JavaWeb_(Spring框架)xml配置文件
系列博文
JavaWeb_(Spring框架)xml配置文件 传送门
JavaWeb_(Spring框架)注解配置 传送门
Xml配置
a)Bean元素:交由Spring管理的对象都要配置在bean标签中;
i.Bean标签介绍和创建方式:空参构造、静态工厂、动态工厂;
ii.Scope属性介绍:singleton、protoptype、request、session;
iii.初始化方法Init-method和 销毁方法destroy-method介绍;
b)属性注入:
i.Set方法注入;
ii.构造函数注入;
iii.复杂类型注入:Array、List、Set、Map、Properties
1、xml配置-bean标签-配置及创建方式
ApplicationContext 配置的所有bean都会在容器创建的时候被创建出来,
如果配置的bean较多,那么在创建容的时候,会产生内存过大的问题;这种情况在机器硬件性能较为落后的时候体现的比较明显;
延迟加载(懒加载) true就是创建容器时不加载配置的bean对象,在获取的时候才创建;
<!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象 name 可以使用特殊字符 name 可以重复 我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的--> <!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象 name 可以使用特殊字符 name 可以重复 我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的--> <!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 --> <!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致--> <!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
2、xml配置-bean标签-scope属性
scope="singleton" 表示<bean>是单例的
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="singleton"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>
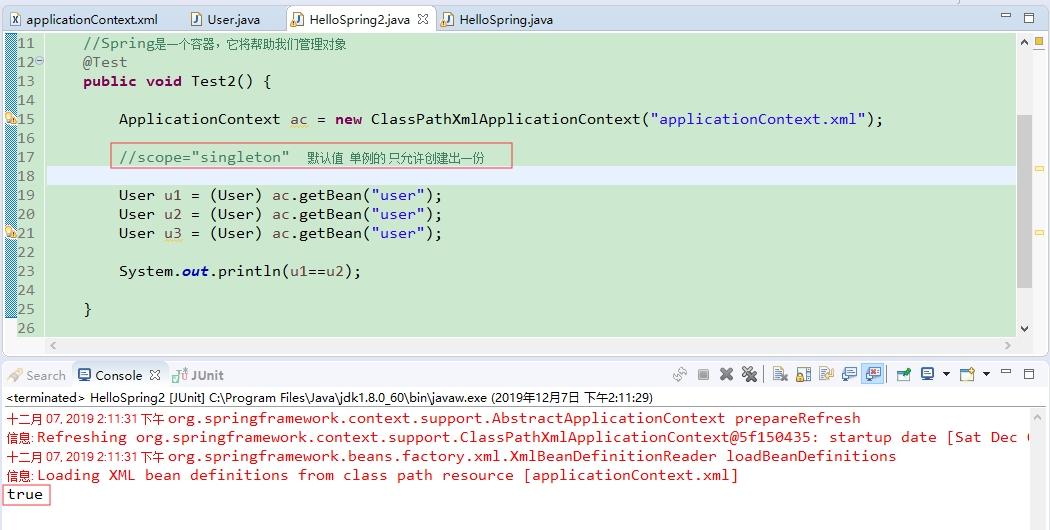

package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class HelloSpring2 { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //scope="singleton" 默认值 单例的 只允许创建出一份 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1==u2); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象 name 可以使用特殊字符 name 可以重复 我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的--> <!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 --> <!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致--> <!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="singleton"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
scope="prototype" 表示<bean>是多例的
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="prototype"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>
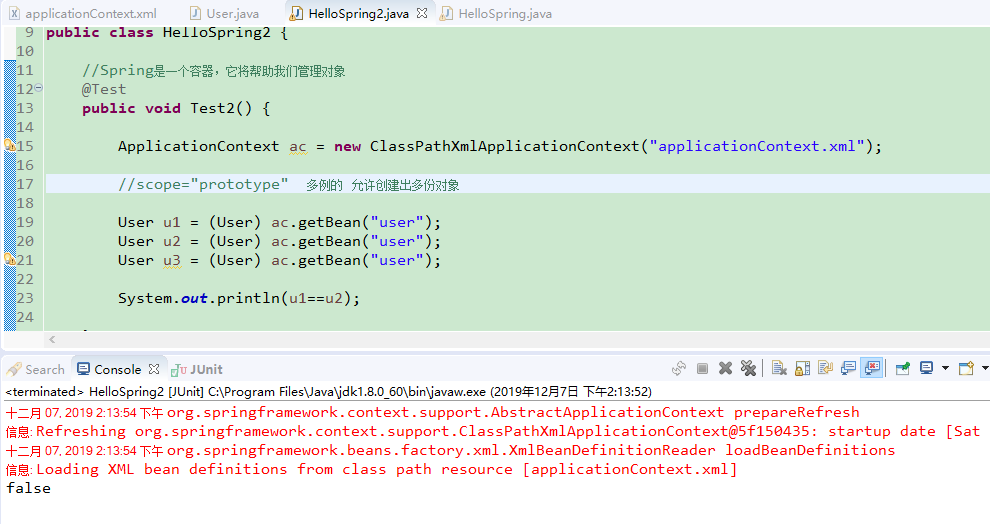

package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class HelloSpring2 { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //scope="prototype" 多例的 允许创建出多份对象 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1==u2); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象 name 可以使用特殊字符 name 可以重复 我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的--> <!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 --> <!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致--> <!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="prototype"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
scrope的其它两个属性request、session(基本用不到这两个属性)
一般情况下使用singleton单例的,特殊情况下使用prototype多例的(使用struts时,它创建的action是多例的)
<!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致--> <!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" scope="prototype"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>
3、xml配置-bean标签-init-method与destroy-method的使用
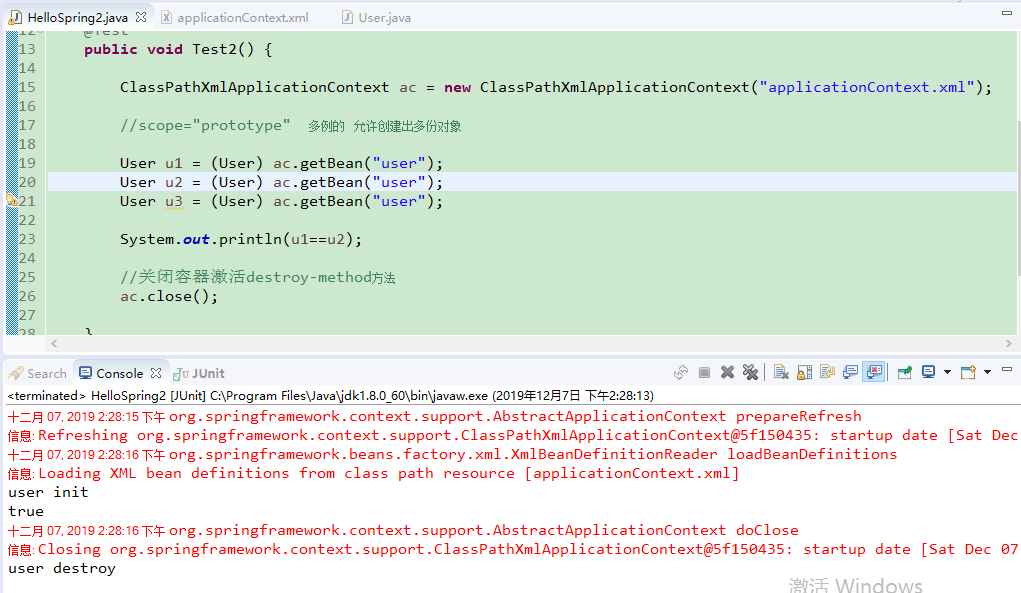
在User.java中添加一个userInit()初始化方法与userDestroy()销毁容器时的方法
public void userInit() { System.out.println("user init"); } public void userDestroy() { System.out.println("user destroy"); }
<bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" init-method="userInit" destroy-method="userDestroy"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean>

package com.Gary.bean; public class User { private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; /*public User() { System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法"); }*/ public Integer getU_id() { return u_id; } public void setU_id(Integer u_id) { this.u_id = u_id; } public String getU_username() { return u_username; } public void setU_username(String u_username) { this.u_username = u_username; } public String getU_password() { return u_password; } public void setU_password(String u_password) { this.u_password = u_password; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + "]"; } public void userInit() { System.out.println("user init"); } public void userDestroy() { System.out.println("user destroy"); } }

package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class HelloSpring2 { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //scope="prototype" 多例的 允许创建出多份对象 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1==u2); //关闭容器激活destroy-method方法 ac.close(); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- name 是起一个名字,我们可以通过这个name来利用容器获取对象 name 可以使用特殊字符 name 可以重复 我们在实际开发中不推荐将多个对象名字命名为重复的--> <!-- id与name作用基本相同,单不推荐使用 不支持特殊字符,不能重复 --> <!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 --> <!-- request 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致--> <!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User" lazy-init ="true" init-method="userInit" destroy-method="userDestroy"> <!-- 为u_id注入了一个id为2的值 --> <property name="u_id" value="2"></property> </bean> </beans>
4、xml配置-属性注入-Set方式注入
注入一个基本类型
创建一个applicationContext_Injection.xml和Test_Injection.java
<!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary"/> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> </bean>
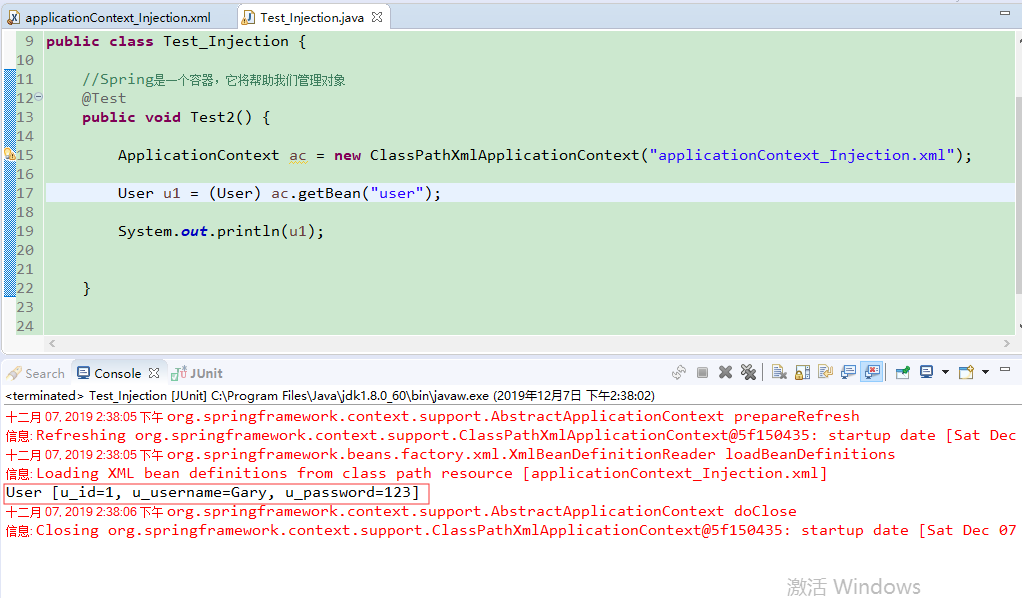

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary"/> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> </bean> </beans>

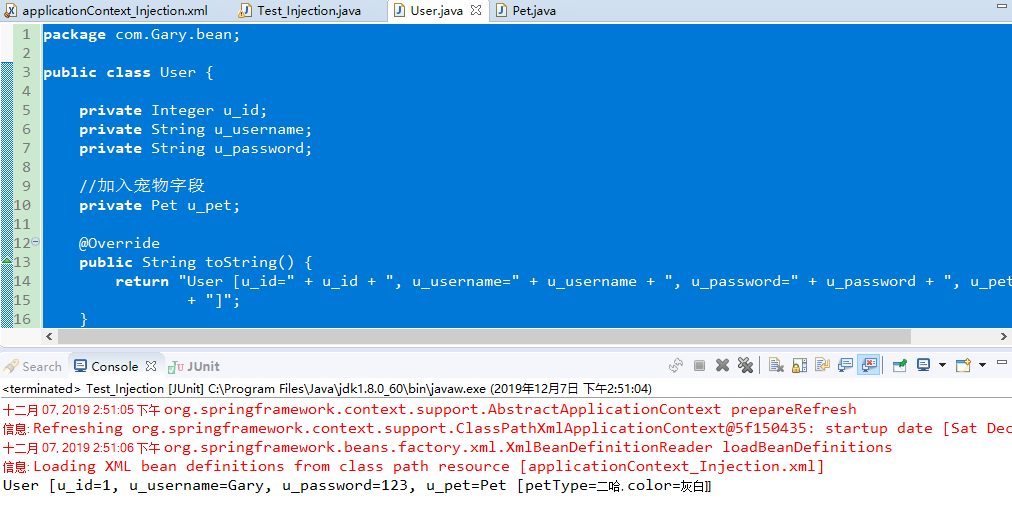
package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1); } }

package com.Gary.bean; public class User { private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; /*public User() { System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法"); }*/ public Integer getU_id() { return u_id; } public void setU_id(Integer u_id) { this.u_id = u_id; } public String getU_username() { return u_username; } public void setU_username(String u_username) { this.u_username = u_username; } public String getU_password() { return u_password; } public void setU_password(String u_password) { this.u_password = u_password; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + "]"; } public void userInit() { System.out.println("user init"); } public void userDestroy() { System.out.println("user destroy"); } }
注入引用类型
创建一个Pet.java宠物类

package com.Gary.bean; public class Pet { //宠物类型 猫 狗 private String petType; //宠物颜色 private String color; @Override public String toString() { return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]"; } public String getPetType() { return petType; } public void setPetType(String petType) { this.petType = petType; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } }
在User.java中加入宠物字段
private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; //加入宠物字段 private Pet u_pet;

package com.Gary.bean; public class User { private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; //加入宠物字段 private Pet u_pet; @Override public String toString() { return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet + "]"; } public Pet getU_pet() { return u_pet; } public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) { this.u_pet = u_pet; } /*public User() { System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法"); }*/ public Integer getU_id() { return u_id; } public void setU_id(Integer u_id) { this.u_id = u_id; } public String getU_username() { return u_username; } public void setU_username(String u_username) { this.u_username = u_username; } public String getU_password() { return u_password; } public void setU_password(String u_password) { this.u_password = u_password; } public void userInit() { System.out.println("user init"); } public void userDestroy() { System.out.println("user destroy"); } }
<!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary"/> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> <!-- 引用类型的注入 --> <property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 --> <bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet"> <property name="petType" value="二哈"/> <property name="color" value="灰白"/> </bean>

package com.Gary.bean; public class User { private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; //加入宠物字段 private Pet u_pet; @Override public String toString() { return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet + "]"; } public Pet getU_pet() { return u_pet; } public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) { this.u_pet = u_pet; } /*public User() { System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法"); }*/ public Integer getU_id() { return u_id; } public void setU_id(Integer u_id) { this.u_id = u_id; } public String getU_username() { return u_username; } public void setU_username(String u_username) { this.u_username = u_username; } public String getU_password() { return u_password; } public void setU_password(String u_password) { this.u_password = u_password; } public void userInit() { System.out.println("user init"); } public void userDestroy() { System.out.println("user destroy"); } }

package com.Gary.bean; public class Pet { //宠物类型 猫 狗 private String petType; //宠物颜色 private String color; @Override public String toString() { return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]"; } public String getPetType() { return petType; } public void setPetType(String petType) { this.petType = petType; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } }

package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary"/> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> <!-- 引用类型的注入 --> <property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 --> <bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet"> <property name="petType" value="二哈"/> <property name="color" value="灰白"/> </bean> </beans>
5、xml配置-属性注入-构造函数注入
在User.java中创建构造函数(一定要带空参构造方法)
public User(String u_username, Pet u_pet) { System.out.println("方法1 String,Pet"); this.u_username = u_username; this.u_pet = u_pet; }

package com.Gary.bean; public class User { private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; public User(String u_username, Pet u_pet) { System.out.println("方法1 String,Pet"); this.u_username = u_username; this.u_pet = u_pet; } //加入宠物字段 private Pet u_pet; @Override public String toString() { return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet + "]"; } public Pet getU_pet() { return u_pet; } public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) { this.u_pet = u_pet; } /*public User() { System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法"); }*/ public Integer getU_id() { return u_id; } public void setU_id(Integer u_id) { this.u_id = u_id; } public String getU_username() { return u_username; } public void setU_username(String u_username) { this.u_username = u_username; } public String getU_password() { return u_password; } public void setU_password(String u_password) { this.u_password = u_password; } public void userInit() { System.out.println("user init"); } public void userDestroy() { System.out.println("user destroy"); } }
在applicationContext_Injection.xml中使用构造方法注入配置<bean>元素
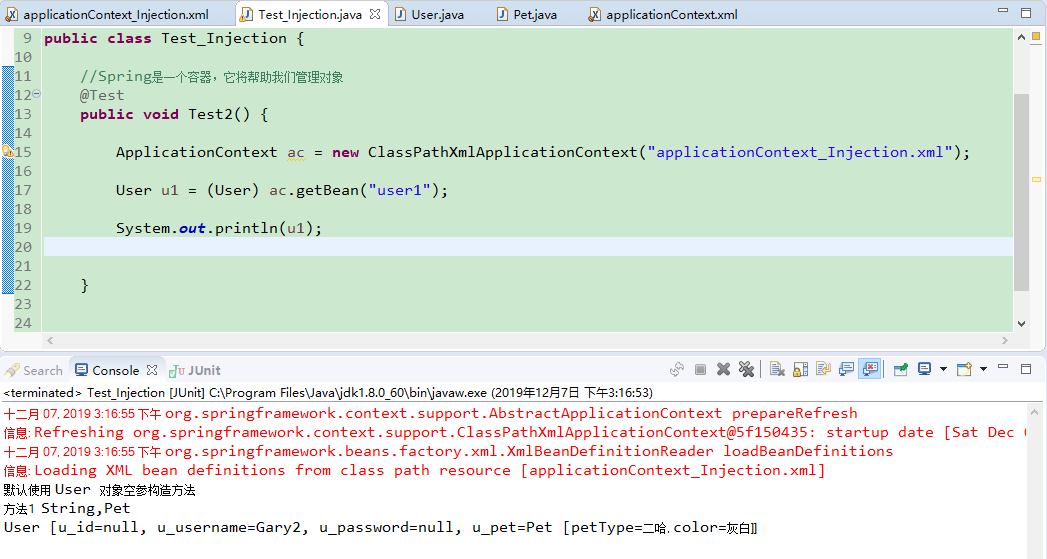
<!-- 构造方法注入 --> <bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2"/> <constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean>


package com.Gary.bean; public class User { private Integer u_id; private String u_username; private String u_password; public User(String u_username, Pet u_pet) { System.out.println("方法1 String,Pet"); this.u_username = u_username; this.u_pet = u_pet; } //加入宠物字段 private Pet u_pet; @Override public String toString() { return "User [u_id=" + u_id + ", u_username=" + u_username + ", u_password=" + u_password + ", u_pet=" + u_pet + "]"; } public Pet getU_pet() { return u_pet; } public void setU_pet(Pet u_pet) { this.u_pet = u_pet; } public User() { System.out.println("默认使用 User 对象空参构造方法"); } public Integer getU_id() { return u_id; } public void setU_id(Integer u_id) { this.u_id = u_id; } public String getU_username() { return u_username; } public void setU_username(String u_username) { this.u_username = u_username; } public String getU_password() { return u_password; } public void setU_password(String u_password) { this.u_password = u_password; } }

package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user1"); System.out.println(u1); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary"/> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> <!-- 引用类型的注入 --> <property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 --> <bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet"> <property name="petType" value="二哈"/> <property name="color" value="灰白"/> </bean> <!-- 构造方法注入 --> <bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2"/> <constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> </beans>
如果有多个构造方法,可以使用type:指定参数的类型,index :指定参数
6、xml配置-属性注入-复杂类型注入Array、List、Set、Map、Properties
在MyCollection.java中定义几个复杂类型变量
//数组 private Object[] array; //list private List list; //set private Set set; //map private Map map; //properties private Properties properties;
<!-- 复杂类型注入 --> <bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection"> <!-- array --> <property name="array"> <array> <value>123</value> <value>abc</value> </array> </property> </bean>

package com.Gary.bean; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; public class MyCollection { //数组 private Object[] array; //list private List list; //set private Set set; //map private Map map; //properties private Properties properties; public Object[] getArray() { return array; } public void setArray(Object[] array) { this.array = array; } public List getList() { return list; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public Set getSet() { return set; } public void setSet(Set set) { this.set = set; } public Map getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map map) { this.map = map; } public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Override public String toString() { return "MyCollection [array=" + Arrays.toString(array) + ", list=" + list + ", set=" + set + "]"; } }

package com.Gary.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.Gary.bean.MyCollection; import com.Gary.bean.User; public class Test_Injection { //Spring是一个容器,它将帮助我们管理对象 @Test public void Test2() { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml"); MyCollection mc = (MyCollection) ac.getBean("collection"); System.out.println(mc); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary" /> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> <!-- 引用类型的注入 --> <property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 --> <bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet"> <property name="petType" value="二哈"/> <property name="color" value="灰白"/> </bean> <!-- 构造方法注入 --> <bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2" type=""/> <constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 复杂类型注入 --> <bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection"> <!-- array --> <property name="array"> <array> <value>123</value> <value>abc</value> </array> </property> </bean> </beans>
同理剩下几个复杂类型配置
<!-- 复杂类型注入 --> <bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection"> <!-- array --> <property name="array"> <array> <value>123</value> <value>abc</value> <ref bean="dog"/> </array> </property> <!-- list --> <property name="list"> <list> <value>456</value> <value>cba</value> <ref bean="user1"/> </list> </property> <!--set --> <property name="set"> <set> <value>111</value> <value>aaa</value> <ref bean="user1"/> </set> </property> <!-- map --> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="username" value="root"/> <entry key="password" value="123"/> <entry key-ref="user1" value-ref="dog"/> </map> </property> <!-- properties --> <property name="prop"> <props> <prop key="name">老李</prop> <prop key="age">25</prop> </props> </property> </bean>

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <!-- 将user对象交给Spring管理,并注入类型 --> <bean name="user" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <property name="u_id" value="1"/> <property name="u_username" value="Gary" /> <property name="u_password" value="123"/> <!-- 引用类型的注入 --> <property name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 注入引用类型 --> <bean name="dog" class="com.Gary.bean.Pet"> <property name="petType" value="二哈"/> <property name="color" value="灰白"/> </bean> <!-- 构造方法注入 --> <bean name="user1" class="com.Gary.bean.User"> <constructor-arg name="u_username" value="Gary2" type=""/> <constructor-arg name="u_pet" ref="dog"/> </bean> <!-- 复杂类型注入 --> <bean name="collection" class="com.Gary.bean.MyCollection"> <!-- array --> <property name="array"> <array> <value>123</value> <value>abc</value> <ref bean="dog"/> </array> </property> <!-- list --> <property name="list"> <list> <value>456</value> <value>cba</value> <ref bean="user1"/> </list> </property> <!--set --> <property name="set"> <set> <value>111</value> <value>aaa</value> <ref bean="user1"/> </set> </property> <!-- map --> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="username" value="root"/> <entry key="password" value="123"/> <entry key-ref="user1" value-ref="dog"/> </map> </property> <!-- properties --> <property name="prop"> <props> <prop key="name">老李</prop> <prop key="age">25</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>



