图的邻接表表示与无环图的拓扑排序
一、 图的最常用的表示方法是邻接矩阵和邻接表。
1,邻接矩阵
邻接矩阵其实就是一个二维数组,对于每条边<u,v>,我们就令A[u][v] = 1,如果图为有权图,我们也可以令A[u][v]等于该权,这么表示的优点是非常简单,但是它的空间需求很大,如果图是稠密的,邻接矩阵是合适的表示方法,如果图是稀疏的,那这种方法就太浪费空间了,下面给出图的邻接矩阵表示例子。

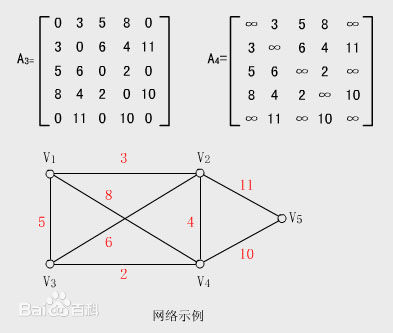
2 邻接表
邻接表是图的常用储存结构之一。邻接表由表头结点和表结点两部分组成,其中图中每个顶点均对应一个存储在数组中的表头结点。如下图所示:
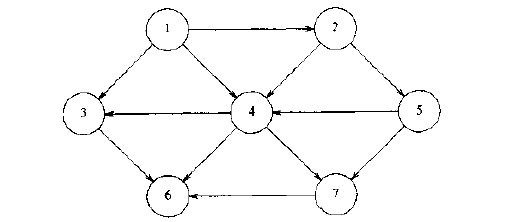
该图的邻接表为:
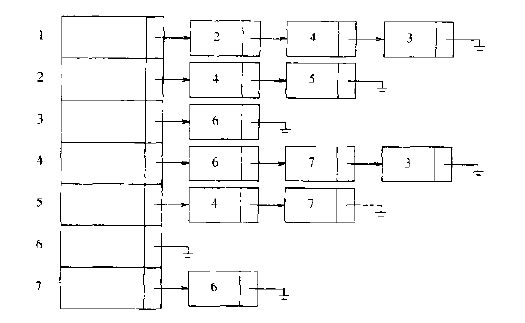
二、拓扑排序
1、定义
对一个有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph简称DAG)G进行拓扑排序,是将G中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点u和v,若<u,v> ∈E(G),则u在线性序列中出现在v之前。
通常,这样的线性序列称为满足拓扑次序(Topological Order)的序列,简称拓扑序列。
注意:
1)只有有向无环图才存在拓扑序列;
2)对于一个DAG,可能存在多个拓扑序列;
2、拓扑序列算法思想
(1)计算所有顶点的入度(若不存在,则这个图存在环),把所有入度为0的点放入一个列队中。
(2)出队一个入度为0的顶点,并输出之,假设为v;
(3)若存在边为<v,w>,则顶点w的入度减1,扫描所有点的入度,入度为0的顶点入队;
重复(2)(3)步,直到所有顶点的入度为0。出队的顺序就为拓扑排序的顺序。
三、代码实现
要排序的图为:
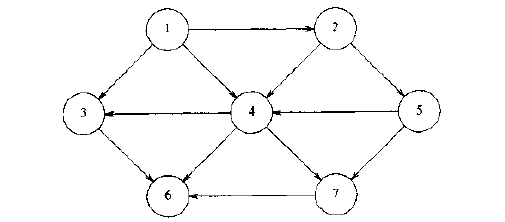
图的表示选用邻接表的表示方法,代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//////////////////////列队的相关定义//////////////////////
typedef struct QueueRecord *Queue;
#define MinQueueSize 10
struct QueueRecord
{
int Capacity; //队的容量
int Front; //队头
int Rear; //队尾
int Size; //队中元素的个数
int *Array; //数组
};
/////////////////////邻接表的相关定义//////////////////////
typedef struct EdgeNode *position;
typedef struct Led_table* Table;
struct EdgeNode //边表结点
{
int adjvex; // 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标
int weight; // 对应边的权值
position next; // 链域,指向下一个邻接点
};
struct Led_table // 邻接表结构
{
int data; //邻接表的大小
position *firstedge; //边表头指针,可以理解为数组
};
///////////////////列队相关函数声明////////////////////////
int IsEmpty(Queue Q); //判断队列是否为空
int IsFull(Queue Q); //判断队列是否满了
void MakeEmpty(Queue Q); //构造一个空列队
Queue CreateQueue(int MaxElements); //创建一个列队
void DisposeQueue(Queue Q); //释放一个列队
void Enqueue(int x, Queue Q); //入队
int Dequeue(Queue Q); //出队
int Front(Queue Q); //返回队首值,不出队
///////////////////列队相关函数定义////////////////////////
int IsEmpty(Queue Q)
{
return Q->Size == 0;
}
int IsFull(Queue Q)
{
if(Q->Size > Q->Capacity )
{
cout << "queue full" << endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
void MakeEmpty(Queue Q)
{
Q->Size = 0;
Q->Front = 1;
Q->Rear = 0;
}
Queue CreateQueue(int MaxElements)
{
Queue Q;
if (MaxElements < MinQueueSize)
{
cout << "queue size is too small" << endl;
}
Q = static_cast<Queue> (malloc(sizeof(struct QueueRecord)));
if(Q == NULL)
{
cout << "out of space!!!";
}
Q->Array =static_cast<int*>(malloc(sizeof(int)*MaxElements));
if(Q->Array == NULL)
{
cout << "out of space!!!";
}
Q->Capacity = MaxElements;
MakeEmpty(Q);
return Q;
}
void DisposeQueue(Queue Q)
{
if (Q != NULL)
{
free(Q->Array );
free(Q);
}
}
static int Succ(int Value, Queue Q) //循环数组,用于回绕
{
if(++Value == Q->Capacity )
Value = 0;
return Value;
}
void Enqueue(int x, Queue Q)
{
if(IsFull(Q))
{
cout << "Full queue" << endl;
}
else
{
Q->Size ++;
Q->Rear = Succ(Q->Rear, Q);
Q->Array [Q->Rear] = x;
}
}
int Dequeue(Queue Q)
{
if(IsEmpty(Q))
{
cout << "Empty Queue" << endl;
return false; //仅表示错误
}
else
{
Q->Size --;
Q->Front = Succ(Q->Front, Q);
return Q->Array[(Q->Front)-1];
}
}
int Front(Queue Q)
{
if(IsEmpty(Q))
{
cout << "Empty Queue" << endl;
return false; //仅表示错误
}
else
return Q->Array[Q->Front];
}
//////////////////////////邻接表相关函数定义///////////////
Table Creat_Lable (int MaxElements) //MaxElements参数为希望创建的节点数
{
Table table1 = static_cast<Table> (malloc(sizeof(struct Led_table)));
table1->data = MaxElements;
if (table1 == NULL)
{
cout << "out of space!!!";
}
table1->firstedge = static_cast<position*>(malloc(sizeof(position)*(table1->data)));
if (table1->firstedge == NULL)
{
cout << "out of space!!!";
}
//给每个表头赋值,从0开始
for (int i = 0; i <= table1->data - 1; ++i)
{
table1->firstedge [i] = static_cast<position>(malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode))); //申请一个节点
if (table1->firstedge [i] == NULL)
{
cout << "out of space!!!";
}
table1->firstedge [i]->adjvex = 0; //表头这个参数存储入度
table1->firstedge [i]->weight = 0; //此参数在此时没有意义
table1->firstedge [i]->next = NULL;
}
return table1;
}
void Insert (Table table1, int v, int w, int weig) //表示存在一条边为<v,w>,且权重为weig
{
position p = static_cast<position>(malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode))); //申请一个节点
if(p == NULL)
{
cout << "out of space!!!";
}
p->adjvex = w;
p->weight = weig;
p->next = table1->firstedge [v]->next;
table1->firstedge [v]->next = p;
}
void CountIndegree(Table table1) //计算顶点的入度,存在头结点中
{
for(int i = 0; i <= table1->data - 1; ++i)
{
position p = table1->firstedge [i]->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
++(table1->firstedge [p->adjvex]->adjvex) ;
p = p->next;
}
}
}
int* Topsort(Table table1) //拓扑排序
{
Queue queue_1 = CreateQueue(15); //创建一个列队
int Counter = 0;
int *TopNum = static_cast<int*>( malloc (sizeof(int)*(table1->data ))); //此数组用来存储结果
int v;
for(int i = 0; i != table1->data; ++i)
{
if(table1->firstedge[i]->adjvex == 0)
{
Enqueue(i,queue_1); //如果顶点i的入度为0,就入队
}
}
while(!IsEmpty(queue_1))
{
v = Dequeue(queue_1);
TopNum[v] = ++Counter; //若TopNum[5] = 3, 则排第三的为v5
position p = table1->firstedge [v]->next;
while (p != NULL) //把这个节点删除后,更新入度
{
--(table1->firstedge [p->adjvex]->adjvex);
if(table1->firstedge [p->adjvex]->adjvex == 0) Enqueue(p->adjvex,queue_1);
p = p->next;
}
}
if(Counter != table1->data )
{
cout << "the graph has a cycle" << endl;
}
DisposeQueue(queue_1);
return TopNum;
}
void print_Topsort_result(int *TopNum,Table table1) //打印拓扑排序结果
{
for(int i = 1; i != table1->data+1 ; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j != table1->data ; ++j)
{
if (TopNum[j] == i)
{
if(i == table1->data)
{
cout << "v" << j;
}
else
{
cout << "v" << j << "->";
}
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
Table table_1 = Creat_Lable (7); //创建一个大小为7的邻接表
//根据图来为邻接表插入数据
Insert (table_1, 0, 1, 2);Insert (table_1, 0, 2, 4);Insert (table_1, 0, 3, 1);
Insert (table_1, 1, 3, 3);Insert (table_1, 1, 4, 10);
Insert (table_1, 2, 5, 5);
Insert (table_1, 3, 2, 2);Insert (table_1, 3, 5, 8);Insert (table_1, 3, 6, 4);
Insert (table_1, 4, 3, 2);Insert (table_1, 4, 6, 6);
Insert (table_1, 6, 5, 1);
CountIndegree(table_1); //计算入度
int* TopNum = Topsort(table_1); //拓扑排序
print_Topsort_result(TopNum,table_1); //打印拓扑排序结果
delete TopNum;
delete table_1;
while(1);
return 0;
}
输出结果为:
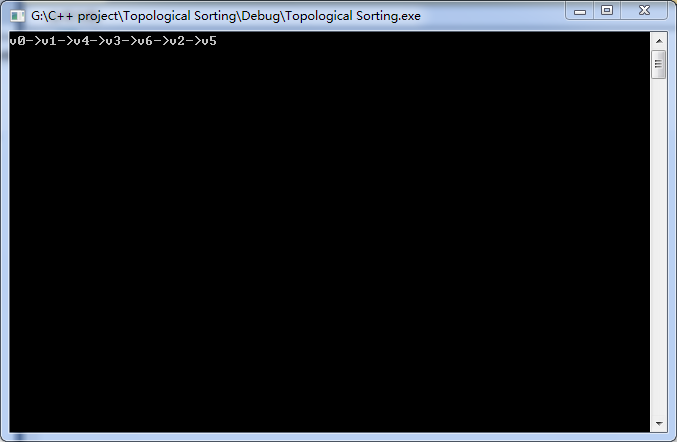
上述算法的思想很重要,要多学习。
夜深了....



