学习总结2
beautifulsoup学习:
#BeautifulSoup将复杂HTML换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是python的对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种
# -Tag
# -NavigableString
# -BeautifulSoup
# -Comment

#BeautifulSoup将复杂HTML换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是python的对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种 # -Tag # -NavigableString # -BeautifulSoup # -Comment from bs4 import BeautifulSoup file =open("myself/index.html","rb") #打开指定文件,用rb(二进制读取方式)方式进行读取 html=file.read().decode("utf-8") #读到内存里,并用html方式保存 bs=BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") #用指定解析器进行解析 #-----------------------------------------基础解析---------------------------------------- #1.Tag 标签及其内容,拿到它所找到的第一个内容 print(bs.title) print(bs.title.string) print(type(bs.title.string)) #判断类型 #2.NavigableString 标签里的内容(字符串) print(bs.a.attrs) #3.BeautifulSoup 表示整个文档 print(type(bs)) print(bs) #4.Comment 是一个特殊的NavigableString,输出的内容不包含注释符号 print(bs.a.string) print(type(bs.a.string)) #-------------------------------------实际应用--------------------------------------- #文档的遍历 print(bs.head.contents) #contects文档遍历的一种属性 获取特定标签的特定内容 print(bs.head.contents[1]) #文档的搜索*** #1.find-all() t_list=bs.find_all("a") #输出a标签的内容 print(t_list) #2.正则表达式搜索,使用search()方法来匹配内容 import re t_list-bs.find_all(re.compile("a")) #按着正则表达式,输出里面包含a的所有相关内容 print(t_list) #方法:传入一个函数(方法),根据函数的要求来搜索 def name_is_exists(tag): return tag.has_attr("name") t_list=bs.find_all(name_is_exists()) #打印列表循环 for item in t_list: print(item) print(t_list) #3.kwarges 参数 #t_list=bs.find_all(id="head") #t_list=bs.find_all(class_=True) t_list=bs.find_all(href="") print(t_list) #3.text参数 t_list=bs.find_all(text="xianmoqihua") t_list=bs.find_all(text=["123","地图","贴吧"]) #4.limit 参数 t_list=bs.find_all("a",limit=3) #限定获取的信息数量 #css选择器 print(bs.select('title')) #通过标签来查找 print(bs.select('.mnav')) #通过类名来查找 print(bs.select('#ul')) #通过id来查找 t_list=bs.select("a[class]='bri']") #通过属性来查找 t_list=bs.select("head > title") #通过子标签来查找 t_list=bs.select(".mnav ~ .bri") print(t_list[0].get_text())
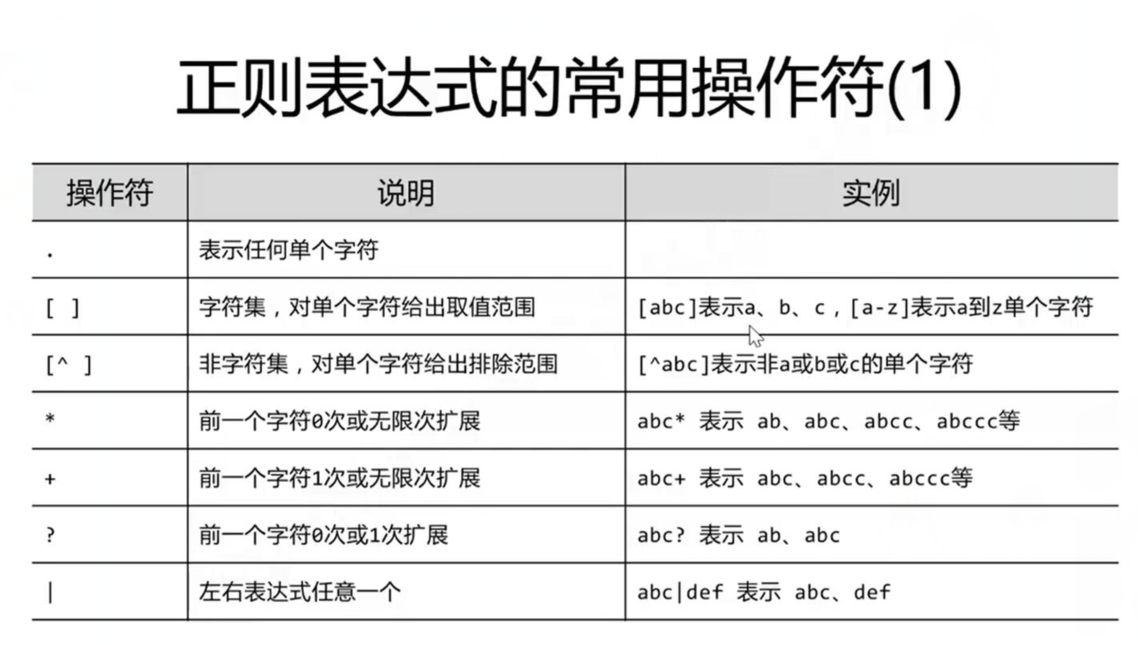


建议在正则表达式中,被比较的字符串前面加上人,不用担心转义字符的问题





