[NOI2011]阿狸的打字机
题意:Luogu
题解:AC自动机
对于fail树,我们有性质:如果有一条边\((u,v)\),则\(u\)代表的字符串必然为\(v\)的后缀
对于trie树,我们有性质:如果有一条边\((u,v)\),则\(u\)代表的字符串必然为\(v\)的前缀
还有一个性质:字串必定是某一后缀的一个前缀
询问是这样的:对于询问\((x,y)\),求第\(x\)个打印的字符串在第\(y\)个打印的字符串中出现了多少次。
考虑对于每一组询问\((x,y)\),我们可以先把询问离线,按y排序
我们还要预处理出每一个串的结束节点\(root\)和这个节点对应的编号\(id\)
按trie树建树的顺序dfs,每递归到一个点,如果这是一个结束节点,就处理掉这个点的所有询问
我们首先把fail树的dfs序求出来,设为\(dfs\_l\)和\(dfs\_r\)
在trie树上dfs时,先对这个点的\(dfs\_l[rt]\)的值+1
对于每个询问\(x\),答案即为\(\big[dfs\_l[root[q[i].x]],dfs\_r[root[q[i].x]\big]\)的区间和
dfs回溯时再-1
所以上树状数组即可
问题来了,为什么可以这样?
下面是一个例子:插入的是hers his she i
这是连了fail指针的trie树(连向根节点的fail指针没放上去)
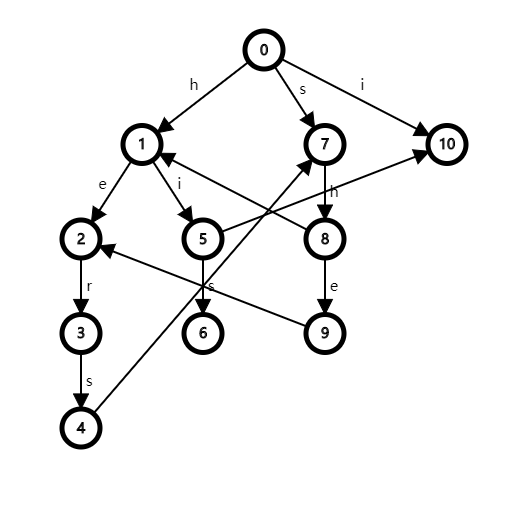
这是fail树
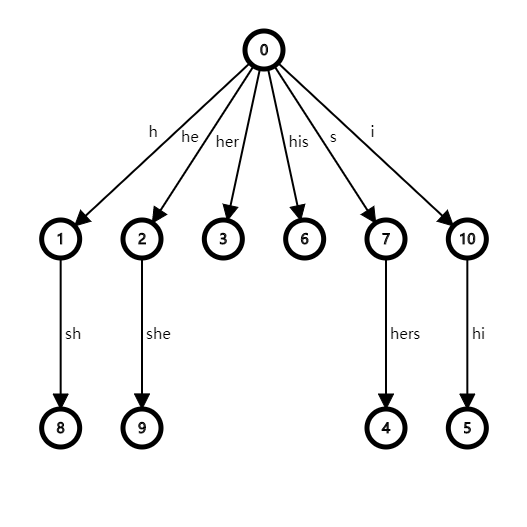
如果我们要查 i 在 his 中的出现次数
我们dfs到了6号节点,\(val[6]+=1\)
这是一个结束节点,所以我们开始处理询问
查询,查\([9,10]\)区间和(也就是10号节点的子树)
答案是1(因为此时trie树上4,5,6节点值都为1,对应在fail树上就是8,6,10节点为1)
统计区间保证了我们要找的模式串(i)是它子树中的所有串的后缀
trie树的dfs方式保证了我们统计的答案是所有原串(his)的前缀(h,hi,his)
两者的交就是所有原串的前缀的后缀是模式串的数量,也就是所求答案
最后上代码,大多数都封了namespace,应该能看懂吧
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline void read(int& x)
{
x = 0; char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar();
}
#define maxn 100005
int root[maxn], id[maxn], ql[maxn], qr[maxn], ans[maxn];
struct Query
{
int x, y, id, ans;
bool operator < (const Query& p) const { return y < p.y; }
}q[maxn];
namespace Tree
{
struct Edge
{
int fr, to;
}eg[maxn << 1];
int head[maxn], edgenum;
inline void add(int fr, int to)
{
eg[++edgenum] = { head[fr],to };
head[fr] = edgenum;
}
int dfn_clock, dfs_l[maxn], dfs_r[maxn];
void dfs(int rt)
{
dfs_l[rt] = ++dfn_clock;
for (int i = head[rt]; i; i = eg[i].fr) dfs(eg[i].to);
dfs_r[rt] = dfn_clock;
}
};
using namespace Tree;
namespace Bitarray
{
int c[maxn];
inline int lowbit(int& x) { return x & (-x); };
inline void update(int& pos, int v) { for (int i = pos; i <= dfn_clock; i += lowbit(i)) c[i] += v; }
inline int query(int pos) { int ans = 0; for (int i = pos; i; i -= lowbit(i)) ans += c[i]; return ans; }
}
using namespace Bitarray;
namespace AC_automaton
{
int son[maxn][26], fail[maxn], fa[maxn], tot, Son[maxn][26];
//有两个son是因为第一次会把原来的trie树补成图(也就是加了fail),然而第二次我们需要dfs的是树
inline void getfail()//我把建fail树封到这里面了
{
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
if (son[0][i]) q.push(son[0][i]), add(0, son[0][i]);
while (!q.empty())
{
int tp = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
{
if (son[tp][i])
{
fail[son[tp][i]] = son[fail[tp]][i];
q.push(son[tp][i]);
add(fail[son[tp][i]], son[tp][i]);
}
else son[tp][i] = son[fail[tp]][i];
}
}
}
};
using namespace AC_automaton;
char s[maxn];
int cnt, Q;
void Dfs(int rt)//得到答案
{
update(dfs_l[rt], 1);
if (id[rt])
for (int i = ql[id[rt]]; i <= qr[id[rt]]; ++i)
q[i].ans = query(dfs_r[root[q[i].x]]) - query(dfs_l[root[q[i].x]] - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) if (Son[rt][i]) Dfs(son[rt][i]);
update(dfs_l[rt], -1);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%s", s);
for (int i = 0, rt = 0; s[i]; ++i)
{
if (s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'z')
{
if (!son[rt][s[i] - 'a']) son[rt][s[i] - 'a'] = ++tot, fa[tot] = rt;
rt = son[rt][s[i] - 'a'];
}
else if (s[i] == 'B') rt = fa[rt];
else root[++cnt] = rt, id[rt] = cnt;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 26; ++j) Son[i][j] = son[i][j];
getfail(); dfs(0);
read(Q);
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++i) read(q[i].x), read(q[i].y), q[i].id = i;
sort(q + 1, q + Q + 1);
for (int i = 1, pos = 1; i <= Q; i = pos)//合并询问
{
ql[q[i].y] = i;
while (q[pos].y == q[i].y) ++pos;
qr[q[i].y] = pos - 1;
}
Dfs(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++i) ans[q[i].id] = q[i].ans;
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++i) printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
There is a negligible beginning in all great action and thought.


