10 # Specify file containing keys for NTP authentication. keyfile /etc/chrony.keys # Get TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system tz database. leapsectz right/UTC # Specify directory for log files. logdir /var/log/chrony # Select which information is logged. #log measurements statistics tracking ~
4. 开启chrony(所有主机)
开启 并 查看状态
systemctl stop chronyd.service
systemctl start chronyd.service
systemctl status chronyd.service
设置开机启动
systemctl enable chronyd.service
跟踪chrony查看
watch chronyc tracking
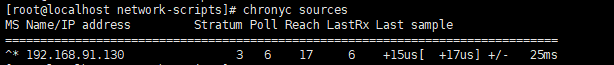
5. 查看同步源状态
chronyc sources
服务器

客户端
注意时区的一致性
查看时区
timedatectl
设置时区命令
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/Toronto
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/Los_Angeles
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35855396/article/details/114891638
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/rookiewyh/article/details/103029193


