结对编程四则运算--JAVA实现(徐静、林文敏)
项目相关要求
-
-n 参数控制生成题目的个数 (√)
Myapp.exe -n 10 // 将生成10个题目
-
-r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围 (√)
Myapp.exe -r 10
// 将生成10以内(不包括10)的四则运算题目。
// 该参数可以设置为1或其他自然数。
// 该参数必须给定,否则程序报错并给出帮助信息。 -
生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数。即若出现e1 − e2,则e1 ≥ e2。(√)
-
生成的题目中若存在e1 ÷ e2,则结果为真分数。(√)
-
每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。(√)
-
程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。(√)
-
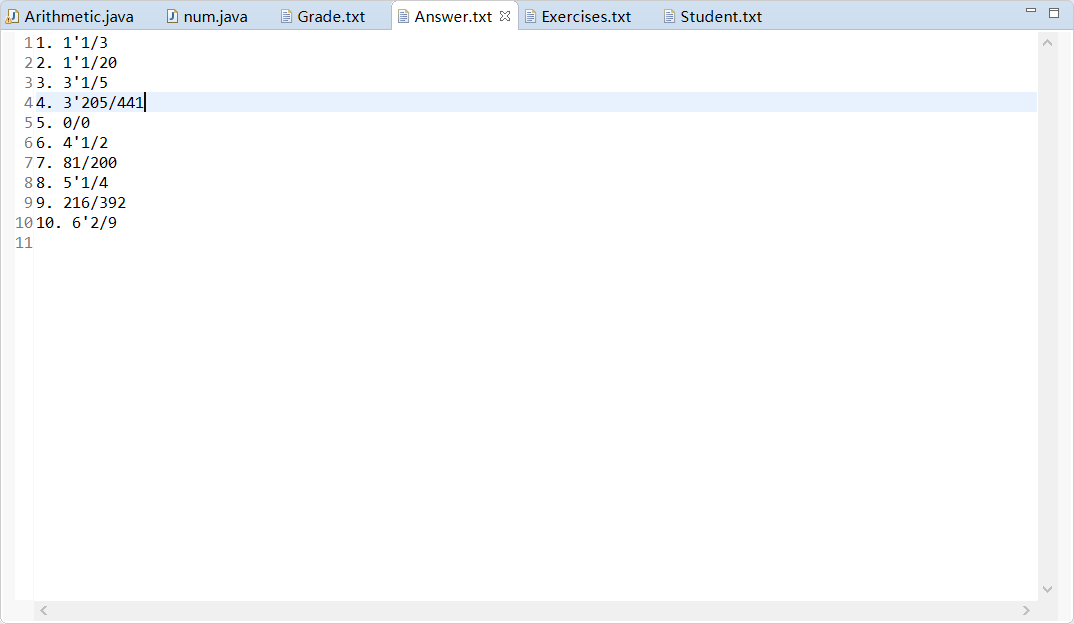
生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件,格式如下: (√)
1、 四则运算题目1
2、 四则运算题目2
……其中真分数在输入输出时采用如下格式,真分数五分之三表示为3/5,真分数二又八分之三表示为2’3/8。
-
在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件,格式如下: (√)
1、 答案1
2、 答案2 -
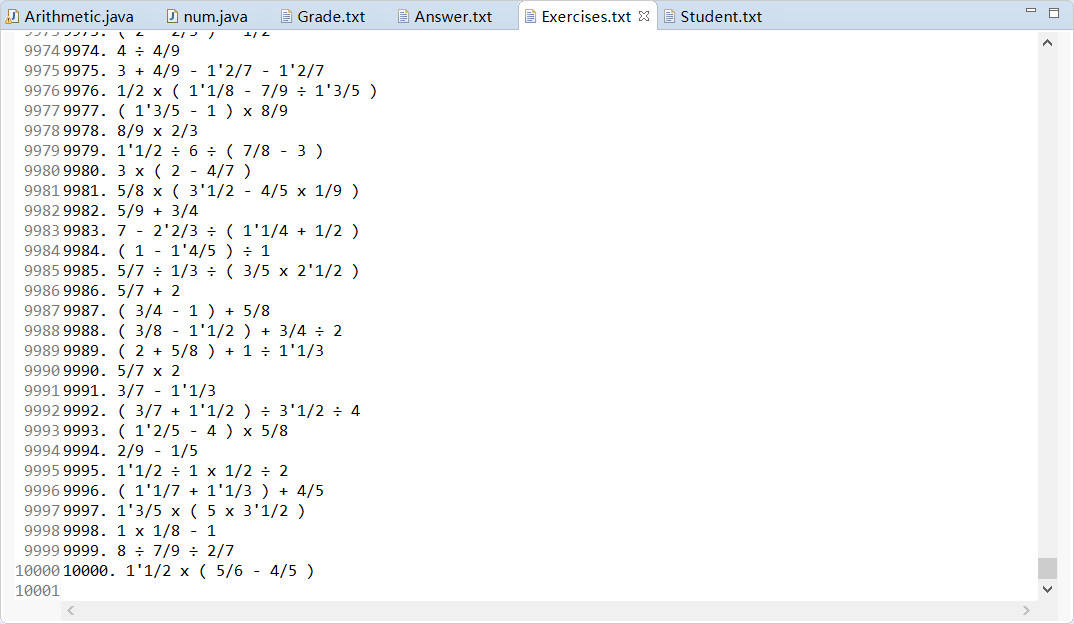
程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。(√)
-
程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,输入参数如下:(√)
Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt
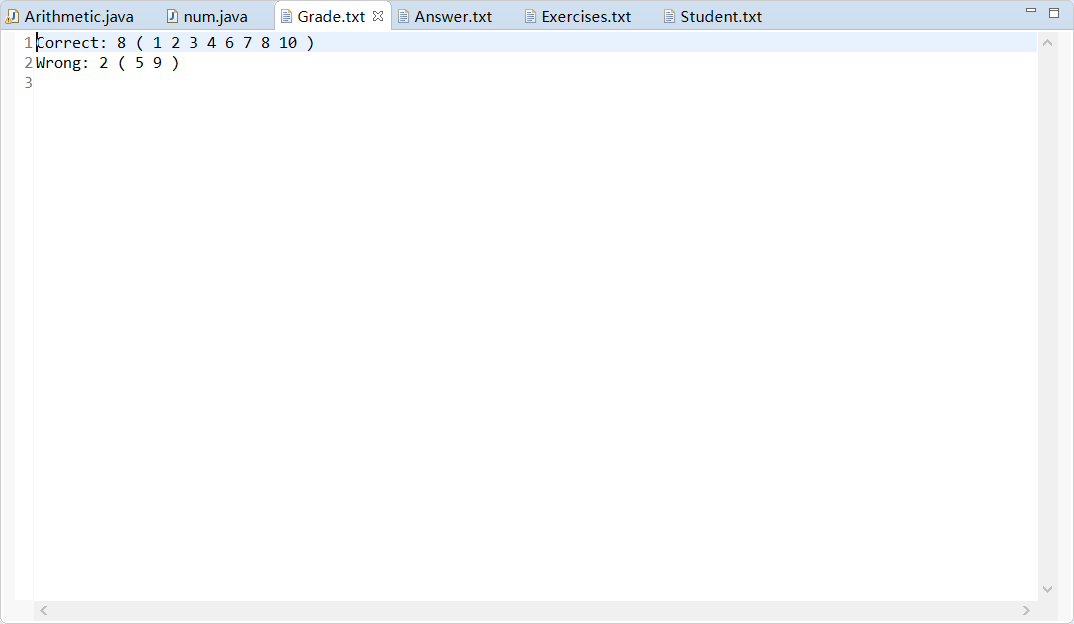
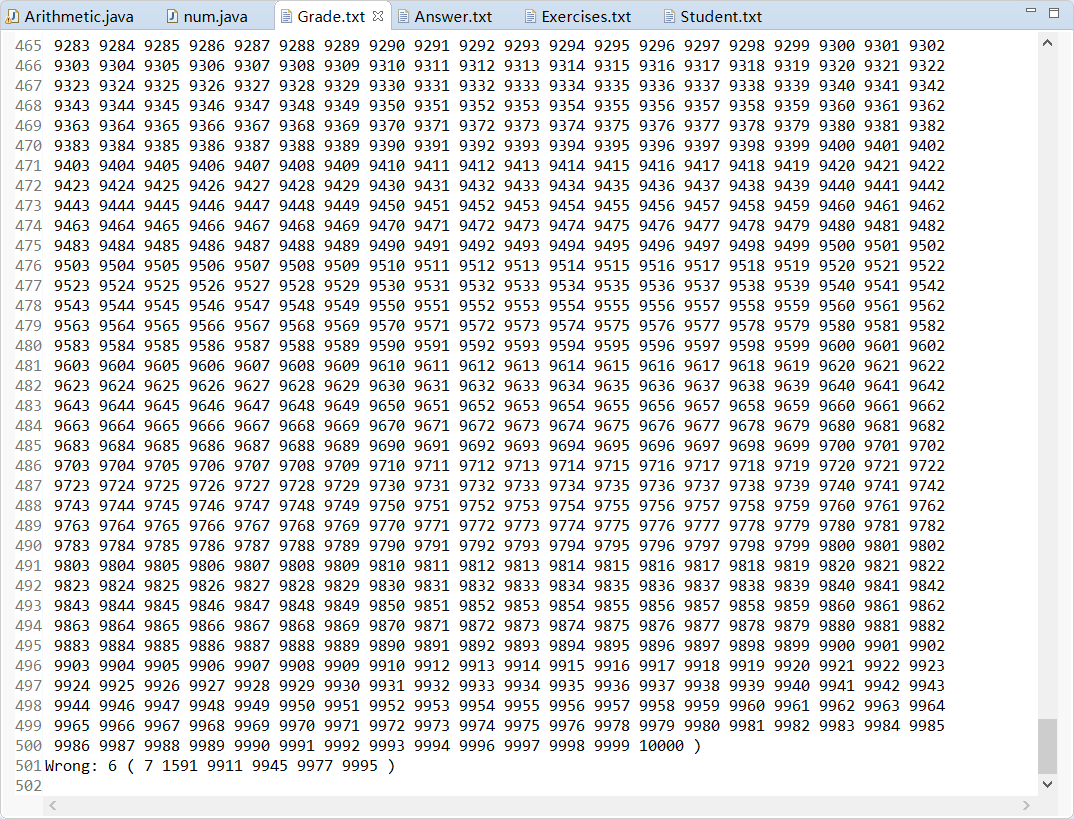
统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)其中“:”后面的数字5表示对/错的题目的数量,括号内的是对/错题目的编号。为简单起见,假设输入的题目都是按照顺序编号的符合规范的题目。
PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 1400 | 1830 |
| Development | 开发 | 1340 | 1250 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 90 | 90 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 15 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 30 | 25 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 720 | 660 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 120 | 100 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 180 | 720 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 120 | 120 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | 60 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 20 |
| 合计 | 1520 | 1940 |
遇到的困难及解决方法
-
问题描述
- 1、如何对字符串型的表达式进行计算
- 2、计算表达式Count方法出现答案不准确及空指针
- 3、假分数转换为真分数时无法解决20/15等数据
- 4、判断答案对错进行数量统计时参数传不进去
- 5、生成题目时生成的都是第一道题,后面的题目无法写入
- 做过的尝试及如何解决
-
1、试过一个一个解析,但是发现不容易实现,后来百度后发现通过二叉树可以很方便快捷的同时解决计算,查重问题
-
2、代码复审发现答案错误是因为除法减法用反了,空指针是因为栈中的元素个数不正确,有些情况没有考虑到
-
3、在生成表达式时就进行约分
-
4、将表达式转换为后缀表达式传入参数
- 5、将生成表达式方法里的返回值exp每生成下一条式子时将上一条式子清空
-
成功解决问题
-
收获:了解并学习了中缀表达式及后缀表达式的转换,多角度思考问题
设计实现过程
流程图
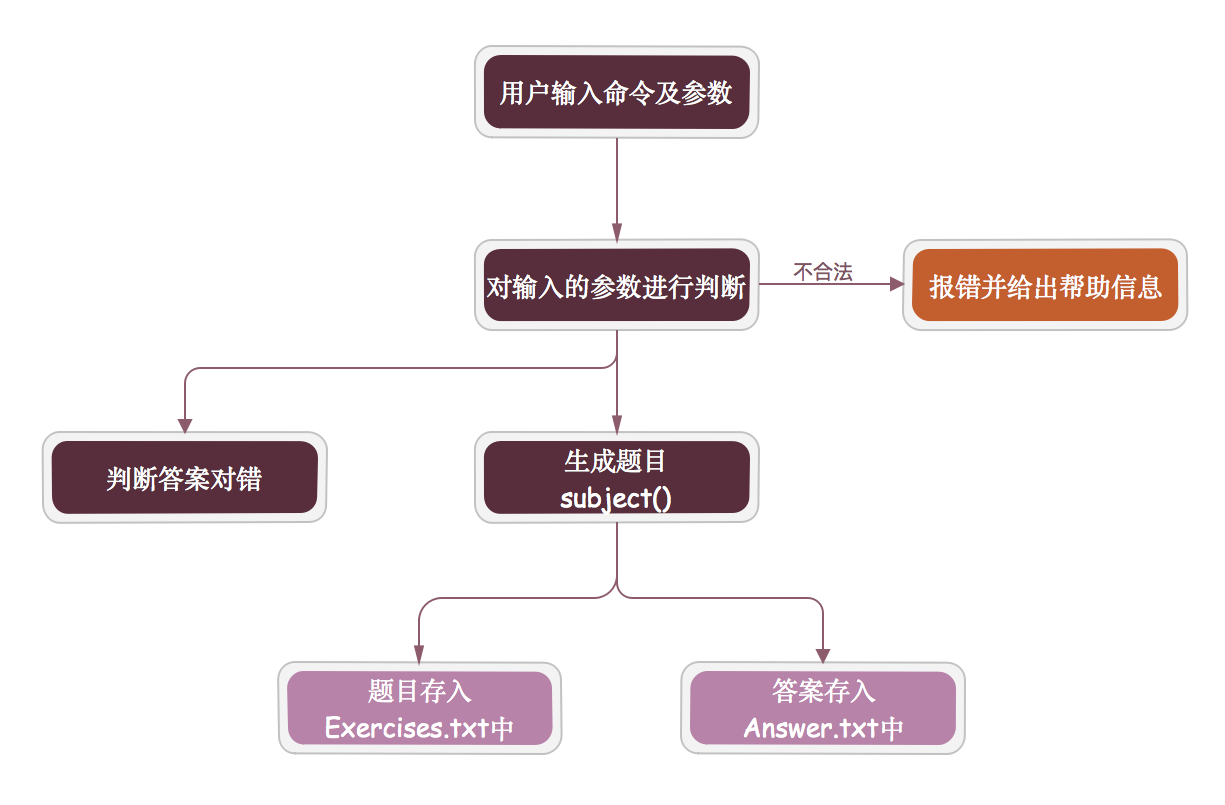
包含以下几个函数:
- subject() // 生成表达式
- change(int n, int d) // 将假分数转换为真分数,第一个参数为分子,第二个为分母
- ifExist(List s) // 用于检查是否有相同的题目,并处理
- save(List s) // 用于将题目存入当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件
- answer(List a) // 用于将题目答案存入当前目录下的Answer.txt文件
- check(File e, File a,File g) // 用于对给定的题目文件和答案文件判断答案文件中的对错并统计至Grade.txt
- count(List<String> list) // 构建树计算表达式,并存入题目列表
- ......
实现过程:
关键代码
生成随机数
// 产生随机数
public static String createnum() {
ThreadLocalRandom rand = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
int a = rand.nextInt(range);
int b = rand.nextInt(range);
if (a == 0) {
a += (int) (Math.random()*range + 1);
}
if (b == 0) {
b += (int) (Math.random()*range + 1);
}
if (b == range) {
b = b-1;
}
num n = new num(a,b);
easy(n);
if (n.a == n.b) {
return Integer.toString(1);
}
if (n.b == 1) {
return Integer.toString(n.a);
}
// System.out.println(n.tostring());
return n.tostring();
}
生成随机运算符
public static String createopr1() {
return opr[(int) (Math.random()*4)];
}
public static String createopr2() {
return opr[(int) (Math.random()*2 + 2)];
}
public static String createopr3() {
return opr[(int) (Math.random()*2)];
}
public static void checkbkt(int bkt_s, int bkt_e,List<String>exp) {
String f;
String s;
String t;
if (bkt_e - bkt_s == 1) {
if (bkt_s == 1) {
f = exp.get(2);
s = exp.get(5);
if (!(f.equals("+") || (f.equals("-"))) && !(s.equals("x") || s.equals("÷"))) {
exp.set(2, createopr3());
exp.set(5, createopr2());
}
} else if (bkt_s == 2) {
f = exp.get(1);
s = exp.get(4);
if (exp.size()<8) {
if ((f.equals("+") || (f.equals("-"))) && (s.equals("x") || (s.equals("÷")))) { // 排除 a + ( b x c ) 此类括号无意义的情况
exp.set(1, createopr2());
}
}
} else if (bkt_s == 3) {
f = exp.get(3);
s = exp.get(6);
if ((f.equals("+") || (f.equals("-"))) && (s.equals("x") || s.equals("÷"))) {
exp.set(3, createopr2());
} else if (((f.equals("+") || f.equals("-"))) && (s.equals("+") || s.equals("-"))) {
exp.set(3, createopr2());
}
}
} else {
if (bkt_s == 1) {
f = exp.get(2);
s = exp.get(4);
t = exp.get(7);
if (!(t.equals("x") || t.equals("÷"))) {
exp.set(7, createopr2());
if (f.equals(s) && (f.equals("+") || f.equals("÷"))) {
exp.set(4, createopr2());
}
}
} else if (bkt_s == 2) {
f = exp.get(1);
s = exp.get(4);
t = exp.get(6);
if ((f.equals("+") || f.equals("-")) && (t.equals("x") || t.equals("÷"))) {
exp.set(1, createopr2());
}
}
}
}
生成表达式
// 生成表达式,并存入题目列表 static void subject() { // 运算符个数 1-3 个 List<String> exp = new ArrayList<String>(); int opr_n = (int) (Math.random()*3 + 1); switch(opr_n) { case 1: exp.add(createnum()); exp.add(createopr1()); exp.add(createnum()); break; case 2: // 括号起始位置 int bkt_s = (int) (Math.random()*3); // 括号结束位置 int bkt_e = 0; // 无括号 if (bkt_s == 0) { bkt_e = 0; } else { bkt_e = bkt_s + 1; } for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { if (bkt_s == i) { exp.add("("); } exp.add(createnum()); if (bkt_e == i) { exp.add(")"); } exp.add(createopr1()); } // 处理括号无意义情况 checkbkt(bkt_s, bkt_e,exp); exp.remove(exp.size()-1); // 删除最后多加入的一个运算符 break; case 3: // 括号起始位置 bkt_s = (int) (Math.random()*4); // 无括号 if (bkt_s == 0) { bkt_e = 0; } else if (bkt_s == 3){ bkt_e = 4; } else { bkt_e = bkt_s + (int) (Math.random()*2 + 1); // [1,3) } for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) { if (bkt_s == i) { exp.add("("); } exp.add(createnum()); if (bkt_e == i) { exp.add(")"); } exp.add(createopr1()); } // 处理括号无意义情况 checkbkt(bkt_s, bkt_e,exp); exp.remove(exp.size()-1); // 删除最后多加入的一个运算符 break; } e.add(exp); System.out.println(toString(exp)); // exp.clear(); }
计算表达式
// 构建树计算表达式,并存入题目列表 public static String count(List<String> list) { Stack<Node> a1 = new Stack<>(); // 数值栈 Stack<String> b = new Stack<>(); // 未处理的运算符栈 // Stack<Node> c = new Stack<>(); // 处理后的运算符栈 for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) { String string = list.get(i); if (!isop(string)) {
// 当前指针为数值 a1.push(new Node(string, null, null, null)); } else { //比较栈顶符号与当前符号的优先级 while (!b.isEmpty() && !(string.equals("(") || (prefer(string)==2 && prefer(b.peek())==1) || (!string.equals(")") && b.peek().equals("(")))) { String symbol = b.pop(); if (symbol.equals("(") && string.equals(")")) { break; } push(symbol, a1); } //如果符号不是")"就进栈 if (!string.equals(")")) { b.push(string); } } } while (!b.isEmpty()) { push(b.pop(), a1); } negative(a1); return a1.peek().result; } // 处理负数 public static void negative(Stack<Node> c) { if (!c.isEmpty()) { for (int i=0; i<c.size(); i++) { Node n = c.get(i); if (n.op.equals("-")) { num l = new num(n.left.result); num r = new num(n.right.result); if (l.a*r.b < r.a*l.b) { Node m = n.left; n.left = n.right; n.right = m; n.setResult(); } } } } } public static void push(String op, Stack<Node> a) { if (!op.equals("(")) { Node r = a.pop(); Node l = a.pop(); Node o = new Node(null, r, l, op); o.result = count(r.result, l.result, op); a.push(o); } } public static String count(String r, String l, String op) { num left = new num(l); num right = new num(r); switch (op) { case "+": return left.add(right).tostring(); case "-": return left.sub(right).tostring(); case "x": return left.mul(right).tostring(); case "÷": return left.div(right).tostring(); } return null; } static class Node { String result; Node right; Node left; String op; public Node(String result, Node right, Node left, String op) { this.result = result; this.right = right; this.left = left; this.op = op; } public void setResult() { if (op!=null) { result = count(right.result, left.result, op); } } public void changelr() { Node m = left; right = left; left = m; } } public static int prefer(String op) { // 判断运算符优先级 if (op.equals("-") || op.equals("+")) { return 1; } else if (op.equals("x") || op.equals("÷")) { return 2; } else { return 3; } } public static boolean isop(String op) { // 判断是否为运算符 if (op.equals("+") || op.equals("-") || op.equals("x") || op.equals("÷") || op.equals("(") || op.equals(")")) { return true; } else { return false; } }
分数转换
public class num {
public int a; // 分子
public int b; // 分母
public num() {
}
public num(String s) { // 处理数值
s = s.trim();
int a,b;
int x = s.indexOf("'");
int y = s.indexOf("/");
if (x != -1) { // 代分数处理
int c = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0, x)); // 代分数的整数部分
b = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(y+1));
a = c * b + Integer.parseInt(s.substring(x+1,y));
} else if (y != -1) { // 分数处理
a = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0,y));
b = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(y+1));
} else { // 整数处理
a = Integer.parseInt(s);
b = 1;
}
check(a,b);
}
public num(int a, int b) {
check(a,b);
}
public void check(int a, int b) {
if (a>=0 && b>0) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
}
public num add(num n) { // 加法 a + b
return new num((this.b*n.a + this.a*n.b), this.b*n.b);
}
public num sub(num n) { // 减法 a - b
return new num((this.a*n.b - this.b*n.a), this.b*n.b);
}
public num mul(num n) { // 乘法 a * b
return new num(this.a*n.a, this.b*n.b);
}
public num div(num n) { // 除法 a / b
return new num(this.a*n.b, this.b*n.a);
}
public int gcd(int a, int b) { // 求分数最大公约数
if (a<b) {
int x = b % a;
return x == 0 ? a : gcd(a,x);
} else if (a>b) {
int y = a % b;
return y == 0 ? b : gcd(b,y);
} else return 1;
}
public static num easy(num n) { // 约分
if (n.a == 0) {
return new num(0, 1);
} else {
int m = n.gcd(n.a, n.b);
if (m == 1) {
return n;
} else {
n.a = n.a/m;
n.b = n.b/m;
return n;
}
}
}
public String change(int n, int d) {
// 将假分数转换为真分数,第一个参数为分子,第二个为分母
//假分数转真分数方法 求 最大整除数+余数/分母
num a = easy(new num(n,d));
int left=a.a/a.b;
int up=a.a-left*a.b;
int down=a.b;
if(left==0) {
return up+"/"+down;
}
else if(down == 1) {
return Integer.toString(n);
}else {
return left+"'"+up+"/"+down;
}
}
public String tostring() { // 转换为字符串
if (this.a>this.b) {
return this.change(a,b);
} else if (this.b ==1){
return Integer.toString(this.a);
} else {
return this.a + "/" + this.b;
}
}
}
查重
// 检查题目列表中是否有相同的题目,并处理 static void ifExist(ArrayList<String> s) { for (int i=0; i<s.size(); i++) { for (int j=i+1; j<s.size();) { Stack<Node> f = e1.get(i); Stack<Node> se = e1.get(j); if (f.size() == se.size() && equals(f.pop(), se.pop())) { s.remove(j); } else { j++; } } } } static boolean equals(Node f, Node s) { if (fullequals(f, s)) { return true; } else if (f.op.equals(s.op) && f.result.equals(s.result)){ if (change(f, s)) { return true; } else { return equals(f.left, s.left) && equals(f.right, s.right); } } return false; } static boolean change(Node f, Node s) { if (f.op.equals("+") || f.op.equals("x")) { f.changelr(); f.setResult(); if (nodeequal(f.left, s.left) && nodeequal(f.right, s.right)) { return true; } } return false; } static boolean nodeequal(Node f, Node s) { return f.op.equals(s.left.op) && f.result.equals(s.left.result); } static boolean fullequals(Node f, Node s) { if (f.op.equals(s.op) && f.result.equals(s.result)) { return fullequals(f.left, s.left) && fullequals(f.right, s.right); } return false; }
写入文件Exercise.txt和Answer.txt
static void save(List<List<String>> s) {
// 用于将题目存入当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件
File question = new File("./Exercises.txt");
if (!question.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在,创建文件: Exercises.txt" );
try {
question.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("文件已存在,文件为: Exercises.txt" );
}
FileWriter fw;
try {
fw=new FileWriter(question);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++) {
String temp="";
for(int j=0;j<s.get(i).size();j++) {
temp+=s.get(i).get(j)+"";
}
String t = (i + 1) + ". " + temp;
bw.write(t);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void answer(List<String> a) {
// 用于将题目答案存入当前目录下的Answer.txt文件
File answer = new File("./Answer.txt");
if (!answer.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在,创建文件: Answer.txt" );
try {
answer.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("文件已存在,文件为: Answer.txt" );
}
FileWriter fw;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(answer);
BufferedWriter bw =new BufferedWriter(fw);
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
String t =i+1+". "+ a.get(i);
bw.write( t);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
统计答案
// 用于对给定的题目文件和答案文件判断答案文件中的对错并统计
File g1 = new File("./src/Grade.txt");
if (!g1.exists()){
try {
g1.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
try (BufferedReader exReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(e));
BufferedReader anReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(a));
BufferedWriter gradeWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(g1))
) {
String ex, an;
int c = 0, w = 0;
StringBuilder correct = new StringBuilder("Correct: %d (");
StringBuilder wrong = new StringBuilder("Wrong: %d (");
while ((ex = exReader.readLine()) != null && (an = anReader.readLine()) != null) {
int exPoint = ex.indexOf(".");
int anPoint = an.indexOf(".");
if (exPoint != -1 && anPoint != -1) {
int i = Integer.valueOf(ex.substring(0,exPoint).trim());
String expression = ex.substring(exPoint + 2);
List<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
al = Arrays.asList(exp);
String realanswer = count(al);
String answer = an.substring(anPoint + 2);
if (realanswer.equals(answer.toString())) {
c++;
correct.append(" ").append(i);
if (c % 20 == 0) {
correct.append("\n");
}
} else {
w++;
wrong.append(" ").append(i);
if (w % 20 == 0) {
wrong.append("\n");
}
}
}
}
gradeWriter.write(String.format(correct.append(" )\n").toString(),c));
gradeWriter.write(String.format(wrong.append(" )\n").toString(),w));
gradeWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
-
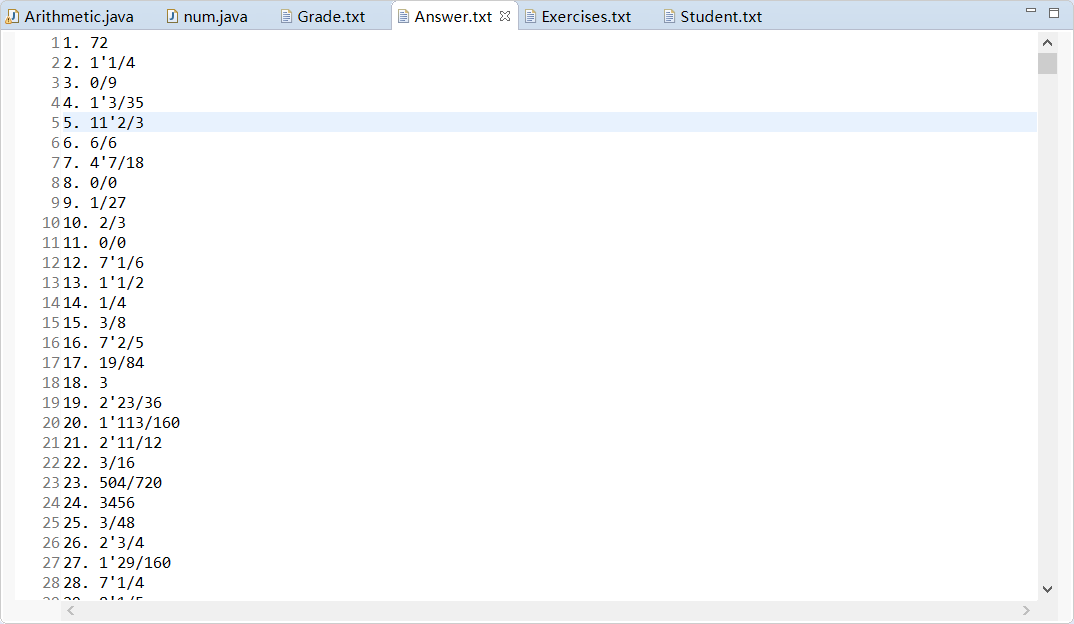
运行结果截图:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 10000道题目部分截图
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 10000道题目
- 10000道答案统计
项目小结
在一开始分析需求的时候没有彻底分析清楚需求,导致设计的时候没有考虑全面,在快结束的时候才发现需求没有完全实现。下次开发的时候不能粗略的按照自己的理解看完需求就马上开始设计,应该认真的看完需求文档之后再进行设计。两人结对编程也能够在自己思路中断的时候能够从队友的思路中得到新的idea,并且能够互相检查彼此的代码有无累赘,学习到了很多。另外没有将代码分为多个类,很多功能写在了同一个类里,进行代码复审的时候修改代码十分麻烦,出现遗漏的情况,以后书写代码应该更加规范。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号