异步编程解决方案 Promise
1. 回调地狱
2. Promise 的使用
3. Promise 的状态
4. Promise 的结果
5. Promise 的 then 方法
6. Promise 的 catch 方法
7. 回调地狱的解决方案
1. 回调地狱
回调地狱: 在回调函数中嵌套回调函数
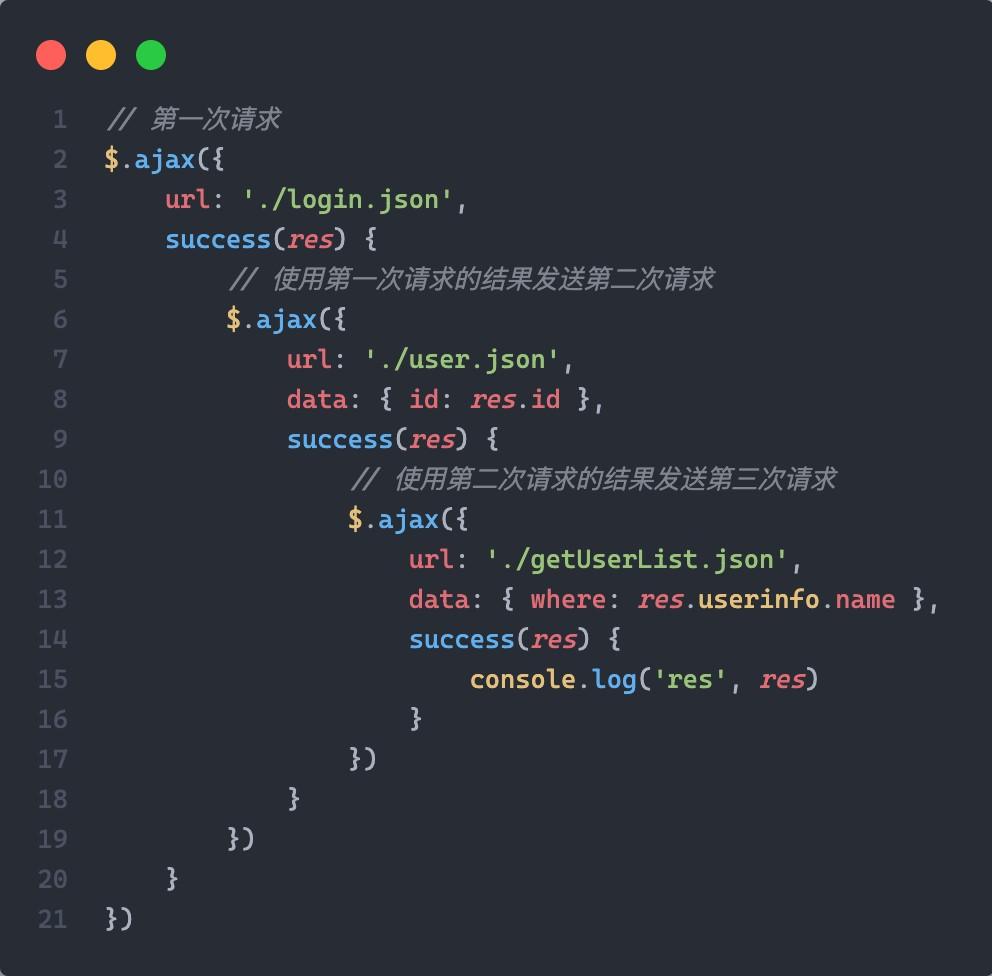
因为 ajax 请求是异步的,所以想要使用上一次请求的结果作为请求参数,所以必须在上一次请求的回调函数中执行下次请求,这种写法非常繁琐,我们亲切的把它称之为 回调地狱
ES6 原生提供了 Promise 对象,Promise 解决了回调地狱的问题
回调地狱代码示例:
// 第一次请求$.ajax({url: './login.json',success(res) {// 使用第一次请求的结果发送第二次请求$.ajax({url: './user.json',data: { id: res.id },success(res) {// 使用第二次请求的结果发送第三次请求$.ajax({url: './getUserList.json',data: { where: res.userinfo.name },success(res) {console.log('res', res)}})}})}})
2. Promise 的使用
Promise 是一个构造函数,接受一个函数作为参数,通过 new 关键字实例化
new Promise((resolve, reject) => { });
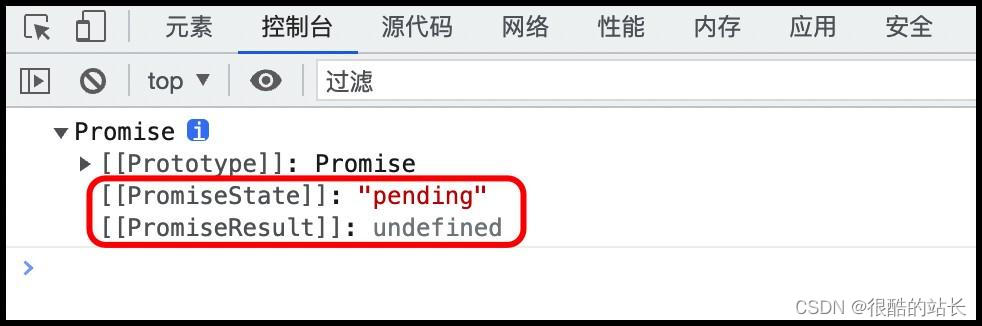
查看 Promise 实例的属性
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { });console.dir(promise);
得出 Promise 实例有两个属性: state(状态),result(结果)
3. Promise 的状态
Promise 实例的三种状态
pending (准备,待解决,进行中)fulfilled(已完成,成功)rejected (已拒绝,失败)
Promise 状态的改变:
通过调用 resolve(),reject() 改变当前 promise 对象的状态,promise 对象的状态改变是一次性的。
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {// 使当前 promise 对象状态改为 fulfilled// resolve()// 使当前 promise 对象状态改为 rejected// reject()});
4. Promise 的结果
Promise 实例的另外一个属性 result 的值就是调用 resolve() 或 reject() 的参数
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve({ name: 'liang' })});console.dir(promise);const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {reject({ name: 'wang' })});console.dir(promise2);

5. Promise 的 then 方法
then 方法是第一个参数在 promise 状态是 fulfilled 执行,第二个参数在 promise 状态是 rejected 执行
then 方法的返回值是一个 promise 对象
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {reject({ name: 'liang' })});p.then(res => {// 当 promise 状态是 fulfilled 执行console.log('成功时调用', res)}, reason => {// 当 promise 状态是 rejected 执行console.log('失败时调用', reason)});
在 then 方法中使用 return 可以将 then 方法返回的 promise 实例改为 fulfilled 状态
在 then 方法中,如果代码出错(错误异常),会将返回的 promise 实例状态改为 rejected
// 如果 promise 的状态不改变 then 方法无法执行const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve()});const t = p.then(res => {console.log('成功时调用', res)// 在 then 方法中使用 return 可以将 then 方法返回的 promise 实例状态改为 fulfilled// return 123// 如果这里的代码出错 会将 t 实例的状态改为 rejectedconsole.log(a);}, reason => {console.log('失败时调用', reason)});t.then(res => {// res 123console.log('t 成功', res)}, reason => {console.log('t 失败', reason)})
6. Promise 的 catch 方法
catch 方法参数中的函数执行时机 ?
1. 当 promise 实例状态改为 rejected 时
2. promise 构造函数的参数方法体中有错误发生(其实也是状态变为 rejected )
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {// 下面两种错误都会触发 catch 方法// reject('有错误')// throw new Error('出错了')});p.catch(res => {console.log('res', res)})
catch 方法 和 then 方法的第二个参数都能捕捉到 promise 实例状态改为 rejected 时的情况,那么平时推荐怎么用 ?下面是 Promise 最常见的写法,推荐这么使用
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve()// reject()});p.then(res => {console.log('res', res)}).catch(reason => {console.log('reason', reason)})
7. 回调地狱的解决方案
回调地狱写法
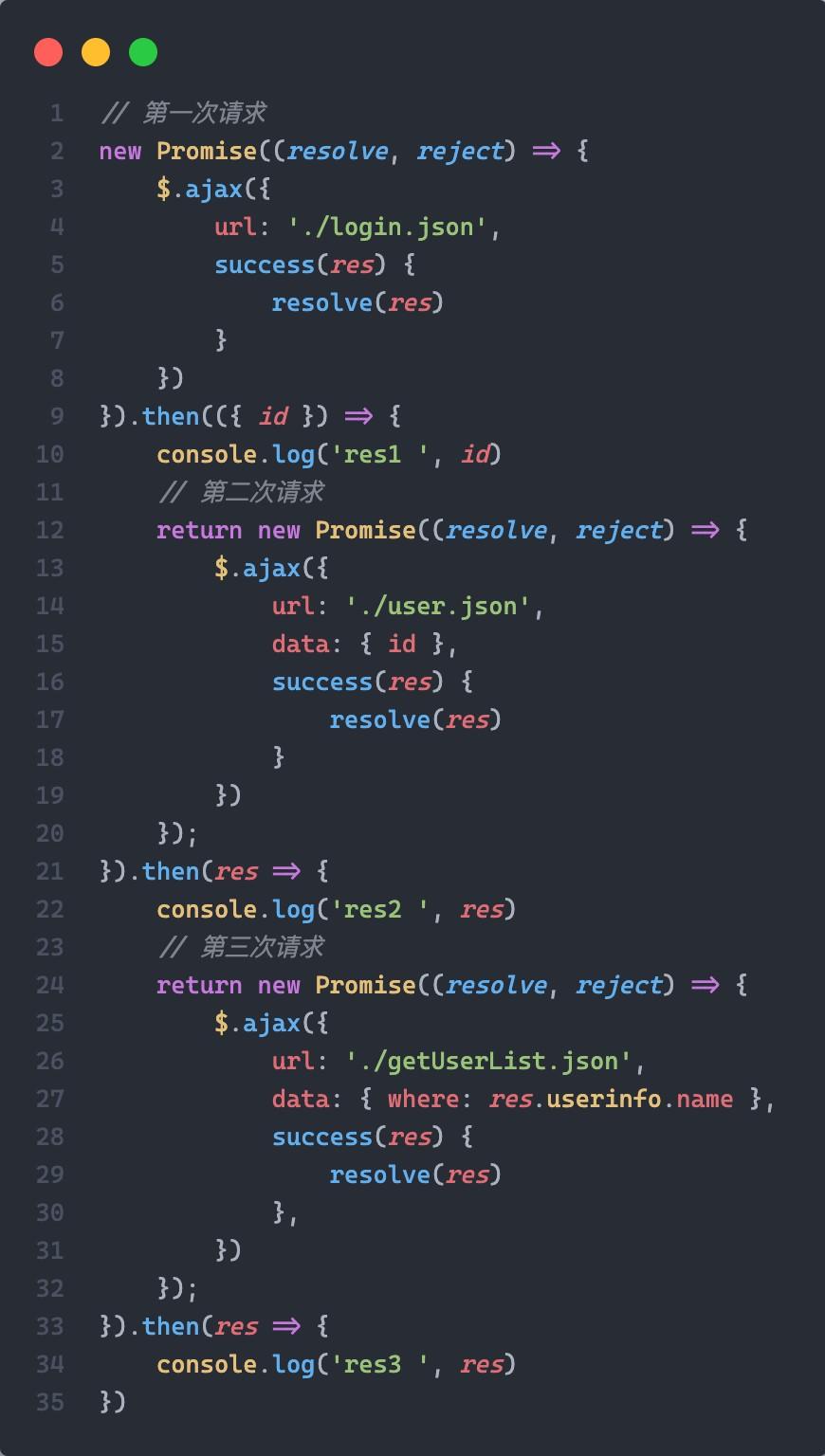
第一次改造: 使用 Promise
第二次改造: 封装函数
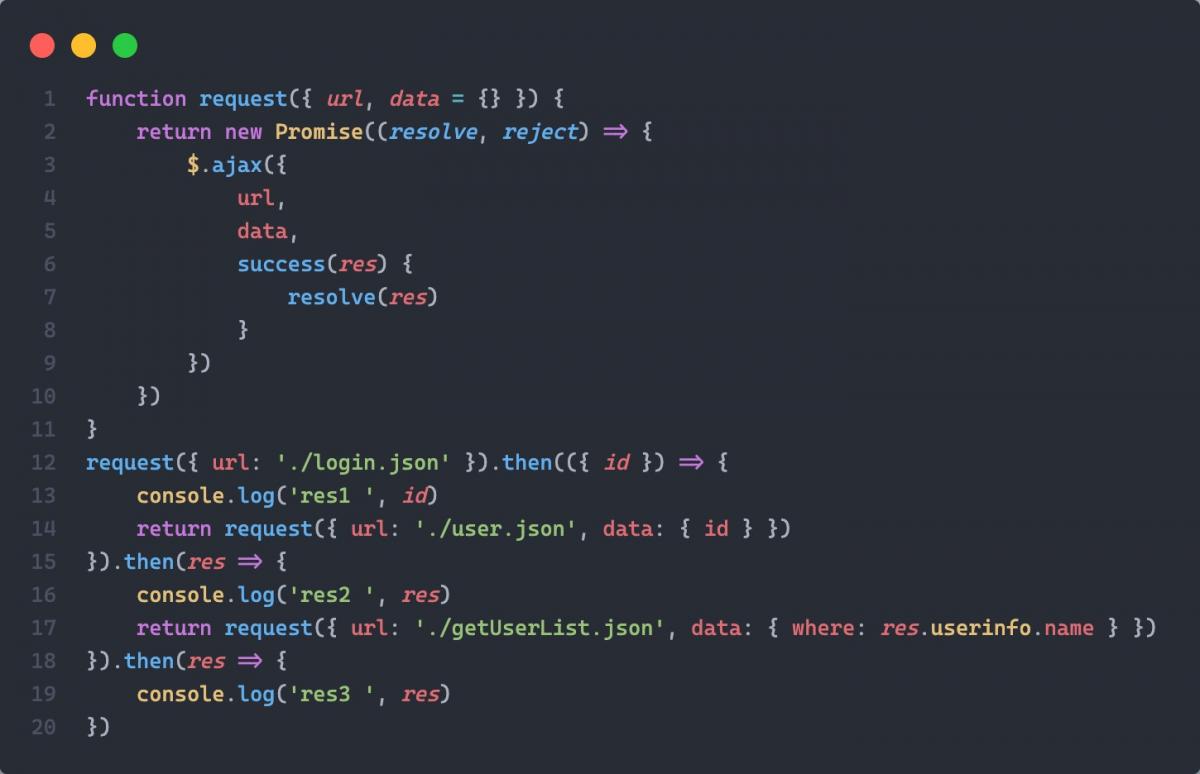
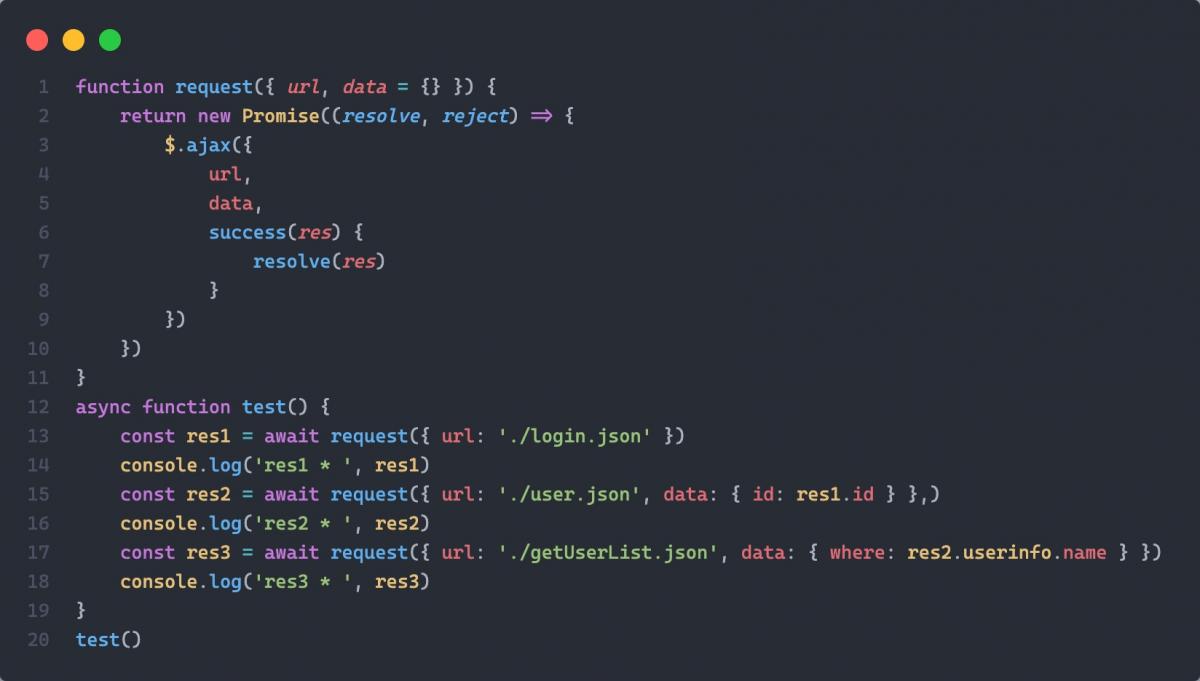
第三次改造: 终极解决方案(使用 async + await)